Ultimate Muscle Gain Diet Plan: Your Comprehensive Guide to Building Muscle
Introduction
Muscle gain diet plans are essential for anyone looking to build muscle effectively and sustainably. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting your fitness journey, understanding the fundamentals of nutrition can significantly impact your muscle growth and overall health.
Building muscle isn’t just about hitting the gym hard; it’s equally about what you put into your body. A well-crafted muscle gain diet plan ensures that your body has the necessary nutrients to repair, rebuild, and grow stronger muscles. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know to create an effective muscle gain diet plan tailored to your individual needs.
Understanding Muscle Gain Diet Plans
Muscle gain diet plans are meticulously crafted nutritional strategies designed to provide the necessary fuel for muscle growth and recovery. These plans focus on the right balance of macronutrients, calorie intake, and meal timing to maximize muscle hypertrophy.
What Is a Muscle Gain Diet Plan?
A muscle gain diet plan outlines the specific foods and nutrients you need to consume to support muscle growth. It typically includes a higher calorie intake than maintenance levels, increased protein consumption, and balanced carbohydrates and fats to fuel workouts and recovery.
Why Is It Important?
Without a proper diet plan, your body may not have the necessary resources to build and repair muscle tissue. A well-structured diet ensures that you’re providing your body with the right nutrients at the right times, enhancing your training efforts and leading to better results.
The Science Behind Muscle Growth
Muscle growth, or hypertrophy, occurs when the body repairs and grows muscle fibers in response to stress, such as weightlifting. Adequate nutrition is crucial in this process, providing the necessary building blocks for muscle repair and growth. Consuming sufficient protein, carbohydrates, and fats, along with vitamins and minerals, supports these physiological processes.
Macronutrients: The Building Blocks
Muscle gain diet plans heavily rely on the balance of macronutrients: proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Each plays a unique role in muscle synthesis and overall health.
Proteins
Proteins are the cornerstone of any muscle gain diet plan. They provide the amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth. Aim for high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, dairy, legumes, and protein supplements.
**Daily Protein Requirements:**
For optimal muscle gain, it’s recommended to consume approximately 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. For example, a 70kg individual should aim for 112 to 154 grams of protein daily.
**Protein Timing:**
Distributing protein intake evenly throughout the day can enhance muscle protein synthesis. Including protein in every meal and snack ensures a steady supply of amino acids to your muscles.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are essential for fueling your workouts and replenishing glycogen stores. Incorporate complex carbs like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits to maintain energy levels and support muscle recovery.
**Types of Carbohydrates:**
– **Complex Carbs:** Provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber (e.g., brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes).
– **Simple Carbs:** Offer quick energy and are best consumed around workout times (e.g., fruits, honey).
**Carb Intake:**
A general guideline is to consume 3-5 grams of carbohydrates per kilogram of body weight, depending on your activity level and muscle gain goals.
Fats
Healthy fats are crucial for hormone production, including testosterone, which plays a significant role in muscle growth. Include sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in your muscle gain diet plan.
**Healthy Fat Sources:**
– **Monounsaturated Fats:** Found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
– **Polyunsaturated Fats:** Including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids from fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
– **Saturated Fats:** Should be consumed in moderation from sources like dairy and lean meats.
**Fat Intake:**
Aim for fats to make up about 20-30% of your total daily calorie intake. Balancing fats is essential for overall health and optimal muscle gain.
