Heal Your Headache Diet: Comprehensive Guide to Dietary Relief
Introduction
Heal your headache diet is essential because it offers a natural and effective approach to managing and preventing headaches. By understanding the connection between what you eat and your headache patterns, you can make informed dietary choices that reduce the frequency and severity of your pain.
Headaches can significantly impact your quality of life, affecting your productivity, mood, and overall well-being. Incorporating the right foods and dietary habits can serve as a powerful tool in your headache management arsenal.
Understanding Headaches

Heal your headache diet begins with understanding the different types of headaches and their triggers. Headaches can be classified into migraines, tension-type headaches, cluster headaches, and more, each with unique causes and symptoms.
Types of Headaches
- Migraines: Often accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light and sound. Migraines can last from a few hours to several days and can be debilitating.
- Tension-Type: Characterized by a dull, aching sensation around the head. These are the most common type of headaches and are often related to stress.
- Cluster Headaches: Severe pain typically on one side of the head, often around the eye. They occur in clusters, meaning multiple attacks over a period.
Common Triggers
Triggers can include stress, hormonal changes, certain foods, dehydration, and irregular sleep patterns. Identifying your specific triggers is a crucial step in healing your headache diet.
Physiological Mechanisms
Understanding the physiological mechanisms behind headaches can help in crafting an effective heal your headache diet. For instance, migraines are believed to involve changes in brain chemistry and blood flow, which can be influenced by dietary factors.
Impact on Daily Life
Chronic headaches can lead to missed workdays, reduced productivity, and emotional distress. A strategic diet plan can mitigate these impacts by reducing the frequency and intensity of headaches.
The Role of Diet in Headache Management
Heal your headache diet plays a significant role in both the prevention and alleviation of headaches. Dietary choices can influence inflammation levels, hydration status, and blood sugar stability, all of which are critical factors in headache management.
Nutrition and Inflammation
Certain foods can either promote or reduce inflammation in the body. An anti-inflammatory diet can help mitigate headache symptoms by addressing underlying inflammatory processes.
Blood Sugar Stability
Maintaining steady blood sugar levels through balanced meals can prevent headaches caused by hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Consistent carbohydrate intake and avoiding excessive sugars are key components of a heal your headache diet.
Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Proper hydration is a cornerstone of healing your headache diet. Dehydration is a well-known headache trigger, and maintaining electrolyte balance is essential for nerve and muscle function.
Identifying Food Sensitivities
Food sensitivities and allergies can lead to chronic headaches. An elimination diet can help identify problematic foods, allowing you to tailor your diet accordingly.
Micronutrient Intake
Ensuring adequate intake of vitamins and minerals such as magnesium, riboflavin, and vitamin B2 is crucial in preventing headaches. These micronutrients play roles in neurological function and vascular health.
Balanced Macronutrients
A balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats ensures sustained energy levels and prevents blood sugar spikes and crashes, which can trigger headaches.
Healthy Fats and Omega-3s
Incorporating healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, can reduce inflammation and support brain health, contributing to headache prevention.
Superfoods for Headache Relief
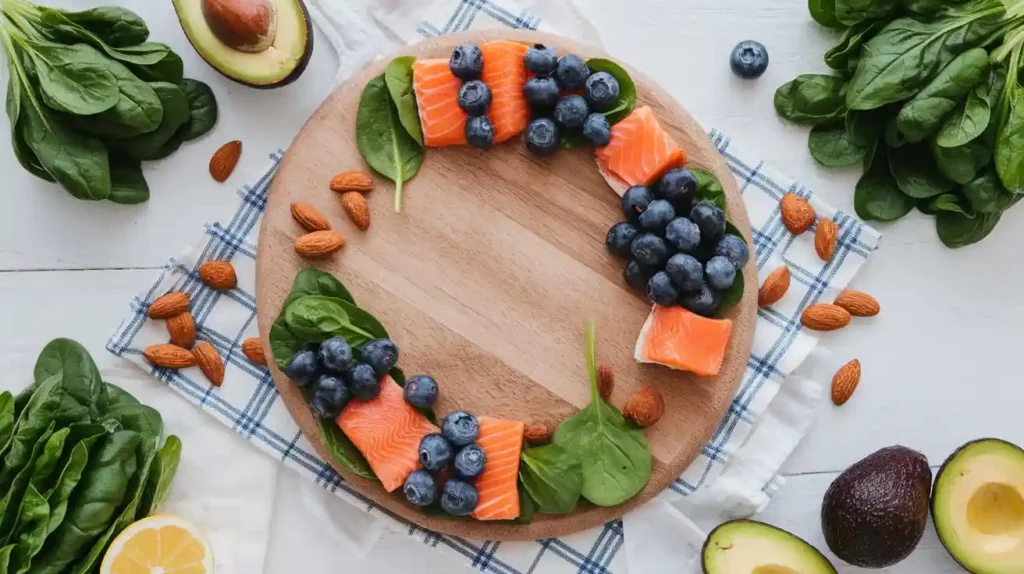
Heal your headache diet by incorporating superfoods known for their headache-alleviating properties. These nutrient-dense foods provide essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health and reduce headache frequency.
