Long-Term Diet After Colon Resection: Comprehensive Guide for Optimal Health
1. Introduction
Long-term diet after colon resection is essential for ensuring a smooth recovery and maintaining overall health. Undergoing a colon resection, whether due to cancer, diverticulitis, or other medical conditions, significantly impacts your digestive system. Adopting a carefully planned diet can help mitigate post-surgical complications, enhance nutrient absorption, and improve your quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of a long-term diet after colon resection, providing you with actionable insights and practical tips to navigate your dietary journey successfully.
2. Understanding Colon Resection
Long-term diet after colon resection begins with understanding the procedure itself. Colon resection involves the surgical removal of a portion of the colon, which can affect digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall gastrointestinal function.
What is Colon Resection?
Colon resection, also known as colectomy, is performed to treat conditions like colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, and ischemic colitis. The extent of the surgery varies depending on the underlying condition and the portion of the colon removed.
Impact on Digestive Health
Removing a section of the colon can lead to changes in bowel habits, nutrient absorption, and overall digestive efficiency. Patients may experience increased bowel frequency, diarrhea, or constipation, necessitating dietary adjustments to manage these symptoms effectively.
3. Importance of Long-Term Diet After Colon Resection
Long-term diet after colon resection plays a pivotal role in recovery and long-term health maintenance. A well-balanced diet can help prevent nutritional deficiencies, support the healing process, and reduce the risk of post-surgical complications.
Proper nutrition aids in:
- Enhancing wound healing and tissue regeneration
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Preventing anemia and other nutrient deficiencies
- Managing bowel movements and reducing gastrointestinal discomfort
- Boosting immune function to prevent infections
Therefore, adopting a long-term dietary strategy is not just beneficial but essential for individuals recovering from colon resection.
4. Nutritional Needs Post-Surgery

Addressing the long-term diet after colon resection involves understanding the specific nutritional needs that arise post-surgery. These needs may vary based on the extent of the surgery, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of any underlying conditions.
Macronutrients
Ensuring adequate intake of macronutrients—proteins, carbohydrates, and fats—is crucial:
- Proteins: Essential for tissue repair and immune function. Sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy and aid in bowel regularity. Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits.
- Fats: Necessary for hormone production and nutrient absorption. Include healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, and fatty fish.
Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals are vital for various bodily functions:
- Iron: Prevents anemia, especially important if there has been significant blood loss during surgery. Sources include red meat, spinach, and fortified cereals.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Support bone health. Found in dairy products, fortified plant milks, and sunlight exposure.
- Vitamin B12: Important for nerve function and red blood cell formation. Present in animal products and fortified foods.
- Folate: Aids in DNA synthesis and repair. Found in leafy greens, legumes, and fortified grains.
Hydration
Maintaining proper hydration is critical, especially if bowel movements are increased post-surgery. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily, and consider electrolyte-rich beverages if necessary.
5. Recommended Foods for Recovery
Incorporating the right foods is a cornerstone of the long-term diet after colon resection. These foods support healing, enhance nutrient absorption, and help maintain bowel health.
Lean Proteins
Lean proteins are essential for repairing tissues and boosting immune function.
- Chicken and turkey
- Fish and seafood
- Eggs
- Tofu and tempeh
- Legumes like lentils and beans
Whole Grains
Whole grains provide sustained energy and support digestive health.
- Oatmeal
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Whole wheat bread and pasta
- Barley
Fruits and Vegetables
Rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, fruits and vegetables are vital for overall health.
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale
- Berries
- Bananas
- Carrots
- Sweet potatoes
Healthy Fats
Incorporate healthy fats to support cellular function and hormone production.
- Olive oil
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel
Dairy or Alternatives
Ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake for bone health.
- Milk, yogurt, and cheese
- Fortified plant-based milks
- Fortified cereals
6. Foods to Avoid After Colon Resection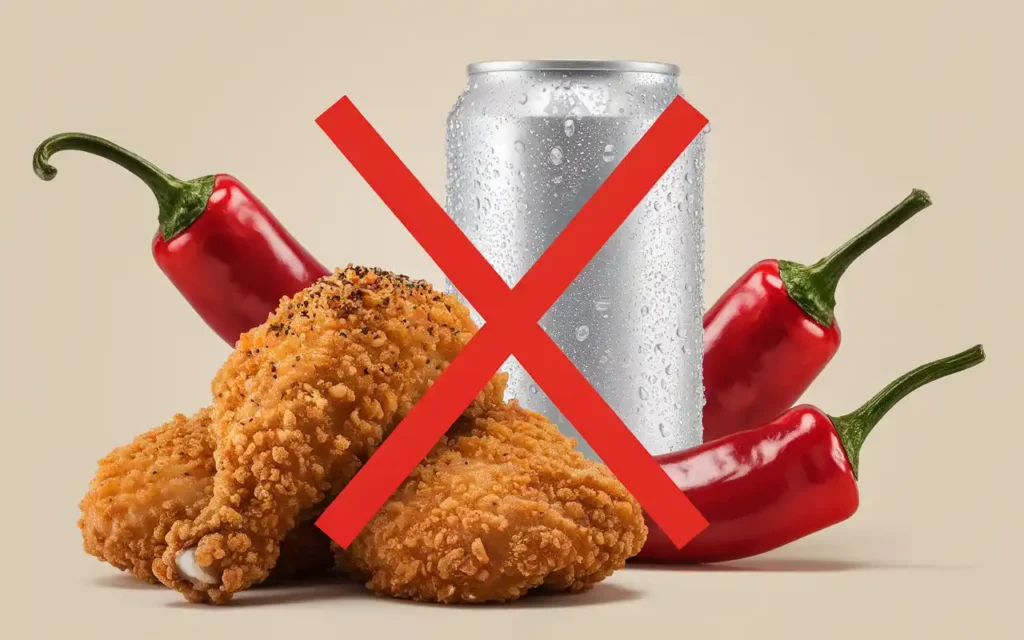
While focusing on beneficial foods is important, the long-term diet after colon resection also involves avoiding certain foods that can exacerbate symptoms or hinder recovery.