| Macronutrient | Role in Muscle Gain | Recommended Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Proteins | Muscle repair and growth | Chicken, fish, beans, protein powders |
| Carbohydrates | Energy and glycogen replenishment | Brown rice, oats, sweet potatoes |
| Fats | Hormone production and energy | Avocados, nuts, olive oil |
Meal Timing for Optimal Muscle Growth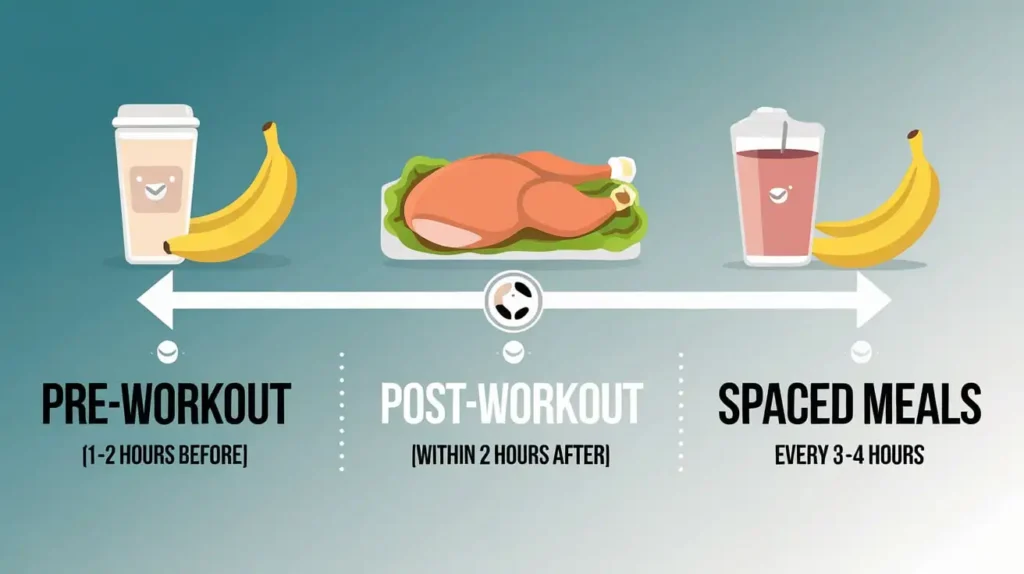
Muscle gain diet plans also emphasize the importance of meal timing. Consuming the right nutrients at specific times can enhance muscle protein synthesis and recovery.
Pre-Workout Nutrition
Eating a balanced meal containing carbohydrates and proteins 1-2 hours before your workout can provide the necessary energy and amino acids to fuel your training session.
**Benefits of Pre-Workout Meals:**
– Increased energy levels
– Enhanced performance
– Reduced muscle breakdown during exercise
**Sample Pre-Workout Meals:**
– Whole grain toast with peanut butter and banana slices
– Greek yogurt with granola and berries
– Oatmeal topped with protein powder and honey
Post-Workout Nutrition
After your workout, it’s crucial to consume a meal rich in proteins and carbohydrates to aid in muscle recovery and replenish glycogen stores. This window is often referred to as the “anabolic window.”
**Benefits of Post-Workout Meals:**
– Accelerated muscle recovery
– Replenishment of glycogen stores
– Enhanced muscle protein synthesis
**Sample Post-Workout Meals:**
– Grilled chicken with quinoa and steamed vegetables
– Protein shake with a banana and a handful of nuts
– Cottage cheese with pineapple and whole grain crackers
- Have a protein-rich snack 30 minutes before training.
- Consume a carb and protein meal within 2 hours post-workout.
- Stay hydrated throughout the day to support metabolic processes.
- Consider small, frequent meals to maintain energy levels.
Supplements: Do You Need Them?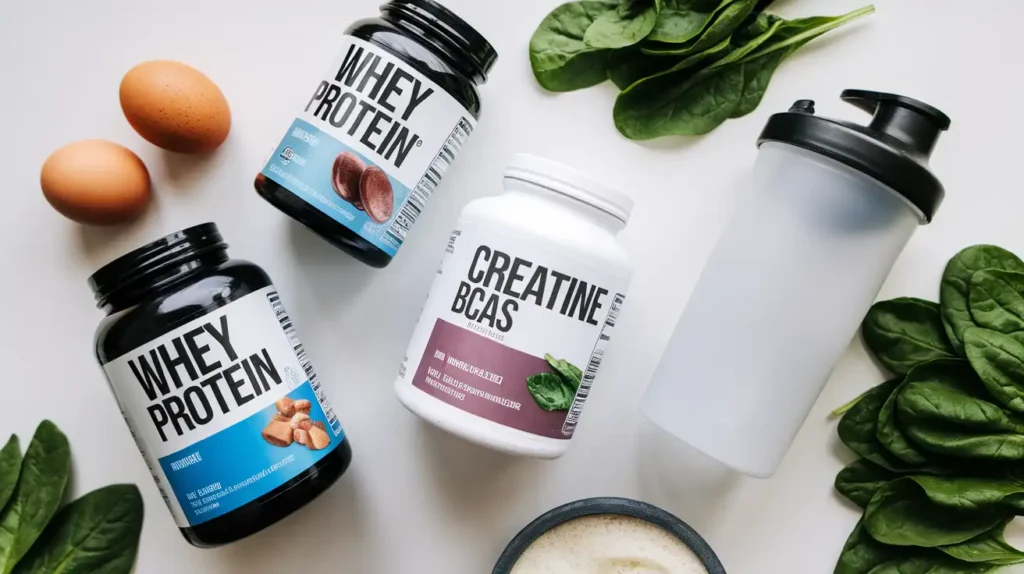
Muscle gain diet plans often incorporate supplements to bridge nutritional gaps and enhance muscle growth. However, supplements should complement, not replace, a balanced diet.
