Comprehensive Guide to a High Fiber Diet Plan
Introduction
A high fiber diet plan is essential for maintaining optimal health and well-being. Incorporating adequate fiber into your daily meals can lead to numerous health benefits, including improved digestion, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know to create and maintain an effective high fiber diet plan.
Benefits of a High Fiber Diet Plan
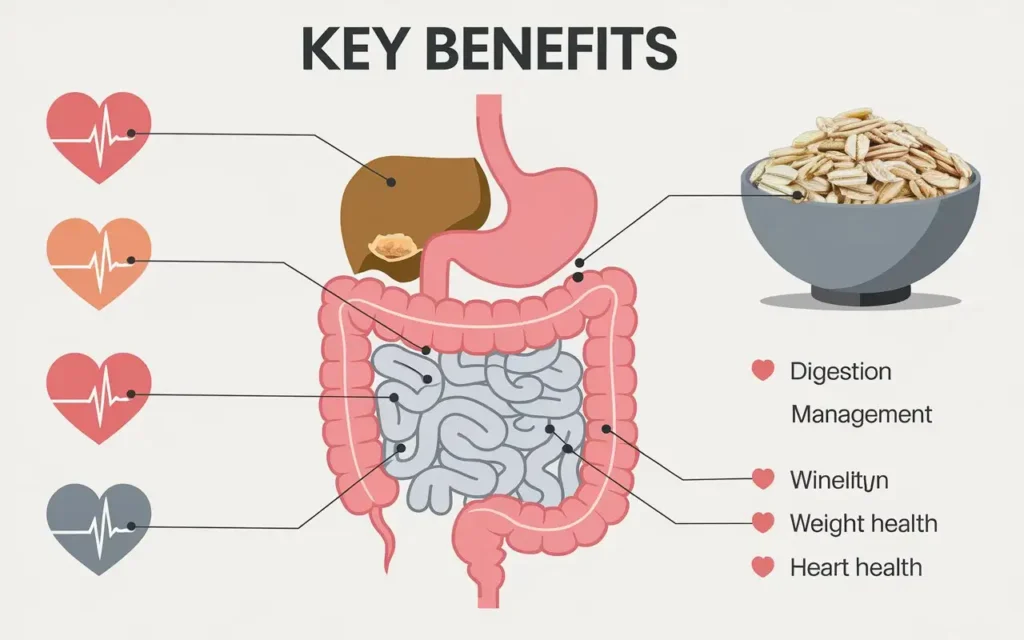
Adopting a high fiber diet plan offers a multitude of health advantages. From enhancing digestive health to supporting heart health, fiber plays a crucial role in various bodily functions.
1. Improved Digestive Health
Fiber aids in regulating bowel movements, preventing constipation, and promoting a healthy digestive tract. It acts as a natural cleanser, helping to eliminate waste efficiently.
2. Weight Management
A high fiber diet plan can help you feel fuller for longer, reducing overall calorie intake and aiding in weight loss or maintenance efforts.
3. Lower Cholesterol Levels
Soluble fiber binds with cholesterol in the digestive system, helping to lower overall cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
4. Blood Sugar Control
Fiber slows the absorption of sugar, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
5. Enhanced Gut Health
A high fiber diet plan promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which are essential for a healthy immune system and overall well-being.
Types of Fiber
Understanding the different types of fiber is crucial when following a high fiber diet plan. There are two main types of dietary fiber: soluble and insoluble.
1. Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance. It helps lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels. Foods rich in soluble fiber include oats, barley, fruits, and legumes.
2. Insoluble Fiber
Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool, aiding in the movement of food through the digestive system. Whole grains, nuts, and vegetables are excellent sources of insoluble fiber.
3. Prebiotic Fiber
Prebiotic fiber serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria, promoting a healthy microbiome. Foods like garlic, onions, and bananas are high in prebiotic fiber.
Fiber-Rich Foods to Include
Incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods is key to a successful high fiber diet plan. Here are some top choices:
1. Fruits and Vegetables
- Apples
- Bananas
- Broccoli
- Carrots
- Raspberries
2. Whole Grains
- Oats
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Whole wheat bread
3. Legumes
- Beans
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
4. Nuts and Seeds
- Almonds
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
5. Fiber Supplements
While it’s best to get fiber from natural sources, supplements can help bridge the gap if needed. Always consult with a healthcare professional before adding supplements to your diet.
