The Colon Cancer Diet: Comprehensive Guide for Prevention and Management
1. Understanding Colon Cancer
The colon cancer diet plays a crucial role in both the prevention and management of colon cancer. Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, originates in the large intestine and can affect the rectum. Understanding the basics of colon cancer is essential to appreciate how dietary choices can influence its development.
What is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer occurs when cells in the colon or rectum grow uncontrollably. It is one of the most common cancers worldwide, affecting millions each year. Early detection through screenings like colonoscopies can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Risk Factors
- Age: Most cases are diagnosed in individuals over 50.
- Family History: Genetics can play a significant role.
- Diet: High intake of red and processed meats.
- Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity, obesity, and smoking.
- Medical Conditions: Inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease.
2. Importance of Diet in Colon Cancer Prevention
The colon cancer diet is essential because it can help reduce the risk of developing colon cancer and aid in the management of the disease. A well-balanced diet provides the body with necessary nutrients to maintain healthy cells and prevent the growth of cancerous cells.
How Diet Influences Colon Cancer Risk
The foods you consume can impact inflammation levels, hormone balance, and overall cellular health. Diets high in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats are linked to lower colon cancer risk, while diets high in red meats and processed foods are associated with increased risk.
Scientific Evidence
Numerous studies have shown a correlation between diet and colon cancer. For instance, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains has been associated with a reduced risk, while high consumption of red and processed meats has been linked to an increased risk.
3. Key Nutrients for a Colon Cancer Diet
The colon cancer diet emphasizes the intake of specific nutrients that support colon health and inhibit cancer growth. Incorporating these nutrients into daily meals can make a significant difference.
Fiber
Dietary fiber aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing colon cancer risk. High-fiber foods include fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants combat free radicals that can damage cells. Foods rich in antioxidants include berries, nuts, dark leafy vegetables, and green tea.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory properties and may inhibit cancer cell growth. Sources include fatty fish like salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins D, E, and selenium are particularly beneficial. They support immune function and help protect cells from damage.
4. Top Foods to Include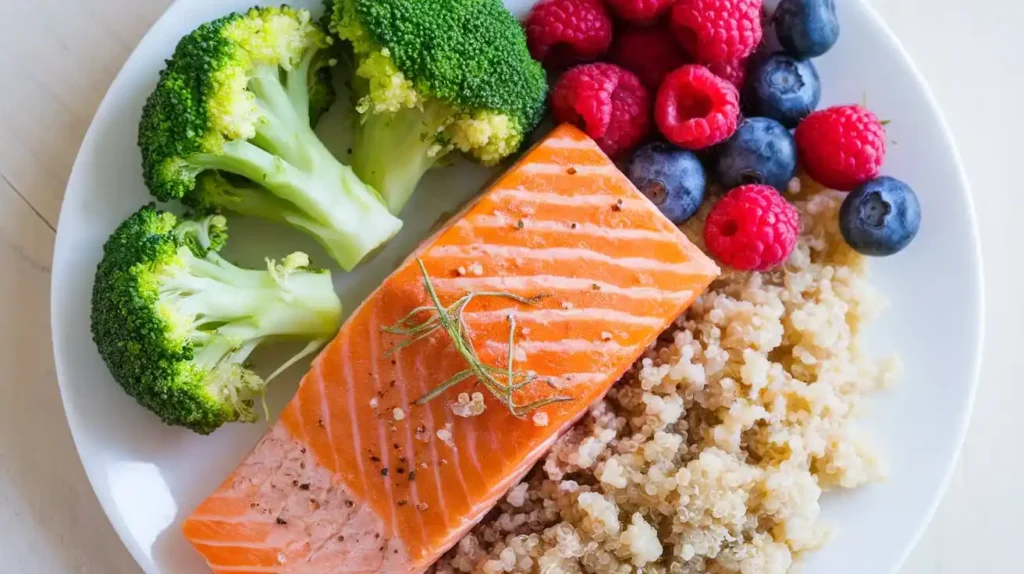
Incorporating the right foods into your diet is a cornerstone of the colon cancer diet. Here are some top recommendations:
Fruits and Vegetables
- Broccoli: Contains sulforaphane, which may help prevent cancer.
- Berries: High in antioxidants and fiber.