Protein Supplements
Whey, casein, and plant-based protein powders are popular supplements that provide convenient protein sources to meet daily requirements.
**Types of Protein Supplements:**
– **Whey Protein:** Fast-digesting, ideal for post-workout
– **Casein Protein:** Slow-digesting, suitable for nighttime
– **Plant-Based Proteins:** Suitable for vegetarians and vegans, such as pea or hemp protein
**When to Use:**
Protein supplements are best used to supplement meals, especially when you’re unable to meet your protein needs through food alone.
Creatine
Creatine monohydrate is one of the most researched supplements, known to improve strength, increase lean muscle mass, and aid in muscle recovery.
**Benefits of Creatine:**
– Enhanced performance in high-intensity training
– Increased muscle mass over time
– Improved recovery and reduced muscle soreness
**How to Use:**
A common approach is to start with a loading phase of 20 grams per day for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day.
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
BCAAs support muscle protein synthesis and reduce muscle soreness, making them a valuable addition to a muscle gain diet plan.
**Benefits of BCAAs:**
– Promote muscle growth
– Decrease muscle fatigue
– Reduce exercise-induced muscle damage
**When to Use:**
BCAAs can be consumed before, during, or after workouts to maximize their benefits.
Other Supplements
Additional supplements that may support muscle gain include:
- Beta-Alanine: Enhances muscular endurance
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Supports overall health and reduces inflammation
- Multivitamins: Ensures you meet daily micronutrient requirements
Creating Your Muscle Gain Meal Plan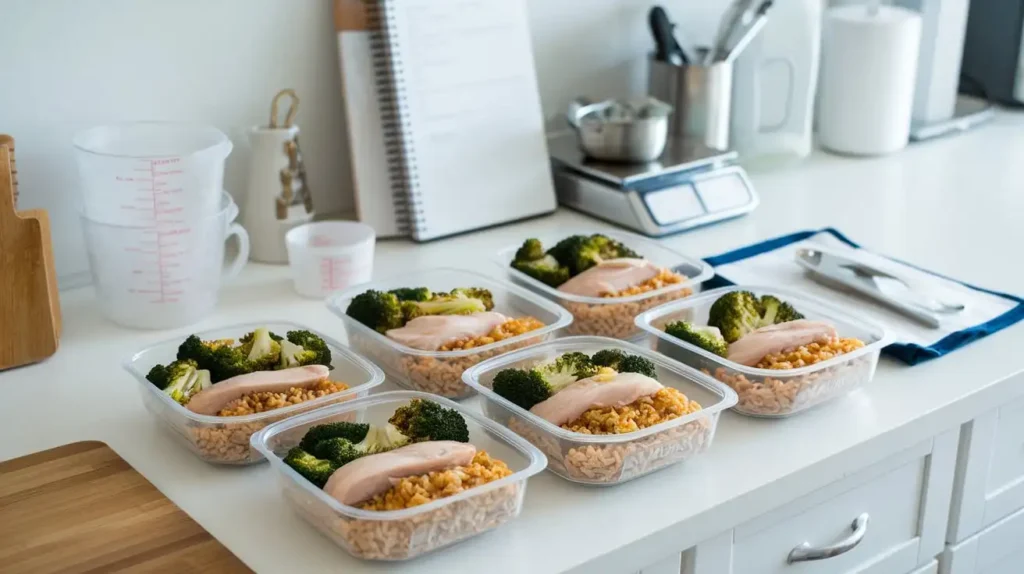
Muscle gain diet plans should be personalized to fit individual needs, preferences, and goals. Here’s how to create an effective meal plan:
Calculate Your Caloric Needs
Determine your basal metabolic rate (BMR) and adjust for activity level to find your daily caloric needs. Aim for a caloric surplus to support muscle growth.
**Steps to Calculate Caloric Needs:**
1. **Determine BMR:** Use the Harris-Benedict equation or online calculators.