Creating Your High Fiber Diet Plan
Designing an effective high fiber diet plan involves careful planning and consideration of your dietary preferences and nutritional needs.
1. Determine Your Fiber Needs
The recommended daily intake of fiber varies based on age, sex, and activity level. Generally, adult women should aim for 25 grams per day, while adult men should target 38 grams.
2. Balance Soluble and Insoluble Fiber
Ensure your diet includes a mix of both soluble and insoluble fiber to reap the full range of health benefits.
3. Plan Balanced Meals
Incorporate fiber-rich foods into every meal. For example, start your day with a bowl of oatmeal topped with fruits and nuts, enjoy a hearty salad for lunch, and include vegetables and legumes in your dinner.
4. Monitor Your Progress
Keep track of your fiber intake using a food diary or a nutrition app to ensure you’re meeting your daily goals.
Meal Prep Tips
Effective meal preparation can make sticking to a high fiber diet plan much easier. Here are some tips to help you get started:
1. Plan Ahead
Create a weekly meal plan that includes fiber-rich recipes. This helps ensure you have the necessary ingredients on hand and reduces the temptation to opt for less healthy options.
2. Batch Cooking
Prepare large quantities of fiber-rich foods like quinoa, beans, and roasted vegetables to use throughout the week in various dishes.
3. Smart Snacking
Keep fiber-packed snacks such as nuts, seeds, and fresh fruits readily available to curb hunger between meals.
4. Utilize Freezer-Friendly Recipes
Make freezer-friendly fiber-rich meals like soups and stews in advance, allowing you to have healthy options available on busy days.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While following a high fiber diet plan, it’s important to be aware of common pitfalls that can hinder your progress.
1. Sudden Increase in Fiber Intake
Dramatically increasing your fiber intake can lead to digestive discomfort. Gradually add more fiber to your diet to allow your body to adjust.
2. Inadequate Hydration
Fiber works best when it absorbs water. Ensure you drink plenty of fluids to aid in digestion and prevent constipation.
3. Ignoring Fiber Balance
Focusing solely on one type of fiber can limit the benefits. Strive for a balanced intake of both soluble and insoluble fiber.
4. Relying Too Much on Processed Foods
Many processed foods marketed as high in fiber may contain added sugars and unhealthy fats. Prioritize whole, natural sources of fiber.
Fiber Supplements
While a high fiber diet plan should primarily focus on natural food sources, supplements can be beneficial in certain situations.
When to Consider Supplements
If you’re unable to meet your fiber needs through diet alone, supplements can help bridge the gap. They are also useful for individuals with specific health conditions that require increased fiber intake.
Types of Fiber Supplements
- Psyllium husk
- Methylcellulose
- Inulin
- Wheat dextrin
Choosing the Right Supplement
Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement. They can help you choose the right type and dosage based on your individual needs.
Success Stories
Hearing about others’ experiences can be incredibly motivating when following a high fiber diet plan. Here are some inspiring success stories:
1. Jane’s Journey to Better Digestion
Jane struggled with chronic constipation for years. After adopting a high fiber diet plan, she experienced significant improvements in her digestive health and overall well-being.
2. Mark’s Weight Loss Success
Mark incorporated more fiber-rich foods into his meals, which helped him feel fuller longer and reduce his calorie intake. Over six months, he lost 30 pounds and maintained his weight loss.
3. Sarah’s Heart Health Improvement
With a family history of heart disease, Sarah decided to focus on a high fiber diet plan. She successfully lowered her cholesterol levels and improved her heart health through dietary changes.
Fiber Myths and Facts
There are numerous misconceptions surrounding fiber and its role in our diets. Understanding the facts can help you make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls.
Myth 1: All Fiber Is the Same
Fact: There are different types of fiber, each with unique benefits. Soluble, insoluble, prebiotic fibers, and resistant starch all play distinct roles in health. It’s essential to include a variety of fiber types in your diet to maximize benefits.
Myth 2: You Can Get Enough Fiber Without Changing Your Diet
Fact: Most people do not consume enough fiber through their regular diets. Incorporating more fiber-rich foods or using supplements may be necessary to meet daily fiber requirements.
Myth 3: High Fiber Diets Cause Weight Gain
Fact: Fiber is low in calories and helps promote satiety, which can aid in weight management. High fiber diets are generally associated with weight loss or maintenance, not weight gain.