- Leafy Greens: Rich in vitamins and minerals.
Whole Grains
Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread provide essential fiber and nutrients.
Legumes
Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of protein and fiber.
Healthy Fats
Incorporate sources of healthy fats such as olive oil, avocados, and nuts to support overall health.
Lean Proteins
Opt for lean meats, poultry, and plant-based proteins to reduce intake of saturated fats.
5. Foods to Avoid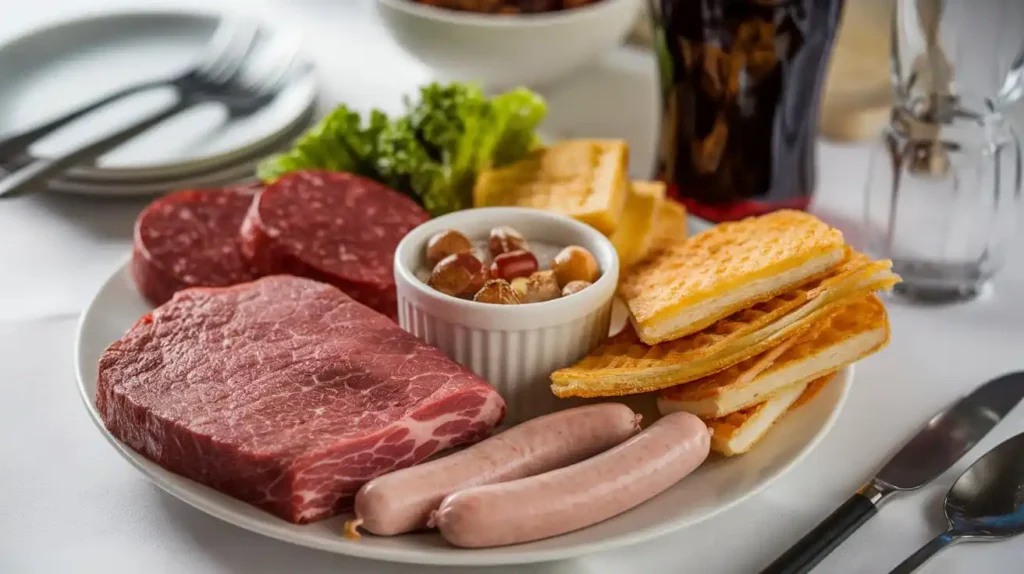
While certain foods support colon health, others can increase the risk of colon cancer. Avoiding these is a key aspect of the colon cancer diet.
Red and Processed Meats
High consumption of red meats like beef and processed meats like sausages has been linked to higher colon cancer risk.
Refined Grains and Sugars
Foods high in refined sugars and grains can lead to weight gain and inflammation.
Alcohol
Excessive alcohol intake is associated with an increased risk of various cancers, including colon cancer.
Saturated and Trans Fats
These unhealthy fats can promote inflammation and weight gain, increasing cancer risk.
6. Meal Planning and Recipes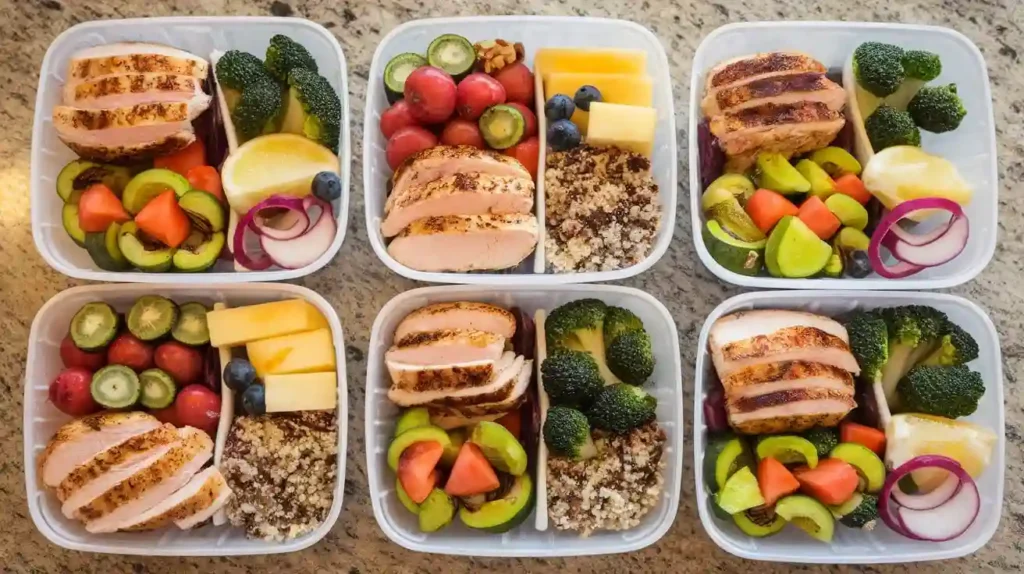
Effective meal planning is essential for adhering to the colon cancer diet. Here are some tips and recipes to get you started.