2. **Factor in Activity Level:** Multiply BMR by an activity factor (e.g., sedentary, lightly active, active, very active).
3. **Add Caloric Surplus:** Typically, add 250-500 calories per day to your maintenance level for muscle gain.
**Example Calculation:**
– BMR: 1,800 calories
– Activity Level (Moderately Active): BMR x 1.55 = 2,790 calories
– Caloric Surplus: +300 calories
– **Total Daily Calories:** 3,090 calories
Distribute Macronutrients
Allocate your calories to proteins, carbohydrates, and fats based on your specific muscle gain goals. A common ratio is 40% carbs, 30% protein, and 30% fats.
**Example Macronutrient Breakdown for 3,000 Calories:**
– **Proteins:** 30% of 3,000 = 900 calories / 4 = 225 grams
– **Carbohydrates:** 40% of 3,000 = 1,200 calories / 4 = 300 grams
– **Fats:** 30% of 3,000 = 900 calories / 9 = 100 grams
Plan Your Meals
Divide your daily caloric and macronutrient intake across multiple meals and snacks to maintain energy levels and support muscle growth.
**Sample Meal Distribution:**
– **Breakfast:** 25% of daily intake
– **Morning Snack:** 10%
– **Lunch:** 25%
– **Afternoon Snack:** 10%
– **Dinner:** 25%
– **Evening Snack:** 5%
Sample Muscle Gain Meal Plan
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with protein powder, berries, and almonds.
- Morning Snack: Greek yogurt with honey and granola.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast, quinoa, and steamed vegetables.
- Afternoon Snack: Protein shake and a banana.
- Dinner: Baked salmon, sweet potatoes, and asparagus.
- Evening Snack: Cottage cheese with sliced pineapple.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with a solid muscle gain diet plan, certain mistakes can hinder your progress. Being aware of these can help you stay on track.
Insufficient Protein Intake
Not consuming enough protein can limit muscle repair and growth. Ensure you’re meeting your daily protein requirements by including protein-rich foods in every meal.
Neglecting Healthy Fats
Fats are essential for hormone production and overall health. Don’t skimp on healthy fat sources, as they play a crucial role in muscle gain and recovery.
Overlooking Caloric Surplus
To gain muscle, you need to consume more calories than you burn. Ensure your diet plan includes a sufficient caloric surplus to provide the energy needed for muscle growth.
- Skipping meals, leading to insufficient nutrient intake.
- Relying too heavily on supplements instead of whole foods.
- Ignoring hydration, which is vital for metabolic functions.
- Not tracking your food intake, making it difficult to adjust your diet as needed.
- Focusing solely on weight gain without considering body composition.
Inconsistent Eating Schedule
Irregular meal times can disrupt your body’s ability to utilize nutrients effectively. Aim for a consistent eating schedule to maintain steady energy levels and support muscle growth.
Overtraining Without Proper Nutrition
Intense training without adequate nutrition can lead to muscle breakdown rather than growth. Ensure your diet plan supports your training intensity and recovery needs.
Personalizing Your Muscle Gain Diet Plan
Every individual is unique, and your muscle gain diet plan should reflect your personal needs, preferences, and goals.
Assess Your Body Type
Understanding your body type (ectomorph, mesomorph, endomorph) can help tailor your diet plan for optimal results.
**Body Types:**
– **Ectomorph:** Naturally lean with a fast metabolism; may require a higher caloric intake
– **Mesomorph:** Naturally muscular with a balanced metabolism; can gain muscle and fat more easily
– **Endomorph:** Naturally higher body fat with a slower metabolism; may benefit from a more controlled caloric intake
Consider Dietary Preferences and Restrictions
Whether you’re vegetarian, vegan, or have specific dietary restrictions, your muscle gain diet plan should accommodate your lifestyle.
| Dietary Preference | Protein Sources |
|---|---|
| Omnivore | Chicken, beef, fish, eggs |
| Vegetarian | Dairy, eggs, legumes, tofu |
| Vegan | Legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan |
| Gluten-Free | Quinoa, rice, gluten-free grains, lean meats |
| Keto | Meat, fish, eggs, high-fat dairy, nuts |
Incorporate Food Preferences
Your muscle gain diet plan should include foods you enjoy to ensure long-term adherence. Experiment with different recipes and meal ideas to keep your diet varied and satisfying.