Myth 4: Fiber Supplements Are as Good as Whole Foods
Fact: While fiber supplements can help increase fiber intake, whole foods provide additional nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that supplements lack. It’s best to prioritize fiber from natural sources.
Myth 5: You Don’t Need Fiber If You Have No Digestive Issues
Fact: Fiber offers a wide range of health benefits beyond digestive health, including heart health, blood sugar control, and weight management. Everyone can benefit from adequate fiber intake, regardless of digestive health status.
Fiber and Hormonal Balance
Fiber plays a significant role in regulating hormones, which are crucial for various bodily functions. Maintaining hormonal balance through a high fiber diet can contribute to overall well-being.
1. Estrogen Regulation
Fiber helps regulate estrogen levels by binding to excess estrogen in the digestive system and facilitating its excretion. This can reduce the risk of hormone-related conditions such as breast cancer and endometriosis.
Estrogen Regulation Benefits
- Reduces the risk of breast cancer by lowering circulating estrogen levels
- Helps prevent endometriosis by maintaining hormone balance
- Supports menstrual health and reduces symptoms of PMS
2. Thyroid Function
Adequate fiber intake supports thyroid health by promoting the elimination of excess hormones and reducing the burden on the thyroid gland. This can help prevent thyroid imbalances and related conditions.
Thyroid Health Tips
- Include iodine-rich fiber sources like sea vegetables in your diet
- Ensure a balanced intake of fiber to support overall hormone regulation
- Consult with a healthcare provider if you have thyroid concerns
3. Insulin and Leptin Regulation
Fiber aids in the regulation of insulin and leptin, hormones involved in blood sugar control and appetite regulation. Proper fiber intake can improve insulin sensitivity and help maintain healthy leptin levels.
Insulin and Leptin Benefits
- Improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes
- Regulates appetite by maintaining stable leptin levels
- Prevents insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome
Fiber for Mental Clarity and Mood
Emerging research highlights the connection between fiber intake and mental health. A high fiber diet can contribute to improved mental clarity, mood stabilization, and overall cognitive function.
1. Enhancing Neurotransmitter Production
Fiber supports the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine by fostering a healthy gut microbiome. These neurotransmitters are essential for mood regulation, focus, and cognitive functions.
Neurotransmitter Benefits
- Improves mood and reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety
- Enhances focus and cognitive performance
- Supports overall brain health and function
2. Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress can negatively impact mental health. Fiber’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce these factors, supporting better mental well-being.
Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Benefits
- Lowers levels of inflammatory markers in the body
- Protects brain cells from oxidative damage
- Reduces the risk of neurodegenerative diseases
3. Promoting Healthy Sleep Patterns
Adequate fiber intake can contribute to better sleep quality by regulating blood sugar levels and supporting the production of sleep-related hormones like melatonin.
Sleep Health Tips
- Consume fiber-rich foods in the evening to stabilize blood sugar levels overnight
- Incorporate magnesium-rich fiber sources like leafy greens and legumes to promote relaxation
- Maintain a balanced diet to support overall sleep quality
Fiber for Different Age Groups
Fiber needs and benefits can vary across different stages of life. Tailoring your high fiber diet plan to suit your age group ensures optimal health and well-being.
1. Children
Adequate fiber is crucial for children’s growth and development. It supports healthy digestion, prevents constipation, and promotes a balanced diet.
Fiber Tips for Children
- Incorporate fruits and vegetables into meals and snacks
- Choose whole grain cereals and breads over refined options
- Encourage drinking plenty of water to support fiber digestion
- Limit intake of sugary and processed foods that are low in fiber
2. Adolescents
During adolescence, fiber supports rapid growth, hormonal changes, and the development of healthy eating habits. It also helps manage weight and prevent digestive issues.
Fiber Tips for Adolescents
- Include a variety of fiber-rich foods in their diet, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Encourage balanced meals with adequate fiber to support energy needs
- Promote healthy snacking with nuts, seeds, and fresh fruits
- Educate on the importance of fiber for long-term health
3. Adults
For adults, fiber plays a vital role in maintaining digestive health, managing weight, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. It also supports mental health and overall vitality.
