The Ultimate Guide to the Paul Saladino Diet
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on the paul saladino diet. This article aims to provide deep insights, practical knowledge, and an evidence-based perspective on this unique approach to nutrition and wellness. Below, you’ll find a Table of Contents to help you navigate through the various sections and subtopics.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to the Paul Saladino Diet
- 2. Origins and Evolution of the Paul Saladino Diet
- 3. Core Principles of the Paul Saladino Diet
- 4. Potential Health Benefits
- 5. Challenges and Controversies
- 6. Scientific Research and Evidence
- 7. Implementing the Paul Saladino Diet Safely
- 8. Lifestyle Factors and the Paul Saladino Diet
- 9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 10. Conclusion and Future Outlook
- References
1. Introduction to the Paul Saladino Diet
Paul saladino diet is essential because it represents a unique nutritional approach that challenges conventional dietary wisdom. By emphasizing animal-based foods, particularly nose-to-tail consumption, this diet proposes that certain plant foods may be less beneficial—or even harmful—than traditionally believed. With its focus on high-quality protein, nutrient density, and the exclusion or limitation of most plant sources, followers of the paul saladino diet often claim significant health improvements, including better digestion, mental clarity, and metabolic flexibility.
This article aims to provide a thorough exploration of the origin, scientific basis, and practical considerations surrounding this diet. We’ll delve into the history, discuss the principles, analyze supporting research, and outline potential challenges and criticisms. Whether you’re new to the concept or already experimenting with an animal-based diet, this guide offers a balanced, in-depth look at what the paul saladino diet entails.
Before diving deeper, it’s important to note that dietary choices are highly individual. While some people thrive on an animal-centric regimen, others may require a more varied nutritional profile. Throughout this article, we’ll maintain an evidence-based, unbiased perspective to help you make informed decisions.
2. Origins and Evolution of the Paul Saladino Diet
Paul saladino diet was not born in a vacuum; it evolved out of growing skepticism about modern dietary guidelines. Dr. Paul Saladino, a functional medicine practitioner, began questioning the role of plant-based foods after observing potential inflammatory responses in certain patients. This led him to investigate ancestral diets and the possible benefits of prioritizing animal foods over plants. Early on, the paul saladino diet emerged as an offshoot of the broader carnivore movement but soon developed unique principles and nuances.
Historically, many indigenous communities relied heavily on animal sources for sustenance, especially those living in harsh environments with limited plant availability. Anthropological evidence from regions like the Arctic (Inuit populations) and grasslands (the Maasai in East Africa) illustrates how animal-based diets have been successfully adopted in certain cultures for centuries. The paul saladino diet draws parallels to these traditional practices, hypothesizing that humans may have evolved to thrive on a meat-centric eating pattern.
Meanwhile, Dr. Saladino’s clinical practice and personal experimentation shaped the modern framework of this approach. He noticed that by eliminating or significantly reducing plant foods, some individuals reported fewer digestive issues, reduced autoimmune flare-ups, and better mental clarity. This diet’s evolution also coincided with increasing research into gut permeability, lectins, and other compounds in plants, which may cause issues in susceptible people. As a result, the paul saladino diet gradually gained attention in online communities, including podcasts, social media platforms, and health forums.
While not universally accepted, the historical context, combined with modern clinical observations, provides a foundation for understanding why many are drawn to this diet. The subsequent sections will go deeper into the key principles, benefits, and controversies that characterize the paul saladino diet in today’s health landscape.
3. Core Principles of the Paul Saladino Diet
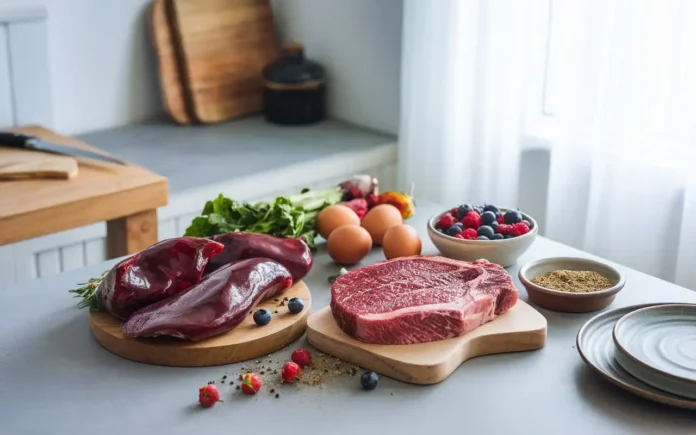
Paul saladino diet is essential because it lays down a set of clear guidelines that differentiate it from other animal-based or ketogenic diets. One of the primary principles is consuming the entire animal—often referred to as “nose-to-tail” eating. In this approach, organ meats like liver, heart, and kidney are highlighted as nutrient powerhouses. These organs provide essential vitamins and minerals, including B12, iron, zinc, and vitamins A, D, E, and K2, all of which are critical for optimal health.