Adjust for Activity Level
Your daily activity level and workout intensity influence your caloric and macronutrient needs. Adjust your diet plan accordingly to match your energy expenditure.
**Activity Level Adjustments:**
– **Sedentary:** Lower caloric intake with a focus on nutrient-dense foods
– **Lightly Active:** Moderate caloric intake with balanced macronutrients
– **Highly Active:** Higher caloric intake with increased carbohydrates and proteins
Tracking Your Progress
Monitoring your progress is crucial to ensure your muscle gain diet plan is effective and to make necessary adjustments.
Keep a Food Diary
Recording what you eat helps you stay accountable and ensures you’re meeting your nutritional goals.
**Benefits of a Food Diary:**
– Identifies eating patterns
– Helps track macronutrient intake
– Aids in adjusting portion sizes and food choices
**Tools to Use:**
– **Apps:** MyFitnessPal, Cronometer
– **Journals:** Physical notebooks for manual tracking
Regular Measurements
Track your weight, muscle measurements, and body fat percentage to gauge muscle growth and overall progress.
**Measurement Tips:**
– Weigh yourself consistently at the same time each day
– Use a tape measure to track muscle girths (e.g., arms, chest, thighs)
– Consider using body fat scales or getting professional body composition analyses
- Use apps like MyFitnessPal to log your meals.
- Take weekly progress photos.
- Schedule regular check-ins with a nutritionist or trainer.
- Monitor strength gains in the gym as an indirect indicator of muscle growth.
- Keep a training log to correlate dietary changes with performance improvements.
Set Realistic Goals
Establish achievable and measurable goals to stay motivated and track progress effectively.
**Goal-Setting Tips:**
– **Short-Term Goals:** Weekly or monthly targets (e.g., gain 2 pounds of muscle in a month)
– **Long-Term Goals:** Annual or semi-annual objectives (e.g., increase muscle mass by 10%)
– **SMART Goals:** Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound
Adjust Your Plan as Needed
Based on your progress tracking, make necessary adjustments to your muscle gain diet plan to overcome plateaus or address deficiencies.
**When to Adjust:**
– If weight gain is too slow or too fast
– If energy levels are consistently low
– If you’re not seeing desired muscle growth despite consistent training
Advanced Strategies for Muscle Gain
Once you’ve established a solid foundation with your muscle gain diet plan, you can incorporate advanced strategies to further optimize muscle growth.
Periodization
Periodization involves cycling through different phases of training and nutrition to prevent plateaus and promote continuous muscle growth.
**Types of Periodization:**
– **Linear Periodization:** Gradually increasing intensity while decreasing volume
– **Undulating Periodization:** Varying intensity and volume within shorter time frames
– **Block Periodization:** Focusing on specific training blocks (e.g., strength, hypertrophy, endurance)
**Nutrition Adjustments:**
– Modify macronutrient ratios based on training phases
– Increase carbohydrates during high-intensity training blocks
– Adjust calorie intake to match training demands
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting can be integrated into a muscle gain diet plan to manage calorie intake and improve metabolic health.
**Common Methods:**
– **16/8 Method:** 16 hours of fasting with an 8-hour eating window
– **5:2 Diet:** Normal eating for 5 days with restricted calories on 2 non-consecutive days
– **Eat-Stop-Eat:** 24-hour fast once or twice a week
**Benefits:**
– Improved insulin sensitivity
– Enhanced fat metabolism
– Potential for increased growth hormone levels
Carb Cycling
Carb cycling involves varying carbohydrate intake on training and rest days to optimize energy levels and fat loss while supporting muscle gain.
**How It Works:**
– **High-Carb Days:** Align with intense training days to fuel workouts and replenish glycogen
– **Low-Carb Days:** Align with rest days to promote fat burning and insulin sensitivity
– **No-Carb Days:** Occasionally implemented to maximize fat loss and metabolic flexibility
**Implementation Tips:**
– Plan high-carb days around your most intense training sessions
– Ensure adequate protein and healthy fats on all days
– Monitor your body’s response and adjust accordingly
Hydration and Muscle Gain
Proper hydration is a critical component of your muscle gain diet plan. Water plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, including nutrient transport, digestion, and muscle function.
Importance of Hydration
Staying adequately hydrated ensures that your muscles function optimally during workouts and aids in recovery.
