Comprehensive Guide to a Healthy Gut Diet Plan
Introduction
A healthy gut diet plan is essential for maintaining overall well-being. Your gut health plays a crucial role in digestion, immunity, and even mental health. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know to create and maintain a healthy gut diet plan that works for you.
In today’s fast-paced world, many individuals overlook the importance of gut health, often leading to various digestive issues and other health complications. By understanding the fundamentals of a healthy gut diet plan, you can make informed dietary choices that support your body’s natural processes.
Whether you’re dealing with chronic digestive problems, seeking to boost your immune system, or aiming to improve your mental well-being, a healthy gut diet plan can be a pivotal component of your health strategy.
1. Understanding the Gut Microbiome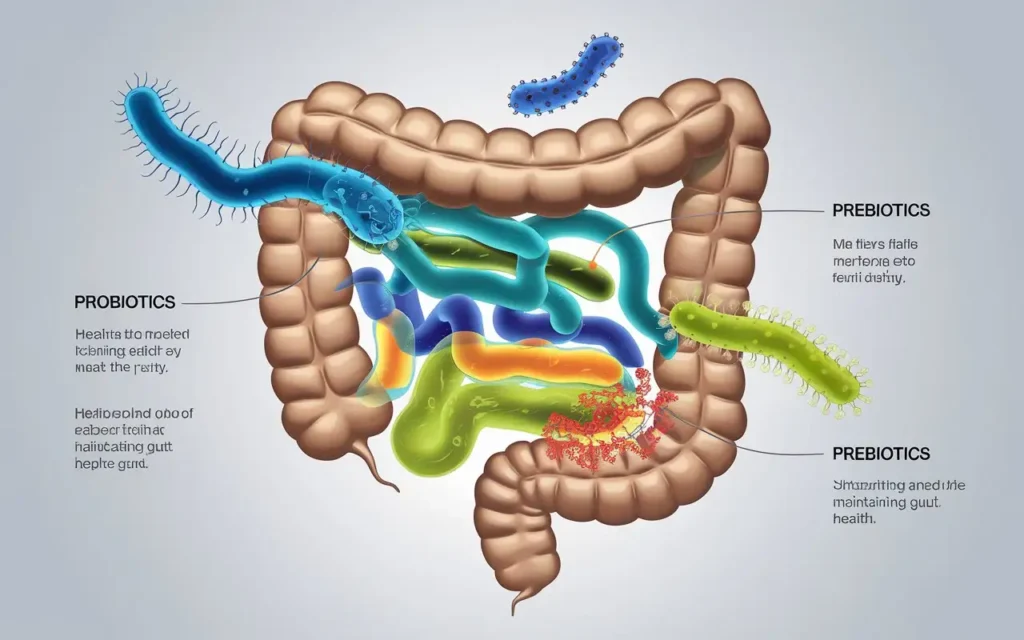
A healthy gut diet plan begins with understanding the gut microbiome. The gut microbiome consists of trillions of microorganisms that reside in your digestive tract, playing a vital role in your health.
What is the Gut Microbiome?
The gut microbiome is a complex community of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. These microbes help in digesting food, producing vitamins, and protecting against harmful pathogens. A diverse and balanced microbiome is crucial for optimal health.
Importance of a Balanced Microbiome
Maintaining a balanced microbiome is crucial. An imbalance, known as dysbiosis, can lead to various health issues, including digestive problems, weakened immunity, and even mental health disorders.
- Enhances digestion and nutrient absorption
- Boosts the immune system
- Supports mental health through the gut-brain axis
- Prevents the growth of harmful bacteria
- Regulates metabolism and weight
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut and brain communicate through a bidirectional pathway known as the gut-brain axis. A healthy gut diet plan can influence mood, stress levels, and cognitive functions by affecting this communication system.
Neurotransmitter Production
Approximately 90% of the body’s serotonin, a key neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation, is produced in the gut. A balanced microbiome supports the production of serotonin, thereby influencing mental well-being.
Stress Response
Chronic stress can disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to inflammation and digestive issues. Conversely, a healthy gut diet plan can mitigate the effects of stress by promoting a resilient microbiome.
Factors Affecting the Gut Microbiome
Several factors influence the composition and health of your gut microbiome, including:
- Diet: The types of foods you consume directly impact microbial diversity.
- Antibiotics: While necessary for treating infections, antibiotics can disrupt the microbiome balance.
- Lifestyle: Stress, sleep patterns, and physical activity play roles in gut health.
- Environment: Exposure to pollutants and toxins can affect microbial communities.
Conclusion
Understanding the gut microbiome is the first step in crafting a healthy gut diet plan. By nurturing a balanced and diverse microbial community, you lay the foundation for improved digestion, enhanced immunity, and better mental health.
2. Benefits of a Healthy Gut Diet Plan
A healthy gut diet plan offers numerous benefits that extend beyond just digestive health. By focusing on gut health, you can improve various aspects of your overall well-being.
Improved Digestive Health
One of the primary benefits is enhanced digestion. A balanced diet supports regular bowel movements and reduces the risk of digestive disorders like IBS and constipation.
Incorporating fiber-rich foods and probiotics in your healthy gut diet plan can alleviate symptoms such as bloating, gas, and indigestion, promoting a smoother digestive process.