The paul saladino diet also advises limiting or eliminating plant foods, especially those high in naturally occurring defense chemicals such as oxalates, lectins, and phytates. According to proponents, these compounds may cause digestive upset, inflammation, or autoimmune reactions in sensitive individuals. While some people choose to consume small quantities of fruit or less problematic plant foods, the overarching concept is to emphasize the nutritional density of animal products while minimizing potential inflammatory agents found in certain plants.
Beyond its restriction of plant-based foods, the paul saladino diet often includes recommendations like prioritizing grass-fed and pasture-raised meat, ensuring adequate salt intake, and focusing on high-quality sources of fat like tallow or suet. Another frequent suggestion is to incorporate bone broth to support gut health and supply collagen. This holistic, whole-foods approach aims to maximize nutrient density while reducing potential dietary stressors.
Below is a simple overview table illustrating the general dos and don’ts within the paul saladino diet framework:
| Recommended Foods | Foods to Limit or Avoid |
|---|---|
| Organ meats (liver, heart, kidney) | Grains (wheat, rice, oats) |
| Muscle meats (steak, ground beef, lamb) | Legumes (beans, lentils, peanuts) |
| Bone broth and collagen-rich cuts | High-lectin vegetables (nightshades) |
| Eggs and certain dairy (if tolerated) | High-oxalate foods (spinach, almonds) |
| Whole-food animal fats (tallow, butter) | Refined and processed oils (canola, soybean) |
These core principles serve as the backbone of the diet. However, individual adaptations may vary depending on health goals, lifestyle factors, and personal tolerance to certain plant foods. Next, we’ll explore the potential health benefits that attract many to test this unique nutritional approach.
4. Potential Health Benefits
Paul saladino diet is essential because its proponents claim a variety of health improvements, often citing personal success stories and preliminary research. One of the most commonly reported benefits is enhanced energy, as removing highly processed carbohydrates and focusing on nutrient-dense animal foods can stabilize blood glucose levels. This metabolic stability may contribute to consistent energy throughout the day, reduced sugar cravings, and improved mental clarity.
For some individuals, adopting the paul saladino diet correlates with improved digestive health. Cutting out grains, legumes, and certain vegetables may help reduce bloating and symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), especially if plant antinutrients or fiber intolerance are contributing factors. Additionally, the high protein and fat content can be satiating, potentially aiding weight management or fat loss when consumed in appropriate quantities.
Another reported benefit is improved autoimmune or inflammatory conditions. While more rigorous studies are needed, anecdotal evidence suggests that reducing certain plant compounds might alleviate symptoms of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, eczema, or psoriasis in susceptible individuals. The paul saladino diet also underscores the role of organ meats in providing crucial micronutrients—vitamins A, D, E, K2, B12, zinc, iron—that are essential for immune function, hormone regulation, and overall vitality.
- Improved Energy Levels: Stable blood sugar may lead to fewer energy crashes.
- Enhanced Gut Health: Reduced bloating and potential IBS symptom relief.
- Autoimmune Support: Possible reduction in inflammatory markers.
- Weight Management: High satiety may help regulate caloric intake.
- Micronutrient Density: Organ meats provide a robust array of essential vitamins and minerals.
While these potential benefits are compelling, it’s crucial to balance optimism with a rational view of the evidence. Personal experiences vary widely, and not everyone will see dramatic transformations. In the next section, we’ll dive into some of the main criticisms and controversies surrounding the paul saladino diet to offer a balanced perspective.
5. Challenges and Controversies
Paul saladino diet is essential because it stirs passionate debate in the nutrition world, drawing both staunch advocates and vocal critics. One significant controversy revolves around the elimination or severe reduction of plant foods. While proponents argue that many plants contain harmful compounds, mainstream nutritional guidelines emphasize plant diversity for fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients. Critics worry that adhering strictly to the paul saladino diet may lead to deficiencies in vitamin C, certain phytochemicals, and dietary fiber if not carefully managed.