High-Fiber Foods Initially
Immediately after surgery, high-fiber foods can be hard to digest. Gradually reintroduce them as tolerated.
- Raw vegetables
- Whole nuts
- Seeds
- Popcorn
Spicy and Irritating Foods
Spices can irritate the digestive tract and should be minimized initially.
- Chili peppers
- Hot sauces
- Spicy condiments
Fatty and Fried Foods
These can slow digestion and lead to discomfort.
- Fried chicken
- French fries
- High-fat dairy products
- Processed meats
Carbonated Beverages
Carbonation can cause bloating and gas.
- Sodas
- Carbonated water
- Beer
Alcohol and Caffeine
These can irritate the digestive system and should be consumed in moderation.
- Alcoholic beverages
- Coffee
- Energy drinks
7. Meal Planning and Preparation

Effective meal planning is a cornerstone of the long-term diet after colon resection. It ensures that you receive balanced nutrition while managing digestive comfort.
Creating a Balanced Meal Plan
A well-structured meal plan should include a balance of proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats, along with ample vitamins and minerals.
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and a side of yogurt.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens and quinoa.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with sweet potatoes and steamed vegetables.
- Snacks: Almonds, sliced fruits, or hummus with whole-grain crackers.
Meal Preparation Tips
Preparing meals in advance can help maintain dietary consistency and reduce stress.
- Batch cook proteins and grains for the week.
- Store pre-cut vegetables and fruits for easy access.
- Use airtight containers to keep meals fresh.
- Incorporate variety to prevent meal fatigue.
Listening to Your Body
Pay attention to how different foods affect your body and adjust your meal plan accordingly. Keeping a food diary can be beneficial in identifying triggers and optimizing your diet.
8. Dietary Supplements and Their Role
In some cases, supplements may be necessary to meet the long-term diet after colon resection nutritional requirements, especially if certain nutrients are lacking due to reduced absorption.
Common Supplements
- Vitamin B12: Essential for nerve function and red blood cell formation.
- Iron: Prevents anemia, particularly important if there has been significant blood loss.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Support bone health and prevent osteoporosis.
- Probiotics: Aid in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reduce inflammation and support heart health.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Before starting any supplements, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate types and dosages tailored to your specific needs.
Integrating Supplements into Your Diet
Supplements should complement your diet, not replace whole foods. Incorporate them as part of your daily routine, preferably with meals to enhance absorption and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort.
9. Managing Side Effects Through Diet
Post-surgery, some patients may experience side effects such as diarrhea, constipation, bloating, or malabsorption. The long-term diet after colon resection can be tailored to manage these symptoms effectively.
Diarrhea Management
- Consume low-fiber foods to reduce bowel movements.
- Stay hydrated with electrolyte-rich beverages.
- Avoid lactose if you are lactose intolerant.
- Incorporate binding foods like bananas and rice.
Constipation Relief
- Increase soluble fiber intake gradually.
- Stay well-hydrated throughout the day.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Consider natural laxatives like prunes or psyllium husk.
Bloating and Gas Reduction
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals.
- Chew food thoroughly to aid digestion.
- Avoid carbonated beverages and chewing gum.
- Identify and eliminate gas-producing foods.
Addressing Malabsorption
- Include enzyme supplements if recommended by your doctor.
- Focus on nutrient-dense foods to maximize absorption.
- Monitor vitamin and mineral levels regularly.
10. Lifestyle Changes for Sustained Health
Beyond diet, certain lifestyle modifications can enhance the effectiveness of your long-term diet after colon resection and promote overall well-being.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, supports digestive function, and boosts mood.
- Walking or light jogging
- Yoga or Pilates
- Strength training
- Swimming
Stress Management
Stress can impact digestive health and overall recovery. Incorporate stress-reducing practices into your daily routine.
- Meditation and mindfulness
- Deep breathing exercises
- Hobbies and leisure activities
- Social support and counseling
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Consistent follow-ups with your healthcare provider ensure that your dietary plan remains effective and adjusts to any changing health needs.
- Routine blood tests to monitor nutrient levels
- Scheduled consultations with dietitians
- Monitoring for any post-surgical complications
Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for healing and maintaining overall health.
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule
- Create a restful sleep environment
- Avoid stimulants like caffeine before bedtime
11. Conclusion
Adopting a well-planned long-term diet after colon resection is vital for your recovery and long-term health. By understanding your nutritional needs, making informed food choices, and implementing effective meal planning strategies, you can significantly improve your quality of life post-surgery.
Remember to consult with healthcare professionals to tailor your diet to your specific needs and to address any challenges that may arise. With dedication and the right guidance, you can navigate the dietary changes successfully and achieve optimal health.
12. References