Enhanced Immune Function
Your gut is home to a significant portion of your immune system. A healthy gut diet plan strengthens immune responses, helping your body fend off infections and illnesses more effectively.
By maintaining a balanced microbiome, your body can better distinguish between harmful pathogens and beneficial microbes, reducing the likelihood of autoimmune reactions and allergies.
Better Mental Health
There is a strong connection between gut health and mental well-being. A healthy gut diet plan can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression by promoting the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin.
Studies have shown that individuals with a diverse gut microbiome often experience lower levels of stress and improved mood, highlighting the importance of dietary choices in mental health management.
Weight Management
A healthy gut diet plan can aid in weight management by influencing metabolism and appetite regulation. Beneficial gut bacteria help break down food more efficiently and may play a role in fat storage.
By fostering a microbiome that supports lean body mass and reduces inflammation, a healthy gut diet can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight and preventing obesity-related conditions.
Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to numerous health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. A healthy gut diet plan can help reduce inflammation by promoting the growth of anti-inflammatory bacteria.
Foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, commonly included in gut-friendly diets, play a significant role in mitigating inflammatory responses within the body.
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
Proper digestion and a balanced microbiome ensure that your body effectively absorbs essential nutrients from the food you consume. This enhances overall health and supports bodily functions.
By focusing on a healthy gut diet plan, you ensure that vitamins, minerals, and other vital nutrients are efficiently absorbed, leading to improved energy levels and reduced risk of deficiencies.
Skin Health Improvement
Gut health has a direct impact on skin health. A balanced microbiome can help manage skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis by reducing systemic inflammation and promoting skin hydration.
Incorporating foods that support gut health, such as probiotics and high-fiber vegetables, can lead to a clearer, more radiant complexion.
Enhanced Energy Levels
A healthy gut diet plan supports efficient digestion and nutrient absorption, which translates to higher energy levels and reduced fatigue. By fueling your body with the right nutrients, you maintain consistent energy throughout the day.
Moreover, reducing digestive discomfort allows your body to focus energy on daily activities rather than managing gastrointestinal distress.
Longevity and Quality of Life
Maintaining a healthy gut through a balanced diet can contribute to increased longevity and an improved quality of life. By preventing chronic diseases and supporting overall health, a healthy gut diet plan plays a role in sustaining vitality into later years.
Investing in gut health today sets the stage for a healthier, more active future.
Conclusion
The benefits of a healthy gut diet plan are extensive, impacting various facets of physical and mental health. By prioritizing gut health, you not only enhance your digestion but also bolster your immune system, improve mental well-being, and support overall vitality.
3. Key Components of a Healthy Gut Diet Plan
A healthy gut diet plan is composed of several key components that work together to support and maintain gut health. Understanding these elements is crucial for crafting a diet that promotes a balanced microbiome.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that help maintain a healthy microbiome, while prebiotics are fibers that feed these bacteria. Together, they play a synergistic role in fostering gut health.
Probiotics
Probiotics can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. They help replenish the good bacteria in your gut, especially after disruptions caused by antibiotics or illness.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers found in foods such as garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, and whole grains. They serve as food for probiotics, enhancing their growth and activity.
Balanced Macronutrients
A diet rich in proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates ensures that your body receives the necessary nutrients for optimal function. Balancing these macronutrients supports overall health and maintains energy levels.
Proteins
Lean proteins like chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes are essential for repairing tissues and supporting immune function. They also help in maintaining muscle mass and promoting satiety.
Healthy Fats
Incorporate sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are vital for brain health, hormone production, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Complex Carbohydrates
Whole grains, vegetables, and legumes provide complex carbohydrates that offer sustained energy and support digestive health. They are also rich in fiber, which is crucial for a healthy gut diet plan.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is essential for digestion and overall health. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day to maintain optimal bodily functions.
Proper hydration aids in the movement of food through the digestive tract, prevents constipation, and supports the absorption of nutrients.
Vitamins and Minerals
Ensuring adequate intake of vitamins and minerals like vitamin D, magnesium, zinc, and B-vitamins supports various bodily functions, including immune response, bone health, and energy production.
Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your healthy gut diet plan to obtain a broad spectrum of essential nutrients.
Fiber-Rich Foods
Dietary fiber, found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut diet plan. It promotes regular bowel movements and feeds beneficial gut bacteria.
There are two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance, aiding in nutrient absorption. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool, facilitating regularity.
Avoiding Gut-Disrupting Substances
Minimizing the intake of substances that can disrupt the gut microbiome is a vital component of a healthy gut diet plan. These include excessive alcohol, artificial sweeteners, and processed foods.
Limiting the consumption of these substances helps maintain a balanced microbiome and prevents inflammation and other digestive issues.
Incorporating Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric, ginger, fatty fish, and berries help reduce inflammation in the gut, promoting a healthier microbiome and preventing chronic diseases.
Including these foods in your healthy gut diet plan can aid in healing and maintaining the integrity of the gut lining.
Mindful Eating Practices
Adopting mindful eating practices, such as eating slowly, chewing thoroughly, and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, supports a healthy gut diet plan. These practices improve digestion and enhance the enjoyment of meals.
Mindful eating also helps prevent overeating and reduces stress-related digestive issues.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity complements a healthy gut diet plan by promoting bowel regularity, reducing stress, and enhancing overall health. Activities like walking, yoga, and strength training are beneficial.