Magnesium-Rich Foods
Magnesium can help relax blood vessels and nerves, reducing headache symptoms. Include foods like:
- Spinach
- Almonds
- Avocados
- Black Beans
- Dark Chocolate
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s possess anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporate:
- Salmon
- Chia Seeds
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds
- Sardines
Hydrating Fruits and Vegetables
Staying hydrated is part of a heal your headache diet. Include:
- Cucumbers
- Watermelon
- Celery
- Oranges
- Strawberries
Anti-Inflammatory Spices
Spices can add flavor while providing health benefits. Add:
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Cinnamon
- Garlic
- Black Pepper
Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are packed with essential nutrients that support overall health:
- Kale
- Swiss Chard
- Collard Greens
- Arugula
- Romaine Lettuce
Whole Grains
Whole grains help maintain stable blood sugar levels:
- Quinoa
- Brown Rice
- Oats
- Barley
- Farro
Fermented Foods
Probiotics in fermented foods can improve gut health, which is linked to headache prevention:
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Kimchi
- Sauerkraut
- Miso
Seeds and Nuts
Seeds and nuts provide healthy fats and proteins:
- Pumpkin Seeds
- Sunflower Seeds
- Cashews
- Pistachios
- Brazil Nuts
Lean Proteins
Lean proteins support muscle and nerve function:
- Chicken Breast
- Turkey
- Tofu
- Tempeh
- Eggs
Dark Leafy Vegetables
These vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals essential for headache prevention:
- Broccoli
- Brussels Sprouts
- Green Beans
- Asparagus
- Cauliflower
Hydration and Headaches

Heal your headache diet emphasizes the importance of proper hydration. Dehydration is a common trigger for headaches, and maintaining adequate fluid intake can prevent their onset.
Daily Water Intake
Experts recommend drinking at least 8 glasses of water daily. However, individual needs may vary based on activity level, climate, and overall health. A general guideline is to consume half your body weight in ounces of water each day.
Hydrating Foods
In addition to drinking water, consuming hydrating foods can boost your fluid intake:
- Oranges
- Strawberries
- Zucchini
- Tomatoes
- Cantaloupe
Electrolyte Balance
Maintaining electrolyte balance is crucial for nerve and muscle function. Include electrolyte-rich foods such as:
- Bananas
- Leafy Greens
- Sweet Potatoes
- Spinach
- Avocados
Infused Water Recipes
Enhance the flavor of your water with natural ingredients to make hydration more enjoyable:
- Lemon and Mint
- Cucumber and Lime
- Strawberry and Basil
- Orange and Blueberry
- Ginger and Pineapple
Monitoring Hydration Levels
Signs of adequate hydration include pale yellow urine, regular bathroom visits, and feeling generally energized. Conversely, dark urine, dry mouth, and fatigue are indicators of dehydration.
Hydration Strategies
Implement these strategies to maintain proper hydration:
- Carry a reusable water bottle
- Set reminders to drink water throughout the day
- Start your day with a glass of water
- Include herbal teas as part of your fluid intake
- Consume hydrating snacks between meals
Avoiding Dehydration
Limit intake of dehydrating beverages such as:
- Caffeinated drinks (coffee, certain teas)
- Alcohol
- Sugary sodas
- Energy drinks
Benefits of Proper Hydration
Proper hydration not only helps in healing your headache diet but also supports overall bodily functions including digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet

Heal your headache diet often incorporates an anti-inflammatory approach to reduce the underlying causes of headaches. By focusing on foods that combat inflammation, you can alleviate headache symptoms naturally.