Fiber Tips for Adults
- Ensure a daily intake of 25-38 grams of fiber, depending on sex and activity level
- Incorporate a balance of soluble and insoluble fiber sources
- Plan meals and snacks to include high fiber foods consistently
- Monitor fiber intake and adjust as needed based on health goals
4. Seniors
As we age, fiber supports digestive health, bone density, and immune function. It also aids in maintaining cognitive health and preventing age-related diseases.
Fiber Tips for Seniors
- Choose easy-to-digest fiber sources like cooked vegetables and soft fruits
- Ensure adequate hydration to support fiber digestion
- Incorporate calcium and magnesium-rich fiber foods to support bone health
- Consult with healthcare providers to tailor fiber intake based on individual health conditions
Fiber and Athletic Performance
Fiber plays a crucial role in supporting athletic performance by providing sustained energy, aiding in digestion, and enhancing overall health. Athletes can benefit from a high fiber diet in several ways.
1. Sustained Energy Release
Fiber slows the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a gradual release of energy. This helps maintain steady energy levels during training and competitions, preventing energy crashes.
Energy Sustenance Tips
- Include whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats in pre-workout meals
- Incorporate fiber-rich fruits and vegetables for long-lasting energy
- Balance fiber intake with adequate protein and healthy fats to optimize energy release
2. Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
Fiber supports a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn enhances the absorption of essential nutrients needed for athletic performance, such as vitamins, minerals, and amino acids.
Nutrient Absorption Benefits
- Improves the absorption of iron, calcium, and magnesium
- Supports the uptake of B vitamins crucial for energy metabolism
- Enhances the bioavailability of antioxidants that protect against oxidative stress
3. Improved Recovery and Reduced Inflammation
Fiber’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce exercise-induced inflammation and support faster recovery. A balanced fiber intake can aid in repairing muscle tissues and reducing soreness.
Recovery Benefits
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced from fiber fermentation reduce inflammation
- Antioxidants in fiber-rich foods combat oxidative stress from intense workouts
- Supports muscle repair and growth through improved nutrient absorption
4. Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Adequate fiber intake, coupled with proper hydration, helps maintain electrolyte balance, which is vital for muscle function and preventing cramps during physical activities.
Hydration Tips for Athletes
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially when increasing fiber intake
- Consume fiber-rich foods with high water content like fruits and vegetables
- Monitor electrolyte levels and replenish as needed during prolonged exercise
5. Preventing Gastrointestinal Issues
Athletes often face gastrointestinal challenges during training and competitions. A high fiber diet, when balanced and properly managed, can help prevent issues like bloating, gas, and constipation.
Gastrointestinal Tips
- Gradually increase fiber intake to allow the digestive system to adapt
- Choose easily digestible fiber sources before workouts, such as bananas and oatmeal
- Avoid high fiber foods immediately before intense physical activity to prevent discomfort
Latest Research on Fiber and Health
Ongoing research continues to uncover the multifaceted benefits of fiber. Staying informed about the latest studies can help you optimize your high fiber diet plan for better health outcomes.
1. Fiber and the Gut-Brain Axis
Recent studies have emphasized the importance of fiber in modulating the gut-brain axis, a communication network between the gut microbiome and the brain. Research published in Nature Neuroscience highlights how fiber-induced changes in gut bacteria can influence mood, cognition, and stress response.
Key Findings
- Fiber intake is associated with increased production of neurotransmitters like serotonin
- Gut bacteria influenced by fiber can affect brain function and mental health
- Fiber supplementation has been shown to reduce anxiety and depressive symptoms in clinical trials
2. Fiber and Metabolic Health
Studies in The Lancet have demonstrated that higher fiber intake is linked to improved metabolic health, including better insulin sensitivity, reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, and healthier lipid profiles.
Metabolic Health Insights
- Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing carbohydrate absorption
- Soluble fiber lowers LDL cholesterol, reducing the risk of heart disease
- High fiber diets are associated with lower body mass index (BMI) and reduced obesity risk
3. Fiber and Immune Function
Emerging research indicates that fiber plays a role in enhancing immune function. A study in Cell Host & Microbe found that fiber-rich diets support a diverse and robust immune system by fostering beneficial gut bacteria.