Exercise also contributes to maintaining a healthy weight, which is linked to a balanced gut microbiome.
Sleep and Stress Management
Quality sleep and effective stress management are integral to a healthy gut diet plan. Poor sleep and chronic stress can disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to digestive and other health issues.
Incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and ensuring 7-9 hours of sleep each night to support gut health.
Conclusion
A healthy gut diet plan is multifaceted, encompassing balanced nutrition, hydration, mindful eating, and lifestyle factors. By integrating these key components, you can foster a robust and diverse gut microbiome, paving the way for improved health and well-being.
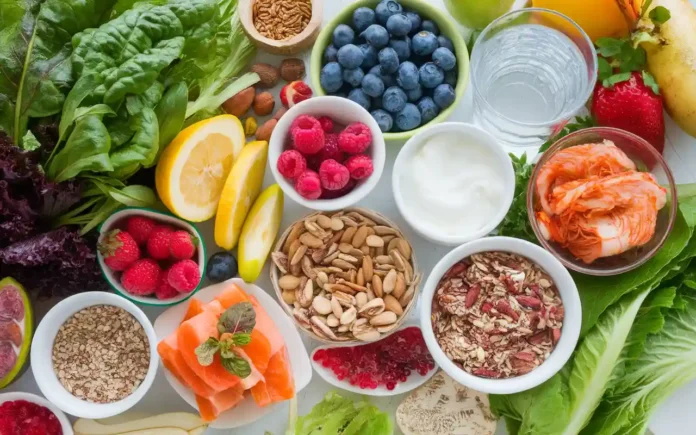
4. Foods to Include in Your Healthy Gut Diet Plan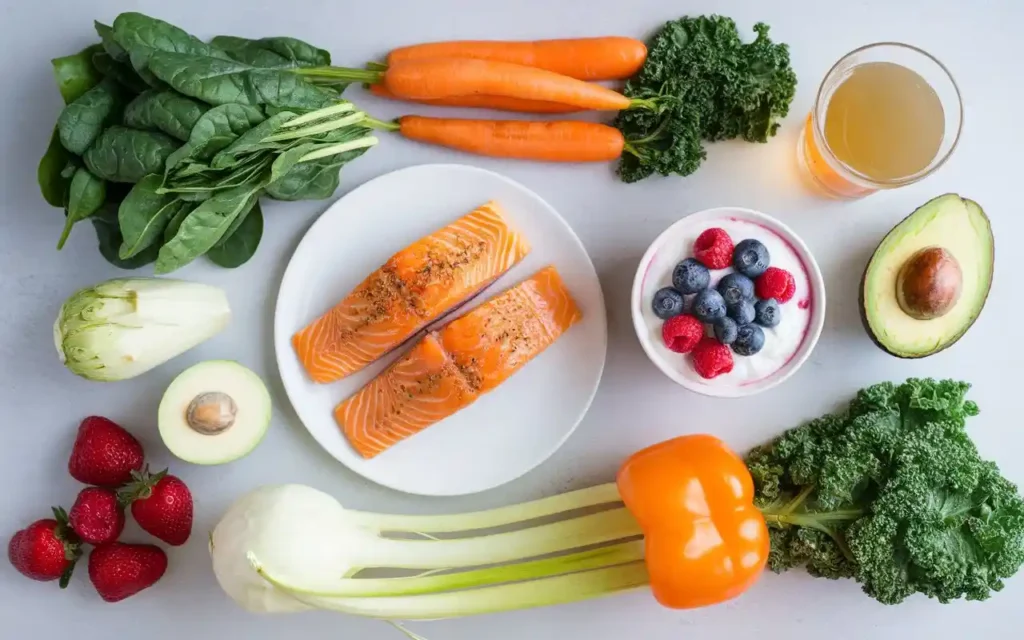
Incorporating the right foods is crucial in a healthy gut diet plan. These foods support the growth of beneficial bacteria and promote overall gut health.
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha are rich in probiotics, which help maintain a healthy microbiome. These foods introduce beneficial bacteria into your digestive system, enhancing microbial diversity.
Yogurt and Kefir
Yogurt and kefir are dairy products fermented with live cultures. They are excellent sources of probiotics, particularly Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, which aid in digestion and immune function.
Sauerkraut and Kimchi
Sauerkraut and kimchi are fermented vegetables rich in probiotics and fiber. They not only support gut health but also add flavor and variety to your meals.
Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented tea beverage containing live cultures and organic acids. It promotes digestion and detoxification while providing a refreshing alternative to sugary drinks.
High-Fiber Foods
Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, act as prebiotics, feeding the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Fiber is essential for maintaining regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits like apples, bananas, berries, and vegetables such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and carrots are excellent sources of dietary fiber. They support a healthy gut diet plan by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Legumes and Whole Grains
Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and beans, along with whole grains such as oats, quinoa, and barley, provide both soluble and insoluble fiber. These fibers aid in digestion and help maintain a balanced microbiome.
Lean Proteins
Lean proteins like chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes provide essential amino acids without overburdening your digestive system. They support muscle repair, immune function, and overall health.
Fish
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties that benefit gut health.
Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, and legumes are excellent alternatives to animal proteins. They are easier to digest and come with additional fiber and nutrients that support a healthy gut diet plan.
Healthy Fats
Incorporate sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil to support overall health. These fats aid in nutrient absorption and provide essential fatty acids that promote a balanced microbiome.