Concerns about saturated fat and cholesterol also arise. Traditional medical advice often cautions against high intake of saturated animal fats due to potential links with heart disease. Though some research suggests that saturated fat may not be as detrimental as once believed, consensus is far from universal. Additionally, some practitioners argue that even if an animal-based diet improves short-term markers like inflammation, long-term cardiovascular implications remain under-studied.
Another challenge is the diet’s sustainability and ethical considerations. Critics question whether widespread adoption of such an animal-centric diet could be environmentally responsible. Production of livestock, particularly cattle, has a larger carbon footprint compared to plant agriculture. Advocates of the paul saladino diet counter that regenerative farming practices and focusing on pasture-raised meats can mitigate some environmental concerns. Nevertheless, the debate remains complex.
Finally, the restrictive nature of this diet can be socially isolating or difficult to maintain. Dining out, traveling, or eating with friends and family becomes more complicated when most plant foods and conventional fare are off-limits. These challenges underscore the importance of careful planning, open-minded research, and personalization if one chooses to pursue the paul saladino diet.
6. Scientific Research and Evidence
Paul saladino diet is essential because it raises pivotal questions about human evolution, gut health, and nutritional adequacy. However, the body of peer-reviewed research specifically evaluating this dietary pattern remains limited. Still, some studies on low-carbohydrate, high-protein diets provide indirect insights, showing improvements in markers such as triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, and blood sugar control. Adherents of the paul saladino diet argue that going fully animal-based may amplify these benefits further.
One area of ongoing investigation is the impact of plant antinutrients on human health. Research demonstrates that compounds like lectins, oxalates, and phytates can interfere with nutrient absorption and potentially trigger inflammatory responses in some individuals. Yet, these substances also have potential benefits—for instance, phytates may exhibit antioxidant properties. Balancing these considerations is crucial, and more comprehensive human trials are needed to draw definitive conclusions.
Similarly, concerns about heart health in diets high in saturated fat and cholesterol require further scrutiny. While meta-analyses have challenged the long-held belief that saturated fat alone is the primary cause of cardiovascular disease, the question remains debated. Observational studies on populations that eat predominantly animal-based diets—like the Maasai—offer some clues, but these communities also differ from Western populations in lifestyle and genetics.
More on Ongoing Research (Click to Expand)
- Gut Microbiome Studies: Emerging research looks at how reduced fiber intake affects gut bacteria. Some findings suggest fiber scarcity may shift the gut microbiome in ways that could be beneficial for certain individuals but detrimental for others.
- Autoimmune Mechanisms: Preliminary case reports indicate that eliminating certain plant compounds can reduce autoimmune triggers in susceptible people, although large-scale controlled trials are lacking.
- Nutrient Density Investigations: Studies continue to analyze the vitamin and mineral profiles of organ meats versus plant-based superfoods, aiming to clarify how complete an animal-based diet can be.
Until more targeted research is conducted, the evidence base for the paul saladino diet will remain a mix of anecdotal reports, extrapolations from similar diets, and preliminary scientific findings.
7. Implementing the Paul Saladino Diet Safely
Paul saladino diet is essential because, despite its controversies, many individuals find it worth trying for potential metabolic or digestive benefits. However, a safe and gradual approach is key. Transitioning abruptly from a standard diet to a fully animal-based regimen can lead to digestive upset, electrolyte imbalances, or “keto flu” symptoms. Instead, proponents of the paul saladino diet often recommend phasing out grains, sugars, and processed foods first, then gradually reducing plant intake if desired.
Consulting with a healthcare provider—especially one knowledgeable about ancestral or functional medicine—can help tailor this approach to your unique needs. Blood tests to check cholesterol, inflammation markers (like CRP), and micronutrient levels can help establish a baseline. This information allows for monitoring as you adapt, ensuring that any nutrient gaps are addressed, and adjustments are made as needed.
Key points for safe implementation include:
- Organ Meats First: Incorporate organ meats gradually, starting with liver once or twice a week.
- Stay Hydrated and Mind Electrolytes: Include mineral-rich salt and consider supplements like magnesium to combat potential deficiencies.
- Monitor Health Markers: Regular blood work can help track improvements or issues.
- Listen to Your Body: If you experience persistent adverse effects, reintroduce certain foods or alter the ratio of fat to protein.
The paul saladino diet can be a powerful tool for some, but it requires diligence and personal experimentation. In the following section, we’ll address how lifestyle factors, such as exercise and stress management, intertwine with this dietary approach.