Immune Function Benefits
- Promotes the growth of bacteria that produce SCFAs, which have immunomodulatory effects
- Enhances the production of antibodies and immune cells
- Reduces the risk of infections by maintaining a healthy gut barrier
4. Fiber and Cancer Prevention
Recent meta-analyses have reinforced the protective role of fiber against certain cancers, particularly colorectal cancer. Research published in JAMA Oncology suggests that higher fiber intake is associated with a lower incidence of colorectal cancer.
Cancer Prevention Insights
- Fiber accelerates bowel movements, reducing the time carcinogens contact the colon lining
- SCFAs produced from fiber fermentation have anti-carcinogenic properties
- High fiber diets are associated with reduced inflammation, lowering cancer risk
5. Fiber and Bone Health
A study in The Journal of Bone and Mineral Research found that dietary fiber, particularly from whole grains and legumes, is positively associated with bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. This suggests that fiber plays a role in preventing osteoporosis and promoting bone health.
Bone Health Benefits
- Enhances calcium absorption, essential for strong bones
- Reduces bone resorption by lowering inflammation
- Supports overall bone integrity and density
6. Fiber and Skin Health
Recent research in The Journal of Dermatology indicates that a high fiber diet can improve skin health by promoting detoxification and reducing inflammation. Fiber helps eliminate toxins that can contribute to skin issues like acne and eczema.
Skin Health Insights
- Fiber aids in detoxifying the body, reducing the burden on the skin
- Anti-inflammatory properties of fiber help alleviate skin conditions
- Improved nutrient absorption from fiber-rich foods supports healthy skin
Fiber and Hormonal Balance
Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining hormonal balance, which is essential for overall health. Proper fiber intake can influence various hormones that regulate metabolism, mood, and reproductive health.
1. Estrogen Balance
Fiber helps regulate estrogen levels by binding to excess estrogen in the digestive system and facilitating its excretion. This process can reduce the risk of hormone-related cancers and alleviate symptoms of hormonal imbalance.
Estrogen Regulation Benefits
- Reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancers by lowering circulating estrogen levels
- Aids in managing symptoms of menopause by balancing hormone levels
- Prevents estrogen dominance, which can lead to conditions like fibroids and endometriosis
2. Thyroid Hormone Support
Adequate fiber intake supports thyroid health by aiding in the elimination of excess thyroid hormones. This helps maintain proper thyroid function and prevents imbalances that can affect metabolism and energy levels.
Thyroid Health Tips
- Include iodine-rich fiber sources like sea vegetables
- Maintain a balanced fiber intake to support overall thyroid function
- Consult with a healthcare provider if you have thyroid concerns or conditions
3. Insulin and Glucagon Regulation
Fiber influences the hormones insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels. By slowing the absorption of carbohydrates, fiber helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and supports metabolic health.
Insulin and Glucagon Benefits
- Improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes
- Helps prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes
- Supports healthy weight management by regulating appetite hormones
4. Leptin and Ghrelin Balance
Fiber plays a role in balancing leptin and ghrelin, hormones that regulate hunger and satiety. Adequate fiber intake can help control appetite and prevent overeating, aiding in weight management.
Appetite Regulation Tips
- Include high fiber foods in meals to promote feelings of fullness
- Choose fiber-rich snacks to curb hunger between meals
- Balance fiber intake with adequate protein and healthy fats for optimal satiety
Fiber for Specific Health Conditions
Fiber plays a pivotal role in managing and preventing various health conditions. Here’s how a high fiber diet can benefit specific health issues:
1. Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
For individuals with IBS, fiber can both alleviate and exacerbate symptoms depending on the type and amount consumed. Soluble fiber is generally well-tolerated and can help manage IBS symptoms, while insoluble fiber may worsen them.
IBS-Friendly Fiber Tips
- Choose soluble fiber sources like oats, apples, and carrots
- Avoid high insoluble fiber foods like whole wheat and raw vegetables during flare-ups
- Incorporate prebiotic fibers in moderation to support gut health
- Consult with a healthcare provider to tailor fiber intake based on individual tolerance
2. Preventing and Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing carbohydrate absorption, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing insulin resistance. This makes it an essential component in preventing and managing type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Management Tips
- Incorporate high fiber foods like legumes, whole grains, and vegetables into meals
- Choose fiber-rich snacks to stabilize blood sugar levels between meals
- Monitor fiber intake and adjust based on blood sugar responses
- Pair fiber with protein and healthy fats to further regulate blood sugar
3. Reducing Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
A high fiber diet supports heart health by lowering cholesterol levels, reducing blood pressure, and decreasing inflammation. These factors collectively reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Cardiovascular Health Tips
- Include soluble fiber sources like oats, barley, and legumes to lower LDL cholesterol
- Incorporate a variety of vegetables and fruits to provide antioxidants and reduce inflammation
- Choose whole grains over refined grains to support heart health
- Limit intake of processed foods and unhealthy fats that can negate fiber’s benefits
4. Supporting Weight Management
Fiber promotes satiety, reduces overall calorie intake, and supports a healthy metabolism, making it an effective tool for weight management. High fiber foods are typically lower in calories and higher in volume, helping you feel fuller longer.