Avocados
Avocados are rich in monounsaturated fats, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. They support gut health by promoting a healthy inflammatory response.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts like almonds, walnuts, and seeds such as chia and flaxseed provide healthy fats and fiber, contributing to a healthy gut diet plan.
Whole Grains
Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, barley, and oats are excellent sources of fiber and nutrients. They support digestive health by providing sustained energy and promoting regular bowel movements.
Oats
Oats are high in soluble fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and supports the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a gluten-free whole grain packed with protein, fiber, and essential amino acids. It supports a healthy gut diet plan by providing the necessary nutrients for overall health.
Herbs and Spices
Incorporating herbs and spices like turmeric, ginger, garlic, and cinnamon can enhance the flavor of your meals while providing anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial benefits that support gut health.
Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with potent anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce gut inflammation and support a balanced microbiome.
Ginger
Ginger aids in digestion, reduces nausea, and has anti-inflammatory effects that benefit gut health.
Conclusion
Including a variety of these foods in your healthy gut diet plan ensures that your gut microbiome receives the necessary nutrients to thrive. By focusing on diverse, nutrient-dense foods, you can support a balanced and healthy digestive system.
5. Foods to Avoid for a Healthy Gut Diet Plan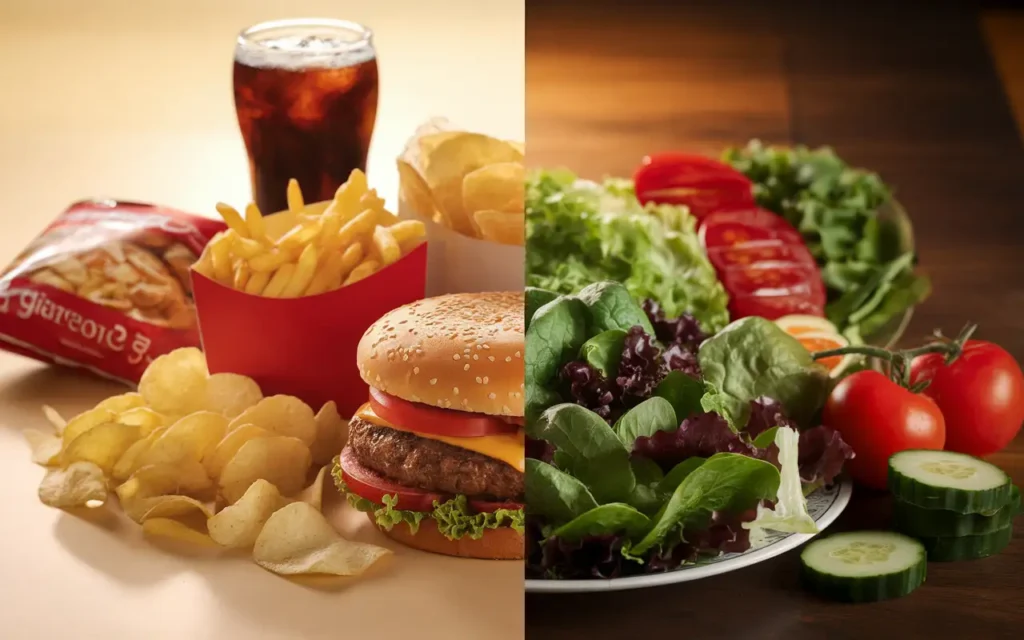
While focusing on what to include, it’s equally important to know which foods to avoid in a healthy gut diet plan. Eliminating or reducing these foods can prevent disruptions to your gut microbiome and reduce the risk of digestive issues.
Processed Foods
Processed foods often contain additives and preservatives that can disrupt the gut microbiome. These foods are typically low in fiber and high in unhealthy fats and sugars, which can promote the growth of harmful bacteria.
Fast Food and Junk Food
Items like burgers, fries, and sugary snacks are high in trans fats, refined sugars, and sodium. These components can lead to inflammation and negatively impact gut health.
Packaged Snacks
Chips, cookies, and other packaged snacks are often loaded with artificial ingredients and lack the necessary nutrients to support a healthy gut diet plan.
Excess Sugar
High sugar intake can promote the growth of harmful bacteria and yeast in the gut. Excessive sugar consumption is linked to an imbalance in the gut microbiome, known as dysbiosis.
Sugary Beverages
Sodas, energy drinks, and sweetened teas contain high levels of sugar that can disrupt gut balance and contribute to weight gain and metabolic issues.
Sweets and Desserts
Candies, pastries, and other sugary treats should be limited as they can feed harmful bacteria and yeast, leading to digestive discomfort and other health problems.
Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners may negatively impact gut bacteria balance and lead to digestive issues. Some studies suggest that these sweeteners can alter the composition of the gut microbiome in ways that promote glucose intolerance and metabolic disorders.
Saccharin and Aspartame
Common artificial sweeteners like saccharin and aspartame have been shown to affect gut microbiota negatively, potentially leading to insulin resistance and other metabolic issues.
Sugar Alcohols
Sugar alcohols like sorbitol and xylitol, often found in sugar-free products, can cause bloating, gas, and diarrhea in some individuals, disrupting a healthy gut diet plan.
High-Fat Foods
Foods high in unhealthy fats, such as trans fats and saturated fats, can cause inflammation and hinder gut health. These fats are often found in fried foods, fatty cuts of meat, and certain dairy products.