Breakfast Ideas
- Oatmeal with Berries: A fiber-rich start to your day.
- Green Smoothies: Packed with antioxidants and vitamins.
Lunch Options
- Quinoa Salad: Includes vegetables and lean protein.
- Vegetable Soup: High in fiber and nutrients.
Dinner Recipes
- Grilled Salmon with Asparagus: Rich in omega-3s.
- Stir-Fried Tofu and Vegetables: A plant-based protein source.
Snack Suggestions
- Hummus with Carrot Sticks: A healthy and satisfying snack.
- Mixed Nuts: Provide healthy fats and protein.
Sample Meal Plan
| Meal | Menu |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal topped with fresh berries and a drizzle of honey. |
| Lunch | Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables and grilled chicken. |
| Dinner | Grilled salmon with steamed broccoli and brown rice. |
| Snacks | Apple slices with almond butter. |
7. Supplements and Their Role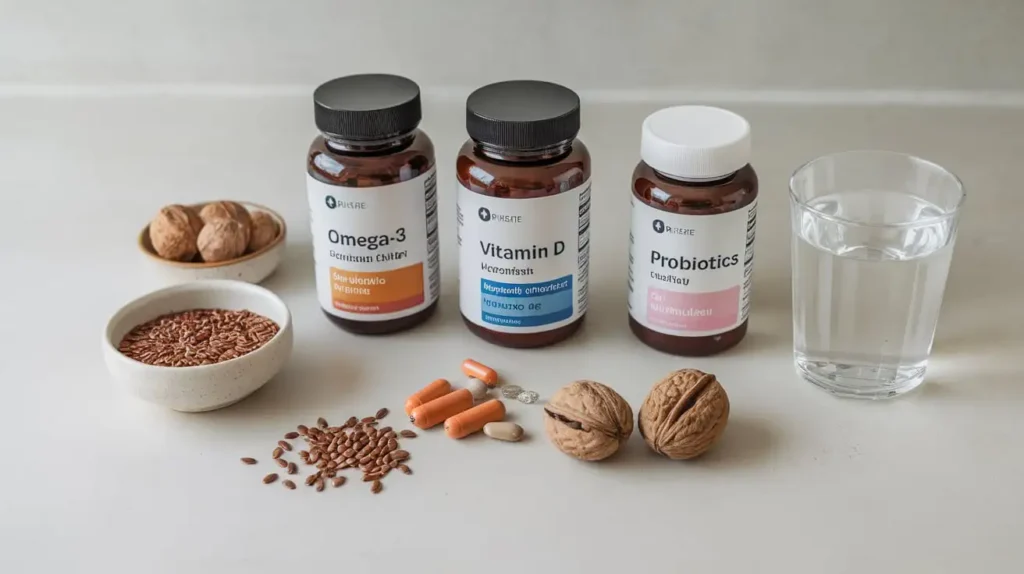
While a balanced diet is paramount, certain supplements can enhance the colon cancer diet by providing additional nutrients.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D supports immune function and may help in cancer prevention. Sources include sunlight, fortified foods, and supplements.
Calcium
Calcium is essential for bone health and may reduce colon cancer risk. It can be obtained from dairy products and fortified alternatives.
Omega-3 Supplements
For those who do not consume enough fatty fish, omega-3 supplements can provide the necessary fatty acids.
Probiotics
Probiotics support gut health, which is crucial for overall digestive function and may aid in preventing colon cancer.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
Before starting any supplement regimen, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and appropriateness.