Weight Management Tips
- Choose high fiber breakfasts to start the day with lasting fullness
- Incorporate fiber-rich vegetables and legumes into main meals
- Opt for fiber-packed snacks like fruits, nuts, and seeds
- Monitor portion sizes of high fiber foods to avoid excessive calorie intake
5. Enhancing Immune Function
Fiber supports a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for a robust immune system. A balanced and diverse microbiome helps defend against pathogens and reduces the risk of infections.
Immune Support Tips
- Include a variety of fiber-rich foods to promote microbiome diversity
- Incorporate prebiotic fibers like garlic, onions, and bananas to feed beneficial bacteria
- Avoid excessive intake of processed foods that can disrupt the microbiome
- Maintain adequate hydration to support immune function and gut health
6. Managing Diverticulosis
Diverticulosis, characterized by the formation of small pouches in the colon, can be managed and prevented with a high fiber diet. Fiber helps keep stool soft and reduces pressure in the colon, preventing the formation and exacerbation of diverticula.
Diverticulosis Management Tips
- Incorporate a variety of fiber-rich foods to ensure balanced intake
- Stay hydrated to help fiber maintain stool consistency
- Avoid high-fat and low-fiber foods that can increase colon pressure
- Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized dietary recommendations
Fiber Myths and Facts
There are numerous misconceptions surrounding fiber and its role in our diets. Understanding the facts can help you make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls.
Myth 1: All Fiber Is the Same
Fact: There are different types of fiber, each with unique benefits. Soluble, insoluble, prebiotic fibers, and resistant starch all play distinct roles in health. It’s essential to include a variety of fiber types in your diet to maximize benefits.
Myth 2: You Can Get Enough Fiber Without Changing Your Diet
Fact: Most people do not consume enough fiber through their regular diets. Incorporating more fiber-rich foods or using supplements may be necessary to meet daily fiber requirements.
Myth 3: High Fiber Diets Cause Weight Gain
Fact: Fiber is low in calories and helps promote satiety, which can aid in weight management. High fiber diets are generally associated with weight loss or maintenance, not weight gain.
Myth 4: Fiber Supplements Are as Good as Whole Foods
Fact: While fiber supplements can help increase fiber intake, whole foods provide additional nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that supplements lack. It’s best to prioritize fiber from natural sources.
Myth 5: You Don’t Need Fiber If You Have No Digestive Issues
Fact: Fiber offers a wide range of health benefits beyond digestive health, including heart health, blood sugar control, and weight management. Everyone can benefit from adequate fiber intake, regardless of digestive health status.
Conclusion
Adopting a high fiber diet plan is a powerful step towards achieving better health and well-being. By understanding the types of fiber, incorporating fiber-rich foods, and avoiding common mistakes, you can create a sustainable and effective diet plan. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals when making significant dietary changes and stay committed to your health goals.
A high fiber diet not only supports digestive health but also contributes to weight management, heart health, and overall vitality. Embrace the variety and versatility of fiber-rich foods to make your diet enjoyable and nutritious.
Stay motivated by tracking your progress, seeking support from professionals or communities, and celebrating your successes along the way. With dedication and the right approach, a high fiber diet plan can lead to lasting positive changes in your health and quality of life.
Additional Resources
For more information on high fiber diet plans and to support your journey towards better health, explore the following resources:
References
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health: Fiber
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Dietary Fiber
- WebMD: High Fiber Diet Plan
- Mayo Clinic: Dietary Fiber
- Nature Neuroscience: Fiber and the Gut-Brain Axis
- JAMA Oncology: Fiber and Colorectal Cancer
- Cell Host & Microbe: Fiber and Immune Function
- The Lancet: Fiber and Metabolic Health