Fried Foods
Fried foods like fried chicken, french fries, and doughnuts are high in unhealthy fats and calories, which can disrupt the gut microbiome and contribute to weight gain.
Processed Meats
Processed meats such as bacon, sausages, and deli meats contain high levels of saturated fats and preservatives that can negatively impact gut health.
Refined Carbohydrates
Refined carbohydrates, including white bread, white rice, and pastries, lack the fiber found in whole grains. This can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar and promote the growth of harmful bacteria.
White Bread and Pasta
White bread and pasta are stripped of their fiber content during processing, making them less beneficial for gut health and more likely to contribute to blood sugar imbalances.
Pastries and Baked Goods
Pastries, cakes, and other baked goods made with refined flour and sugar can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome and lead to inflammation.
Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can irritate the gut lining, leading to increased intestinal permeability and inflammation. This disrupts the balance of the microbiome and can cause digestive issues.
Hard Liquors and Spirits
Hard liquors and spirits are high in alcohol content and can be particularly harsh on the digestive system, exacerbating gut issues and inflammation.
Sweet Wines and Liqueurs
Sweet wines and liqueurs contain higher levels of sugar, which can further disrupt gut balance when consumed in excess.
Conclusion
Identifying and avoiding these detrimental foods is a critical aspect of a healthy gut diet plan. By minimizing the intake of processed foods, excessive sugars, artificial sweeteners, unhealthy fats, and refined carbohydrates, you can support a balanced and thriving gut microbiome, leading to improved overall health.
6. Creating a Balanced Meal Plan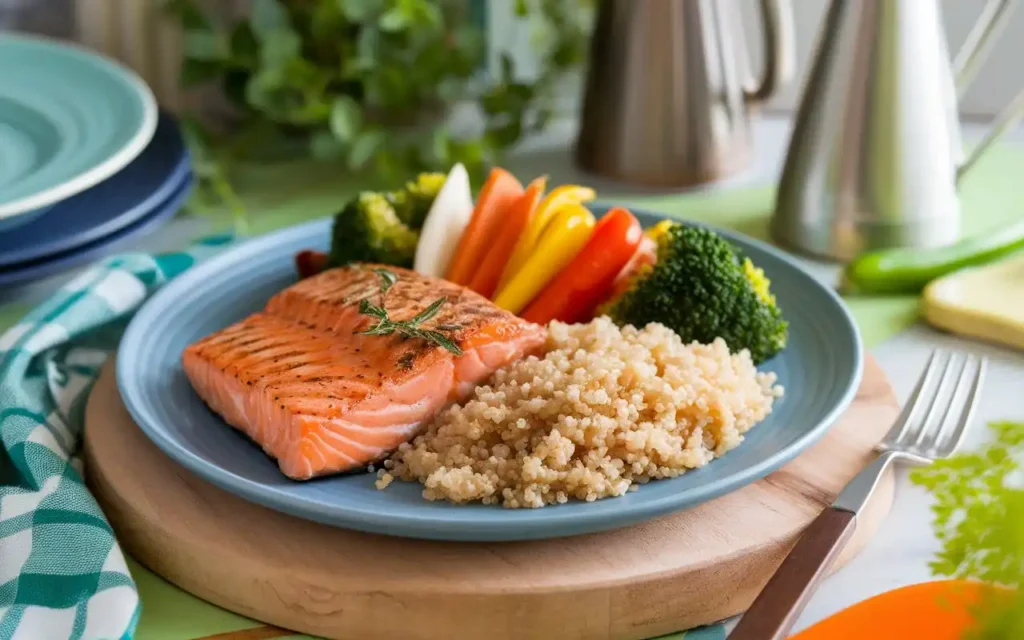
Designing a healthy gut diet plan involves creating balanced meals that incorporate a variety of nutrients to support your gut health. A well-structured meal plan ensures that you receive all the necessary nutrients while maintaining a diverse and thriving microbiome.
Breakfast Ideas
Start your day with a probiotic-rich yogurt parfait topped with fresh berries, a sprinkle of granola, and a drizzle of honey. This combination provides probiotics, fiber, and natural sweetness to kickstart your metabolism.
Another option is a smoothie made with kefir, spinach, banana, chia seeds, and a handful of oats. This blend offers a mix of probiotics, vitamins, minerals, and fiber for sustained energy.
Lunch Options
Opt for a quinoa salad loaded with mixed vegetables, chickpeas, and a lemon-tahini dressing. This meal is rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, supporting a healthy gut diet plan.
Alternatively, enjoy a bowl of miso soup with tofu, seaweed, and green onions paired with a side of steamed vegetables and brown rice. This combination provides probiotics and a balanced nutrient profile.
Dinner Recipes
Enjoy grilled salmon with a side of steamed broccoli, sweet potatoes, and a mixed green salad. Salmon is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for gut health.
Another dinner option is a vegetable stir-fry with tofu, bell peppers, carrots, and snap peas served over brown rice or quinoa. This meal offers a variety of nutrients and fiber to support a balanced microbiome.
Snacks and Treats
Choose snacks like hummus with veggie sticks, a handful of nuts, or a piece of dark chocolate to satisfy cravings healthily. These options provide fiber, healthy fats, and antioxidants.
For a sweet treat, try chia pudding made with almond milk and topped with fresh fruit. This snack is rich in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics.