Key Anti-Inflammatory Foods
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
- Turmeric
- Green Tea
- Fatty Fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Olive Oil
- Leafy Greens (spinach, kale)
- Nuts and Seeds (walnuts, flaxseeds)
- Garlic and Onions
- Dark Chocolate
- Whole Grains (quinoa, brown rice)
Foods to Avoid
Minimize intake of pro-inflammatory foods such as:
- Processed Meats (sausages, bacon)
- Refined Carbohydrates (white bread, pastries)
- Excessive Sugar
- Trans Fats (found in some margarines and processed snacks)
- Saturated Fats (found in red meat and full-fat dairy products)
- Artificial Additives (MSG, aspartame)
- Excessive Alcohol
Benefits of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches by lowering systemic inflammation, improving vascular health, and supporting neurological function.
Meal Planning
Plan meals around anti-inflammatory principles by focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and balanced macronutrients. Here’s a sample meal plan:
| Meal | Menu |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal topped with blueberries, chia seeds, and a drizzle of honey. |
| Lunch | Grilled salmon salad with mixed greens, avocado, and olive oil dressing. |
| Snack | Handful of walnuts and an apple. |
| Dinner | Quinoa stir-fry with broccoli, bell peppers, and tofu, seasoned with turmeric and garlic. |
Incorporating Spices
Spices like turmeric and ginger not only add flavor but also possess potent anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporate them into your cooking regularly.
Monitoring Inflammation Levels
While it’s challenging to measure inflammation directly, monitoring your headache patterns and overall well-being can provide insights into the effectiveness of an anti-inflammatory diet.
Additional Tips
- Choose organic produce to minimize exposure to pesticides and additives.
- Opt for grass-fed or wild-caught animal products when possible.
- Limit processed and packaged foods.
- Stay consistent with your dietary changes for optimal results.
Elimination Diets
Heal your headache diet may involve elimination diets to identify and remove specific food triggers. This systematic approach helps in pinpointing foods that may be causing or exacerbating headaches.
Steps to Implement an Elimination Diet
- Identify Potential Trigger Foods: Common culprits include caffeine, alcohol, dairy, gluten, and certain preservatives.
- Eliminate These Foods: Remove identified foods from your diet for 4-6 weeks. This period allows your body to adjust and symptoms to potentially decrease.
- Reintroduce Foods Gradually: After the elimination phase, reintroduce each food one at a time, typically every 3-5 days, while monitoring for any headache symptoms.
- Document Reactions: Keep a detailed food diary to track your intake and any corresponding headache patterns.
- Analyze Results: Determine which foods may be triggers based on your observations and adjust your diet accordingly.
Common Trigger Foods
- Caffeine (coffee, tea, chocolate)
- Alcohol (especially red wine)
- Chocolate
- Aged Cheeses
- Processed Meats (sausages, deli meats)
- Monosodium Glutamate (MSG)
- Artificial Sweeteners (aspartame, sucralose)
- Certain Fruits (citrus, bananas)
- Nuts (peanuts, walnuts)
- Gluten-Containing Foods (wheat, barley, rye)
Tracking and Documentation
Maintain a food diary to monitor your intake and any corresponding headache patterns. Include details such as:
- What you ate and drank
- Time of consumption
- Headache occurrence and severity
- Other symptoms (nausea, sensitivity to light)
Benefits of Elimination Diets
Elimination diets can help you identify specific food triggers, allowing you to customize your heal your headache diet for maximum effectiveness. This personalized approach can lead to significant reductions in headache frequency and intensity.
Potential Challenges
- Dietary Restrictions: Eliminating multiple food groups can make meal planning challenging.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Ensure you maintain a balanced diet to avoid deficiencies.
- Adherence: Strict adherence is necessary for accurate results, which can be difficult for some individuals.
- Patience: It may take several weeks to identify all triggers.
Overcoming Challenges
- Seek Professional Guidance: A registered dietitian can provide support and ensure nutritional balance.
- Plan Ahead: Prepare meals in advance to stay on track.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key to accurately identifying triggers.
- Use Alternatives: Find suitable alternatives for eliminated foods to maintain variety in your diet.