**Benefits of Proper Hydration:**
– Enhanced muscle contraction and performance
– Improved nutrient absorption
– Reduced risk of cramps and injuries
– Support for metabolic processes involved in muscle growth
Daily Water Intake Recommendations
The general guideline for water intake is:
- Men: Approximately 3.7 liters (125 ounces) per day
- Women: Approximately 2.7 liters (91 ounces) per day
**Factors Influencing Water Needs:**
– **Exercise Intensity and Duration:** More intense and longer workouts increase water requirements
– **Climate:** Hot and humid environments necessitate higher fluid intake
– **Individual Metabolism:** Varies based on body size and activity level
Hydration Strategies
Implement these strategies to maintain optimal hydration:
- Start your day with a glass of water
- Carry a water bottle during workouts
- Consume electrolyte-rich beverages if sweating heavily
- Include hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges in your diet
Signs of Dehydration
Be aware of the signs of dehydration, which can impede muscle gain and overall health:
- Dark yellow urine
- Dry mouth and lips
- Fatigue and dizziness
- Muscle cramps and spasms
Rest and Recovery
While a well-structured muscle gain diet plan is crucial, rest and recovery are equally important for muscle growth and overall health.
Importance of Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for muscle recovery and growth. During sleep, the body repairs muscle tissues and releases growth hormones.
**Sleep Recommendations:**
– Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night
– Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
– Create a restful environment by minimizing light and noise
**Benefits of Adequate Sleep:**
– Enhanced muscle repair and growth
– Improved cognitive function and focus
– Reduced risk of injury and overtraining
Active Recovery
Incorporate active recovery days into your training schedule to promote blood flow and reduce muscle soreness without intense exertion.
**Active Recovery Activities:**
– Light cardio (e.g., walking, cycling)
– Stretching and flexibility exercises
– Yoga or Pilates
– Foam rolling and self-myofascial release
Rest Days
Designate specific days for complete rest to allow your muscles to recover fully.
**Rest Day Tips:**
– Avoid strenuous activities
– Focus on gentle movements and stretching
– Prioritize relaxation and stress management
Managing Stress
Chronic stress can impede muscle growth by increasing cortisol levels, which can lead to muscle breakdown.
**Stress Management Techniques:**
– Practice mindfulness and meditation
– Engage in hobbies and activities you enjoy
– Maintain a balanced work-life schedule
– Seek professional help if needed
Mental Factors in Muscle Gain
Your mental state plays a significant role in your ability to adhere to a muscle gain diet plan and achieve your fitness goals.
Motivation and Consistency
Staying motivated and consistent is key to long-term muscle gain. Developing a strong mindset can help you overcome challenges and maintain your diet and training regimen.
**Strategies to Boost Motivation:**
– Set clear, achievable goals
– Celebrate small victories
– Visualize your success
– Surround yourself with supportive individuals
Mindful Eating
Practicing mindful eating helps you stay in tune with your body’s hunger and fullness cues, preventing overeating and promoting healthier food choices.
**Mindful Eating Tips:**
– Eat slowly and savor each bite
– Avoid distractions like TV or smartphones during meals
– Listen to your body’s hunger signals
– Focus on the taste, texture, and aroma of your food
Overcoming Plateaus
Muscle gain plateaus are common, but with the right strategies, you can overcome them and continue progressing.
**Plateau-Busting Tips:**
– Vary your workout routines
– Reassess and adjust your diet plan
– Increase training intensity or volume
– Incorporate new training techniques like supersets or drop sets
Building a Support System
Having a support system can enhance your adherence to a muscle gain diet plan by providing encouragement and accountability.
**Support System Components:**
– Training partners or workout buddies
– Nutritionists or dietitians
– Online communities or forums
– Family and friends who support your goals
Conclusion
A well-structured muscle gain diet plan is fundamental to achieving your muscle-building goals. By understanding the importance of macronutrients, meal timing, and personalized nutrition, you can optimize your diet to support muscle growth effectively. Remember to avoid common pitfalls, track your progress diligently, and adjust your plan as needed to ensure continued success on your fitness journey.
Incorporate the strategies and insights outlined in this guide to build a sustainable and effective muscle gain diet plan. Combine proper nutrition with consistent training, adequate rest, and a positive mindset to maximize your muscle growth and overall health.
Stay committed, stay informed, and enjoy the transformative journey towards a stronger, healthier you.
References