Sample Meal Plan
| Meal | Example | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Yogurt parfait with berries and granola | Probiotics, fiber, antioxidants |
| Morning Snack | Apple slices with almond butter | Fiber, healthy fats |
| Lunch | Quinoa and chickpea salad with lemon-tahini dressing | Protein, fiber, healthy fats |
| Afternoon Snack | Hummus with carrot and celery sticks | Fiber, protein |
| Dinner | Grilled salmon with steamed broccoli and sweet potatoes | Omega-3s, fiber, vitamins |
| Evening Treat | Chia pudding with fresh fruit | Fiber, omega-3s, probiotics |
Meal Prep Strategies
Planning and preparing meals in advance can help you adhere to a healthy gut diet plan even amidst a busy schedule. Here are some strategies:
- Batch Cooking: Prepare large quantities of staples like quinoa, roasted vegetables, and grilled proteins to use throughout the week.
- Portion Control: Divide meals into individual portions to make grabbing a healthy option quick and easy.
- Ingredient Prep: Chop vegetables, cook grains, and prepare dressings ahead of time to streamline meal assembly.
- Use Containers: Invest in quality meal prep containers that keep food fresh and organized.
Flexibility and Variety
A successful healthy gut diet plan should be flexible and varied to prevent dietary monotony and ensure a wide range of nutrients. Rotate different foods and recipes to keep meals interesting and nutritionally balanced.
Adapting to Preferences and Restrictions
Your healthy gut diet plan should accommodate personal preferences, dietary restrictions, and cultural considerations. Whether you’re vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, or have specific food allergies, there are plenty of options to tailor your diet plan accordingly.
Conclusion
Creating a balanced meal plan is a cornerstone of a healthy gut diet plan. By incorporating diverse, nutrient-dense foods and employing effective meal prep strategies, you can maintain a consistent and enjoyable diet that supports your gut health and overall well-being.
7. Supplements to Support Your Healthy Gut Diet Plan
While a balanced diet is paramount, certain supplements can further enhance your healthy gut diet plan. These supplements can fill nutritional gaps and provide additional support for your digestive system.
Probiotic Supplements
Probiotic supplements can help replenish beneficial bacteria, especially after antibiotic use or during times of gut imbalance. They come in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders.
Choosing the Right Probiotic
Select a probiotic supplement that contains multiple strains of bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, and has a high CFU (colony-forming units) count to ensure efficacy.
Benefits of Probiotics
Probiotics aid in digestion, enhance immune function, and may alleviate symptoms of IBS, diarrhea, and other digestive disorders.
Prebiotic Fibers
Prebiotic fibers like inulin and fructooligosaccharides support the growth of probiotics in your gut. They are available as powders or capsules and can be easily incorporated into your diet.
Sources of Prebiotics
Prebiotics can also be obtained naturally from foods such as garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, and whole grains.
Benefits of Prebiotics
Prebiotics promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, improve digestion, and enhance nutrient absorption.
Digestive Enzymes
Digestive enzyme supplements aid in breaking down food more efficiently, reducing digestive discomfort such as bloating, gas, and indigestion.
Types of Digestive Enzymes
Common digestive enzymes include amylase, protease, and lipase, which help digest carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, respectively.
Benefits of Digestive Enzymes
They support proper nutrient absorption, alleviate symptoms of enzyme deficiencies, and enhance overall digestive health.
Vitamins and Minerals
Ensure adequate intake of vitamins and minerals like vitamin D, magnesium, zinc, and B-vitamins to support overall health and gut function.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a role in immune function and maintaining the integrity of the gut lining. Supplementation may be necessary, especially in individuals with limited sun exposure.
Magnesium
Magnesium supports muscle function, including the muscles involved in digestion, and helps prevent constipation.
Zinc
Zinc is essential for immune function and maintaining the gut barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream.
B-Vitamins
B-vitamins, particularly B12 and folate, are important for energy production and the synthesis of neurotransmitters that influence mood and cognition.
Fiber Supplements
Fiber supplements like psyllium husk can help ensure adequate fiber intake, supporting regular bowel movements and feeding beneficial gut bacteria.
Types of Fiber Supplements
Common fiber supplements include soluble fiber (e.g., psyllium) and insoluble fiber (e.g., cellulose). Choose a supplement that aligns with your dietary needs and tolerance levels.
Benefits of Fiber Supplements
They aid in maintaining bowel regularity, reducing cholesterol levels, and controlling blood sugar spikes.
Omega-3 Supplements
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that support gut health. Fish oil supplements are a common source of omega-3s.
Benefits of Omega-3s
They help reduce inflammation in the gut, support immune function, and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Multivitamins
Multivitamin supplements can provide a broad spectrum of essential nutrients that support overall health and complement a healthy gut diet plan.
Choosing a Multivitamin
Select a multivitamin that covers the basic vitamins and minerals without exceeding the recommended daily allowances to avoid potential toxicity.
Benefits of Multivitamins
They help fill nutritional gaps, support metabolic processes, and enhance overall vitality.
Herbal Supplements
Herbal supplements like ginger, peppermint, and aloe vera can support digestive health by reducing inflammation, soothing the gut lining, and alleviating digestive discomfort.
Ginger
Ginger supplements can help reduce nausea, improve digestion, and possess anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for gut health.