8. Lifestyle Changes Beyond Diet
The colon cancer diet is just one aspect of a comprehensive approach to reducing colon cancer risk. Incorporating other healthy lifestyle changes can further enhance prevention efforts.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces inflammation, both of which are important in cancer prevention.
Avoiding Tobacco
Smoking is a known risk factor for many cancers, including colon cancer. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce risk.
Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Reducing alcohol intake can lower the risk of developing various cancers.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of colon cancer. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Regular Screenings
Routine colonoscopies can detect precancerous polyps early, allowing for timely intervention and prevention of cancer development.
9. Common Myths and Facts
There are many misconceptions surrounding the colon cancer diet. Understanding the facts can help individuals make informed dietary choices.
Myth 1: Only High-Fiber Foods Prevent Colon Cancer
Fact: While fiber is important, a combination of various nutrients, antioxidants, and healthy fats also plays a crucial role in prevention.
Myth 2: Supplements Alone Can Prevent Colon Cancer
Fact: Supplements should complement a balanced diet, not replace it. Whole foods provide a synergistic blend of nutrients that supplements alone cannot offer.
Myth 3: A Colon Cancer Diet is Boring and Restrictive
Fact: With a wide variety of foods and recipes available, a colon cancer diet can be both enjoyable and flavorful.
Myth 4: Only Older Adults Need to Worry About Colon Cancer
Fact: While risk increases with age, younger individuals can also develop colon cancer, especially with genetic predispositions and lifestyle factors.
10. Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Adopting the colon cancer diet should be done in consultation with healthcare professionals to ensure it meets individual health needs and conditions.
Dietitians and Nutritionists
These experts can provide personalized dietary plans tailored to individual health profiles and preferences.
Oncologists
For those diagnosed with colon cancer, oncologists can integrate dietary strategies into overall treatment plans.
Regular Check-Ups
Continuous monitoring and regular health check-ups ensure that dietary changes are effective and adjustments are made as needed.
Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice on maintaining a colon cancer-preventive diet.
References
Conclusion
Adopting the colon cancer diet is a proactive step towards reducing the risk of colon cancer and supporting overall digestive health. By incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, avoiding harmful ones, and making complementary lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly impact their long-term health outcomes. Remember to consult healthcare professionals when making significant dietary changes to ensure they align with your personal health needs.
10. Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Adopting the colon cancer diet should be done in consultation with healthcare professionals to ensure it meets individual health needs and conditions.
Dietitians and Nutritionists
These experts can provide personalized dietary plans tailored to individual health profiles and preferences. They assess dietary habits, nutritional needs, and potential deficiencies to create a balanced and effective colon cancer-preventive diet.
Oncologists
For those diagnosed with colon cancer, oncologists can integrate dietary strategies into overall treatment plans. They work closely with dietitians to ensure that the diet supports the patient’s treatment regimen, manages side effects, and promotes recovery.
Regular Check-Ups
Continuous monitoring and regular health check-ups ensure that dietary changes are effective and adjustments are made as needed. Regular screenings and consultations help in early detection and timely intervention.
Support Groups
Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice on maintaining a colon cancer-preventive diet. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can enhance adherence to dietary changes and provide motivation.
Integrative Medicine Practitioners
These professionals combine conventional medical treatments with alternative therapies. They can offer holistic approaches to diet and lifestyle modifications that complement traditional treatments for colon cancer.
11. The Science Behind the Colon Cancer Diet
The colon cancer diet is grounded in extensive scientific research that explores the relationship between diet and cancer prevention. Understanding the science helps in making informed dietary choices.
Role of Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for colon cancer. Diets rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and lower cancer risk.
Gut Microbiome Health
The gut microbiome plays a critical role in digestive health and immune function. A diet high in fiber and probiotics supports a healthy microbiome, which can protect against colon cancer.
Genetic Factors and Diet
Individuals with a family history of colon cancer may have genetic predispositions that interact with dietary factors. Personalized dietary plans can mitigate genetic risks and enhance protective effects.
Metabolic Health
Maintaining metabolic health through balanced blood sugar levels and healthy weight management is essential. Diets that prevent insulin resistance and obesity contribute to lower colon cancer risk.
12. Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-life examples demonstrate the effectiveness of the colon cancer diet in preventing and managing colon cancer. These stories provide inspiration and practical insights.
Case Study 1: Emily’s Journey to Prevention
Emily, a 52-year-old woman with a family history of colon cancer, adopted the colon cancer diet to reduce her risk. By incorporating high-fiber foods, reducing red meat intake, and increasing her physical activity, Emily successfully maintained a healthy weight and improved her overall health markers.
Case Study 2: John’s Battle with Colon Cancer
John was diagnosed with colon cancer at age 60. Alongside his medical treatments, he followed a colon cancer-preventive diet recommended by his oncologist and dietitian. This holistic approach helped him manage treatment side effects, maintain strength, and support his recovery process.
Success Story: Community Impact
A community wellness program implemented the colon cancer diet guidelines, resulting in increased awareness and healthier eating habits among participants. Regular workshops, meal planning sessions, and support groups contributed to significant improvements in dietary adherence and overall health.
13. Recipes to Enhance Your Colon Cancer Diet
Delicious and nutritious recipes make the colon cancer diet enjoyable and sustainable. Here are some recipes to incorporate into your daily meal plan.
Breakfast Recipes
- Blueberry Almond Oatmeal: A hearty and fiber-rich breakfast to start your day.
- Spinach and Mushroom Omelette: Packed with vegetables and protein.
Lunch Recipes
- Chickpea and Avocado Salad: A satisfying and nutrient-dense meal.
- Sweet Potato and Black Bean Burrito: Combines complex carbohydrates and plant-based protein.
Dinner Recipes
- Roasted Vegetable Quinoa Bowl: A balanced meal with grains and vegetables.
- Turmeric Salmon with Asparagus: Anti-inflammatory spices paired with omega-3-rich fish.
Snack Recipes
- Greek Yogurt with Honey and Walnuts: A protein-packed snack.
- Carrot and Cucumber Sticks with Hummus: Crunchy and satisfying.
Detailed Recipe: Turmeric Salmon with Asparagus
Ingredients:
- 4 salmon fillets
- 2 tablespoons olive oil
- 1 teaspoon ground turmeric
- Salt and pepper to taste
- 1 bunch asparagus, trimmed
- Lemon wedges for serving
Instructions:
- Preheat the oven to 400°F (200°C).
- In a small bowl, mix olive oil, turmeric, salt, and pepper.
- Place the salmon fillets and asparagus on a baking sheet.
- Brush the turmeric mixture over the salmon and asparagus.
- Bake for 15-20 minutes, or until the salmon is cooked through and the asparagus is tender.
- Serve with lemon wedges.
14. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Addressing common questions can help clarify doubts and provide additional insights into the colon cancer diet.
Q1: Can the colon cancer diet prevent colon cancer entirely?
A: While the colon cancer diet can significantly reduce the risk, it cannot guarantee complete prevention. Genetics, lifestyle factors, and environmental influences also play roles.
Q2: How long does it take to see benefits from the colon cancer diet?
A: Benefits can vary, but many individuals notice improvements in digestive health and energy levels within a few weeks. Long-term adherence contributes to sustained cancer risk reduction.
Q3: Is the colon cancer diet suitable for everyone?
A: Generally, yes, but individual needs may vary. It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals to tailor the diet to specific health conditions and nutritional requirements.
Q4: Can I follow the colon cancer diet if I have other health conditions?
A: Yes, but it’s crucial to work with healthcare providers to ensure that the diet aligns with other medical treatments and dietary restrictions.
Q5: Are there any side effects associated with the colon cancer diet?
A: A balanced colon cancer diet is generally safe. However, sudden increases in fiber intake can cause digestive discomfort for some individuals. Gradually adjusting the diet can help mitigate such issues.
15. Monitoring Your Progress
Tracking your adherence to the colon cancer diet helps in assessing its effectiveness and making necessary adjustments.
Keeping a Food Diary
Documenting daily food intake can help identify patterns, ensure nutrient diversity, and maintain accountability.
Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine blood tests and screenings can monitor health markers such as cholesterol levels, blood sugar, and inflammatory markers.
Setting Realistic Goals
Establish achievable dietary and lifestyle goals to maintain motivation and track progress over time.