Case Study: Success with Elimination Diet
Jane, a 35-year-old graphic designer, suffered from chronic migraines for years. After implementing an elimination diet under the guidance of a dietitian, she identified that aged cheeses and processed meats were major headache triggers. By removing these from her heal your headache diet, Jane experienced a significant reduction in migraine frequency and severity within three months.
Final Tips
- Be patient and give the elimination diet enough time to work.
- Stay organized with meal planning and tracking tools.
- Consult with healthcare professionals to ensure a safe and effective elimination process.
Meal Timing and Headaches

Heal your headache diet also considers the timing of meals to maintain steady blood sugar levels and prevent headaches.
Regular Eating Schedule
Eating at consistent times helps regulate blood sugar and prevent hypoglycemia-related headaches. Skipping meals can lead to drops in blood sugar, triggering headache symptoms.
Balanced Meals
Ensure each meal includes a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to sustain energy levels and prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes.
Avoiding Skipping Meals
Skipping meals can lead to drops in blood sugar, triggering headaches. Plan meals and snacks to maintain energy throughout the day.
Snack Smartly
Incorporate healthy snacks between meals to keep blood sugar levels stable:
- Greek yogurt with berries
- Hummus with vegetable sticks
- Apple slices with almond butter
- Whole grain crackers with cheese
- Mixed nuts and dried fruit
Late-Night Eating
Avoid heavy or large meals close to bedtime, as they can disrupt sleep and contribute to morning headaches.
Intermittent Fasting Considerations
If you practice intermittent fasting, ensure that your eating windows include nutrient-dense foods and sufficient calories to prevent headaches caused by prolonged fasting periods.
Meal Prep Strategies
Plan and prepare meals in advance to adhere to your eating schedule. This reduces the likelihood of skipping meals or opting for unhealthy options.
Listening to Your Body
Pay attention to hunger and satiety cues. Eating when hungry and stopping when full can help maintain optimal blood sugar levels and prevent overeating.
Hydration Timing
Alongside meal timing, ensure you’re drinking water consistently throughout the day. Sometimes, dehydration can be mistaken for hunger.
Benefits of Proper Meal Timing
Proper meal timing can lead to:
- Reduced frequency of headaches
- Improved energy levels
- Better mood and cognitive function
- Enhanced metabolic health
Sample Daily Meal Schedule
| Time | Meal |
|---|---|
| 7:00 AM | Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach and whole grain toast |
| 10:00 AM | Snack: Greek yogurt with blueberries |
| 12:30 PM | Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens and olive oil dressing |
| 3:00 PM | Snack: Apple slices with almond butter |
| 6:30 PM | Dinner: Baked salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli |
| 9:00 PM | Optional Snack: Herbal tea and a handful of nuts |
Supplements for Headache Relief
Heal your headache diet may include specific supplements that support neurological health and reduce headache frequency.
Magnesium Supplements
Magnesium can help relax blood vessels and nerves, reducing headache symptoms. Recommended daily intake varies, but generally, 400-500 mg is suggested for adults. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting supplementation.
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
Riboflavin has been shown to decrease the frequency of migraines. A typical dose is 400 mg per day. It supports energy production in cells, which may help reduce headache occurrences.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10)
CoQ10 supports mitochondrial function and may reduce migraine occurrence. The recommended dosage ranges from 100-300 mg per day. It also acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to increased headache frequency. Supplementing with Vitamin D can support overall health and potentially reduce headache symptoms. Dosage should be based on blood levels and healthcare provider recommendations.
Omega-3 Supplements
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate headaches. A typical dose is 1-2 grams per day.
Melatonin
Melatonin can improve sleep quality, which is crucial for headache prevention. A standard dose is 3-5 mg taken before bedtime.
Butterbur Extract
Butterbur is an herbal supplement that has been shown to reduce migraine frequency. Ensure you choose a PA-free (pyrrolizidine alkaloids-free) extract to avoid liver toxicity. Typical doses range from 50-75 mg twice daily.
Feverfew
Feverfew is another herbal supplement used to prevent migraines. It may reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. A common dose is 50-100 mg daily.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen to ensure safety and efficacy. Supplements can interact with medications and may not be suitable for everyone.