Peppermint
Peppermint oil supplements are effective in relieving symptoms of IBS, including bloating, gas, and abdominal pain.
Conclusion
While supplements can significantly enhance a healthy gut diet plan, they should complement, not replace, a balanced diet. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation to ensure it aligns with your individual health needs and conditions.
8. Common Mistakes in Following a Healthy Gut Diet Plan
Avoiding common pitfalls is essential when adhering to a healthy gut diet plan. Recognizing and correcting these mistakes can enhance the effectiveness of your dietary efforts and promote sustained gut health.
Ignoring Fiber Intake
Not consuming enough fiber can hinder the growth of beneficial bacteria in your gut. Fiber is crucial for maintaining regular bowel movements and supporting a balanced microbiome.
To avoid this mistake, ensure that each meal includes a source of fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, or legumes.
Solution:
Incorporate a variety of fiber-rich foods into your diet, and consider adding a fiber supplement if necessary. Gradually increase fiber intake to allow your digestive system to adjust.
Overreliance on Supplements
While supplements can support your diet, they should not replace whole foods. Whole foods provide a complex matrix of nutrients, fiber, and beneficial compounds that supplements alone cannot replicate.
Relying too heavily on supplements can lead to nutrient imbalances and overlook the importance of dietary diversity.
Solution:
Use supplements to complement your diet, not substitute it. Focus on obtaining most of your nutrients from whole foods while using supplements as needed based on professional advice.
Inconsistent Eating Patterns
Irregular meal times can disrupt your digestive system and gut health. Skipping meals or eating at inconsistent times can lead to digestive discomfort and hinder nutrient absorption.
Solution:
Establish a consistent eating schedule with regular meal and snack times. This routine supports stable digestion and helps maintain a balanced microbiome.
Neglecting Hydration
Insufficient water intake can lead to constipation and other digestive issues. Hydration is vital for the movement of food through the digestive tract and the overall functioning of the gut.
Solution:
Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day. Incorporate herbal teas and water-rich foods like cucumbers and watermelon to boost hydration levels.
Overconsumption of High-Fat and High-Sugar Foods
Excessive intake of unhealthy fats and sugars can promote inflammation and disrupt the gut microbiome. These foods can lead to an imbalance in beneficial and harmful bacteria.
Solution:
Limit the consumption of fried foods, sugary snacks, and beverages. Focus on incorporating healthy fats and natural sugars from whole foods instead.
Lack of Variety in Diet
A monotonous diet can limit the diversity of your gut microbiome, which is essential for robust gut health. Eating a wide range of foods introduces different nutrients and supports various microbial species.
Solution:
Introduce new foods regularly and aim for a colorful plate at each meal. Experiment with different fruits, vegetables, grains, and protein sources to enhance microbial diversity.
Ignoring Food Intolerances and Allergies
Consuming foods that your body cannot tolerate can lead to inflammation and disrupt gut health. Food intolerances and allergies can cause digestive discomfort and negatively impact the microbiome.
Solution:
Identify and eliminate foods that trigger adverse reactions. Consider working with a healthcare professional to determine specific intolerances and adjust your diet accordingly.
Overuse of Antibiotics and Other Medications
While antibiotics are necessary for treating infections, overuse can disrupt the gut microbiome by killing beneficial bacteria. Other medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also affect gut health.
Solution:
Use antibiotics only when prescribed by a healthcare professional and follow the recommended dosage. Discuss the potential gut health impacts of other medications with your doctor and explore alternatives if necessary.
Skipping Probiotic-Rich Foods
Neglecting probiotic-rich foods can limit the replenishment of beneficial bacteria in your gut. Probiotics are essential for maintaining a balanced microbiome and supporting digestive health.
Solution:
Incorporate fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi into your daily diet. Consider adding a probiotic supplement if needed, under professional guidance.
Conclusion
Avoiding these common mistakes is crucial for the success of your healthy gut diet plan. By being mindful of your dietary choices and addressing potential pitfalls, you can enhance your gut health and achieve sustained well-being.
9. Success Stories: Transforming Lives with a Healthy Gut Diet Plan
Real-life testimonials showcase the transformative power of a healthy gut diet plan. These stories highlight the positive changes individuals have experienced by prioritizing their gut health through dietary adjustments.
Jane’s Journey to Better Health
Jane struggled with chronic bloating and fatigue for years. After adopting a healthy gut diet plan, she noticed significant improvements in her energy levels and digestive comfort within a few weeks.
“I used to feel sluggish and bloated all the time. Incorporating more fiber and probiotics into my diet made a world of difference. I feel energized and my digestion has never been better!” – Jane D.
Mark’s Weight Loss Success
Mark combined a healthy gut diet plan with regular exercise and lost 30 pounds while improving his overall gut health. He credits the diet for his sustained weight loss and enhanced metabolism.
“Losing weight was always a struggle for me. By focusing on my gut health and making smarter food choices, I not only shed the excess weight but also felt more confident and healthier overall.” – Mark S.
Linda’s Mental Health Improvement
Linda faced anxiety and mood swings that affected her daily life. Following a healthy gut diet plan helped stabilize her mood and reduce anxiety symptoms significantly.
“I’ve always believed that my mental health was separate from my diet, but changing my eating habits had a profound impact on my mood and stress levels. I feel more balanced and in control.” – Linda M.