Adjusting Your Diet
Based on monitoring results, make informed adjustments to your diet to address any deficiencies or to enhance its effectiveness in cancer prevention.
Seeking Feedback
Consult with healthcare professionals regularly to receive feedback and refine your dietary plan as needed.
16. The Role of Hydration in the Colon Cancer Diet
Proper hydration is a vital component of the colon cancer diet, supporting digestion and overall health.
Importance of Water
Water aids in the digestion of fiber, helps prevent constipation, and supports the elimination of toxins from the body.
Recommended Intake
Generally, adults should aim for at least 8 glasses (64 ounces) of water per day, but individual needs may vary based on activity level and climate.
Hydrating Foods
Incorporate foods with high water content such as cucumbers, watermelon, oranges, and celery to enhance hydration.
Avoiding Dehydration
Limit intake of dehydrating beverages like excessive caffeine and alcohol, which can impede digestive health.
Tips for Staying Hydrated
- Carry a reusable water bottle throughout the day.
- Set reminders to drink water regularly.
- Infuse water with natural flavors like lemon, mint, or berries for added taste.
17. Understanding Food Labels
Being able to read and understand food labels is essential for maintaining the colon cancer diet.
Reading Nutrition Facts
Pay attention to serving sizes, calories, and nutrient content. Focus on high-fiber, low-sugar, and low-sodium options.
Identifying Hidden Sugars
Check for various names of sugars like high-fructose corn syrup, cane sugar, and agave nectar to avoid excessive sugar intake.
Understanding Ingredient Lists
Look for whole food ingredients and avoid products with artificial additives, preservatives, and trans fats.
Choosing Whole Grains
Opt for products that list whole grains as the first ingredient, ensuring higher fiber content.
Portion Control
Be mindful of portion sizes to maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for reducing colon cancer risk.
18. Incorporating Superfoods into Your Diet
Superfoods are nutrient-dense and can enhance the colon cancer diet by providing essential vitamins and antioxidants.
Cruciferous Vegetables
Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts are rich in compounds that may inhibit cancer cell growth.
Berries
Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are high in antioxidants and fiber.
Green Tea
Green tea contains polyphenols that have anti-cancer properties and support overall health.
Turmeric
The active compound curcumin in turmeric has strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Garlic
Garlic contains allicin, which has been shown to have anti-cancer properties.
19. Managing Side Effects Through Diet
For individuals undergoing treatment for colon cancer, the colon cancer diet can help manage side effects and support recovery.
Nausea and Vomiting
Incorporate bland, easy-to-digest foods like crackers, bananas, and ginger tea to alleviate nausea.
Fatigue
Consume nutrient-rich foods that provide sustained energy, such as whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Loss of Appetite
Eat smaller, more frequent meals and include high-calorie, nutrient-dense snacks to maintain weight and energy levels.
Digestive Issues
Focus on high-fiber foods to promote regular bowel movements, but adjust fiber intake based on individual tolerance.
Maintaining Hydration
Ensure adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration, especially if experiencing diarrhea or vomiting.
20. Future Directions in Colon Cancer Diet Research
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into how diet influences colon cancer risk and management. Staying informed about the latest developments can enhance the colon cancer diet.
Personalized Nutrition
Advancements in genetics and microbiome research are paving the way for personalized dietary recommendations based on individual genetic profiles and gut health.
Functional Foods
Research into functional foods—those that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition—is expanding. These foods may offer targeted benefits for cancer prevention and treatment.
Integrative Approaches
Combining dietary strategies with other preventive measures, such as stress management and physical therapy, is an emerging area of interest.
Innovative Supplementation
New supplements and fortified foods are being developed to address specific nutritional gaps and enhance the effectiveness of the colon cancer diet.
Longitudinal Studies
Long-term studies are essential for understanding the sustained impact of dietary patterns on colon cancer incidence and survival rates.
References
Conclusion
Adopting the colon cancer diet is a proactive step towards reducing the risk of colon cancer and supporting overall digestive health. By incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods, avoiding harmful ones, and making complementary lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly impact their long-term health outcomes. Continuous education, monitoring, and consultation with healthcare professionals further enhance the effectiveness of this dietary approach. Embrace a holistic strategy that combines diet, exercise, and regular medical check-ups to achieve optimal health and cancer prevention.