Potential Side Effects
While supplements can be beneficial, they may also cause side effects. Common side effects include:
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Allergic reactions
- Interactions with medications
- Over-supplementation risks
Quality and Purity
Choose high-quality supplements from reputable brands to ensure purity and potency. Look for third-party testing and certifications.
Integrating Supplements into Your Diet
Incorporate supplements into your daily routine by taking them at the same time each day, preferably with meals to enhance absorption and reduce the risk of stomach upset.
Lifestyle Factors and Diet
Heal your headache diet is complemented by healthy lifestyle practices that support overall well-being and headache prevention.
Stress Management
Incorporate stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Chronic stress is a significant trigger for headaches, and managing it can reduce their occurrence.
Regular Physical Activity
Engage in regular exercise to improve circulation and reduce stress levels. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can be particularly beneficial.
Sleep Hygiene
Maintain a consistent sleep schedule and create a restful sleep environment to prevent sleep-related headaches. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Avoiding Triggers
Identify and avoid non-dietary headache triggers such as strong odors, bright lights, and loud noises. Creating a headache-friendly environment can significantly reduce headache frequency.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help manage stress and prevent tension-type headaches. Techniques include progressive muscle relaxation and guided imagery.
Posture and Ergonomics
Maintain good posture, especially if you work at a desk for long periods. Poor posture can lead to muscle tension and headaches.
Avoiding Excessive Screen Time
Limit prolonged exposure to screens, as eye strain can trigger headaches. Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds.
Environmental Factors
Ensure your living and working environments are well-ventilated and free from excessive noise and strong smells, which can act as headache triggers.
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help identify and manage any underlying health conditions that may contribute to headaches.
Hydration and Diet Synergy
Combine proper hydration with a balanced diet to maximize the effectiveness of your heal your headache diet. This synergy supports overall health and reduces headache risk.
Social Support
Maintain strong social connections and seek support from friends, family, or support groups. Emotional well-being plays a role in headache management.
Advanced Strategies for Healing Your Headache Diet
Beyond the foundational aspects, advanced strategies can further enhance your heal your headache diet and provide additional relief from headaches.
Personalized Nutrition Plans
Working with a registered dietitian can help create a personalized nutrition plan tailored to your specific needs, preferences, and headache triggers.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can identify specific nutritional deficiencies or sensitivities, allowing for more targeted dietary interventions.
Intermittent Fasting
Some individuals find that intermittent fasting helps stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce headache frequency. However, it should be approached cautiously and personalized to avoid potential triggers.
Functional Medicine Approach
A functional medicine approach looks at the root causes of headaches, considering factors like gut health, hormonal balance, and chronic inflammation. Integrating this with your diet can provide comprehensive relief.
Biofeedback and Dietary Integration
Using biofeedback techniques alongside dietary changes can enhance your ability to control physiological responses to stress and reduce headache occurrences.
Mind-Gut Connection
Understanding the connection between your gut health and headaches can lead to dietary adjustments that support a healthy microbiome, potentially reducing headaches.
Supplements Tailored to Your Needs
Beyond the basic supplements, advanced strategies may include tailored supplements based on individual deficiencies or health conditions.
Incorporating Adaptogens
Adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha and rhodiola can help the body adapt to stress, which may in turn reduce headache frequency.
Detoxification Protocols
Periodic detoxification protocols, under professional supervision, can help eliminate toxins that may contribute to headaches.
Tracking and Technology
Utilize apps and wearable technology to track your diet, hydration, sleep, and headache patterns for more precise management and adjustments to your heal your headache diet.
Holistic Therapies
Integrate holistic therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and chiropractic care with your dietary strategies for comprehensive headache relief.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Stay informed about the latest research in nutrition and headache management to continuously adapt and improve your diet and lifestyle strategies.
Conclusion
Heal your headache diet offers a multifaceted approach to managing and preventing headaches through strategic dietary choices and lifestyle modifications. By understanding the relationship between food and headaches, incorporating superfoods, maintaining hydration, and considering meal timing, you can significantly reduce headache frequency and intensity.
Remember to consult with healthcare professionals before making significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen. Personalized approaches are often the most effective in achieving lasting relief.
Implementing these strategies requires commitment and consistency, but the rewards include not only fewer headaches but also improved overall health and well-being.
Start your journey towards a headache-free life by taking control of your diet and making informed, health-conscious choices every day.
References