Tom’s Recovery from IBS
Tom suffered from Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) for years, experiencing frequent abdominal pain and irregular bowel movements. Implementing a healthy gut diet plan helped him manage his symptoms effectively.
“Managing IBS was challenging, but adjusting my diet to include more probiotics and reduce trigger foods made a significant difference. I now have fewer flare-ups and better control over my digestive health.” – Tom R.
Emma’s Enhanced Immunity
Emma was prone to frequent colds and infections. By following a healthy gut diet plan, she strengthened her immune system and experienced fewer illnesses.
“I used to catch colds all the time, but since focusing on my gut health, I’ve been much healthier. A strong immune system makes me feel more secure and less anxious about getting sick.” – Emma L.
Alex’s Increased Energy and Productivity
Alex often felt drained and unproductive during the day. Adopting a healthy gut diet plan boosted his energy levels and enhanced his productivity at work.
“I used to struggle with afternoon slumps, but changing my diet to include more whole foods and probiotics has kept my energy levels steady throughout the day. I’m more focused and efficient.” – Alex K.
Rachel’s Skin Health Transformation
Rachel battled acne and eczema for years. Incorporating a healthy gut diet plan led to clearer skin and reduced inflammation.
“My skin issues were a constant source of frustration. Once I started eating a balanced diet rich in probiotics and anti-inflammatory foods, my skin cleared up, and the inflammation decreased significantly.” – Rachel T.
Michael’s Improved Sleep Quality
Michael had trouble sleeping and often felt unrested. A healthy gut diet plan improved his sleep quality and overall restfulness.
“I used to lie awake at night, but since focusing on my gut health, my sleep has become more restful. I wake up feeling refreshed and ready for the day.” – Michael B.
Sarah’s Enhanced Athletic Performance
Sarah, an avid runner, wanted to improve her performance and recovery. A healthy gut diet plan provided the necessary nutrients and energy to boost her athletic endeavors.
“Proper nutrition is key to athletic performance. By following a healthy gut diet plan, I’ve noticed better endurance, faster recovery times, and overall improved performance in my runs.” – Sarah W.
Conclusion
These success stories illustrate the profound impact a healthy gut diet plan can have on various aspects of life. From improved physical health and weight management to enhanced mental well-being and athletic performance, prioritizing gut health can lead to transformative changes. Let these stories inspire you to embark on your own journey towards a healthier gut and a more vibrant life.
10. Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common queries about a healthy gut diet plan can help you make informed decisions and navigate your journey to better gut health.
What is a healthy gut diet plan?
A healthy gut diet plan focuses on foods that support the gut microbiome, including probiotics, prebiotics, high-fiber foods, and balanced nutrients. It emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods and limits intake of sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives.
How long does it take to see results?
Individual results may vary, but many people start noticing improvements in digestion and energy levels within a few weeks. Significant changes in gut health, such as increased microbial diversity, may take several months of consistent dietary adherence.
Can I follow a healthy gut diet plan if I have dietary restrictions?
Yes, a healthy gut diet plan can be tailored to accommodate various dietary needs, including vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, and more. It’s important to ensure that your meal plan includes alternative sources of essential nutrients based on your specific restrictions.
Do I need to take supplements?
While supplements can support your diet, they are not mandatory. It’s best to obtain nutrients from whole foods, as they provide a complex matrix of vitamins, minerals, and beneficial compounds. However, supplements can be useful in filling nutritional gaps or addressing specific health needs, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Can a healthy gut diet plan help with weight loss?
Yes, a healthy gut diet plan can aid in weight loss by promoting efficient digestion, enhancing metabolism, and reducing inflammation. The emphasis on fiber-rich foods and balanced macronutrients helps control appetite and supports a healthy weight.
Are there any side effects to a healthy gut diet plan?
Most individuals tolerate a healthy gut diet plan well. However, increasing fiber intake too rapidly can cause bloating, gas, and digestive discomfort. It’s advisable to gradually incorporate fiber-rich foods and stay hydrated to minimize these effects.
How can I maintain a healthy gut diet plan while eating out?
When dining out, choose restaurants that offer healthy, whole-food options. Opt for dishes that include vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Avoid fried foods, excessive sauces, and processed items. Don’t hesitate to ask for modifications to suit your healthy gut diet plan.
Is it necessary to eliminate all dairy for a healthy gut diet plan?
No, eliminating all dairy is not necessary unless you have a lactose intolerance or dairy allergy. Fermented dairy products like yogurt and kefir can be beneficial for gut health due to their probiotic content. Choose lactose-free or plant-based alternatives if needed.
How does stress affect my gut health?
Stress can negatively impact gut health by altering the gut microbiome and increasing intestinal permeability. Chronic stress may lead to digestive issues such as IBS, bloating, and constipation. Incorporating stress management techniques alongside a healthy gut diet plan can support overall gut health.
Can I have a healthy gut diet plan if I have a busy lifestyle?
Absolutely. Planning and meal prepping can help you adhere to a healthy gut diet plan even with a hectic schedule. Focus on quick, nutritious meals and snacks that are easy to prepare and take on the go.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of a healthy gut diet plan empowers you to make informed dietary choices that support your overall health. By addressing these frequently asked questions, you can navigate common challenges and optimize your journey towards a healthier gut and enhanced well-being.
Additional Resources
For further reading and in-depth information on maintaining a healthy gut diet plan, explore the following authoritative resources:
References