8. Lifestyle Factors and the Paul Saladino Diet
Paul saladino diet is essential because nutrition alone doesn’t paint the full picture of wellness. Adequate exercise, sleep, and stress management all influence how well your body responds to any diet. When adopting the paul saladino diet, you’ll likely need to adjust certain lifestyle factors to ensure optimal results.
Regular physical activity helps regulate insulin sensitivity, supports cardiovascular health, and can improve mental well-being. Strength training, in particular, complements an animal-based diet by building muscle mass and increasing nutrient demands that are readily met by high-quality animal protein. Meanwhile, proper sleep is critical for hormone regulation, particularly cortisol, which can affect blood sugar and energy levels.
Stress management should not be overlooked. Chronic stress triggers a cascade of hormonal responses that may negate some dietary benefits, leading to inflammation or poor metabolic health. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, breathwork, or simply spending time outdoors can be invaluable. The synergy between these elements—diet, exercise, sleep, and stress balance—forms the bedrock of a holistic wellness strategy within the framework of the paul saladino diet.
Below is a quick list of lifestyle tips to complement this diet:
- Embrace Strength Training: Aim for 2-4 sessions of resistance workouts per week.
- Focus on Sleep Quality: Aim for 7-9 hours of consistent sleep nightly.
- Mindful Stress Reduction: Incorporate daily practices like journaling, deep breathing, or meditation.
- Sunlight and Nature: Spend time outdoors to boost vitamin D levels and mental well-being.
By aligning your lifestyle habits with the nutritional objectives of the paul saladino diet, you create an environment in which your body can potentially thrive. Next, we’ll address common questions that often arise when people consider or adopt this way of eating.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Paul saladino diet is essential because many people have curiosity or concerns regarding its sustainability, nutritional completeness, and day-to-day implementation. Here are some of the most frequent questions and their answers:
Q1: Do I need to eat organ meats regularly?
A: While not mandatory, organ meats like liver are nutrient-dense and form a core part of the paul saladino diet. They provide essential vitamins and minerals that can be harder to obtain from muscle meat alone.
Q2: Is it safe to avoid all plant foods?
A: Many people report feeling better without certain plants, but long-term studies are limited. Some individuals reintroduce fruit or “safer” vegetables after an initial elimination phase. Personal tolerance can vary widely.
Q3: What about fiber and gut microbiome health?
A: Fiber is commonly associated with digestive health, but supporters of the paul saladino diet argue that an animal-based regimen provides other nutrients that support a healthy gut. Still, if you have concerns, consult a healthcare provider.
Q4: Can I do high-intensity workouts on this diet?
A: Many athletes adapt successfully, but you may need an adjustment period. Some people add a small amount of carbohydrate from fruit or honey for extra energy.
Q5: How do I ensure my blood lipids stay healthy?
A: Regular lipid panels and discussions with a knowledgeable physician are essential. Some individuals see improved markers, while others may notice rises in LDL. Ongoing monitoring is crucial for personalized care.
10. Conclusion and Future Outlook
Paul saladino diet is essential because it sparks a reevaluation of our foundational beliefs about nutrition, plant foods, and the role of animal products in human health. Emerging from ancestral eating traditions, combined with modern functional medicine insights, this approach has gathered a dedicated following that reports metabolic, digestive, and even autoimmune benefits. However, like any highly specialized diet, the paul saladino diet also faces criticism for potential nutrient gaps, questions about long-term cardiovascular risks, and environmental sustainability concerns.
Ultimately, the decision to adopt, modify, or reject this dietary framework should be guided by individual health markers, ethical perspectives, and personal values. Future research will hopefully shed more light on how animal-based diets affect different populations, from healthy individuals to those with specific medical conditions. Organizations and practitioners focusing on regenerative agriculture may also play a pivotal role in addressing sustainability questions tied to a meat-centric approach.
Whether you’re exploring the paul saladino diet out of curiosity, for health reasons, or to challenge the status quo of conventional nutrition guidelines, the conversation is far from over. Ongoing studies, debates, and personal experimentation will continue to shape how this diet evolves. For now, an open-minded yet critical stance can help you navigate the unique promises and pitfalls it presents. By combining thorough research, medical guidance, and an understanding of your own body’s signals, you can make informed choices about embracing—or adapting—the paul saladino diet as part of your overall wellness journey.
Paul saladino diet remains a dynamic topic in the health landscape, and further exploration, transparency, and scientific inquiry will determine its future acceptance or rejection. If you choose to embark on this path, remain vigilant, track your progress, and adjust as necessary to ensure a balanced and sustainable approach.
References
The following external links offer additional insights and research:




