Comprehensive Guide to a Healthy Cockatiel Diet
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Cockatiel Diet
- Essential Nutrients for Cockatiels
- Recommended Foods for a Balanced Diet
- Foods to Avoid in Your Cockatiel Diet
- Meal Planning for Cockatiels
- Supplements in Cockatiel Diet
- Seasonal Diet Adjustments
- Hydration and Its Role in Diet
- Common Dietary Deficiencies
- Conclusion and Best Practices
1. Introduction to Cockatiel Diet
A well-balanced cockatiel diet is essential for the health and longevity of your feathered friend. Cockatiels, being intelligent and active birds, require a diverse range of nutrients to thrive. Understanding the components of a healthy cockatiel diet ensures that your pet receives the necessary sustenance to maintain energy, vibrant plumage, and overall well-being.
Cockatiels are omnivorous, meaning they require a variety of food types to meet their nutritional needs. Their diet should include seeds, pellets, fruits, vegetables, and occasional treats. Each component plays a specific role in maintaining different aspects of their health, from feather quality to digestive efficiency.
In this guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of a cockatiel diet, providing you with the knowledge and tools to create an optimal feeding plan for your bird. Whether you are a new cockatiel owner or looking to improve your current feeding regimen, this comprehensive guide will serve as an invaluable resource.
2. Essential Nutrients for Cockatiels

The foundation of a proper cockatiel diet lies in providing the essential nutrients that support various bodily functions. These nutrients include proteins, vitamins, minerals, fats, carbohydrates, and fiber. Each plays a unique role in maintaining the health and vitality of your cockatiel.
2.1 Proteins
Proteins are vital for muscle development, feather growth, and overall cellular repair. In a cockatiel diet, proteins should come from high-quality sources such as legumes, seeds, and specially formulated pellets.
Recommended Protein Sources:
- Legumes: Cooked beans and lentils provide essential amino acids.
- Seeds: While seeds are a good source of protein, they should be balanced with other food types to prevent excess fat intake.
- Pellets: High-quality pellets are designed to provide a balanced protein content tailored to your cockatiel’s needs.
It is important to avoid over-reliance on seeds for protein, as this can lead to nutritional imbalances and obesity.
2.2 Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins like A, D, and E, along with minerals such as calcium and iron, play crucial roles in maintaining healthy vision, bone strength, and immune function. A cockatiel diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables is an excellent way to ensure adequate intake of these essential nutrients.
Key Vitamins and Their Sources:
- Vitamin A: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin D: Synthesized through exposure to sunlight or provided via UVB lighting, essential for calcium absorption.
- Vitamin E: Present in nuts, seeds, and green vegetables.
Essential Minerals:
- Calcium: Crucial for bone health and egg production in females. Sources include broccoli, kale, and calcium supplements.
- Iron: Important for blood health, found in spinach, beans, and fortified pellets.
- Zinc: Supports immune function, available in seeds and fortified foods.
2.3 Fats and Carbohydrates
While fats provide a concentrated energy source, they must be included in moderation to prevent obesity. Carbohydrates from grains and vegetables offer a quick energy source for active cockatiels.
Healthy Fat Sources:
- Seeds: Provide healthy fats but should be given in controlled portions.
- Avocado: Avoided due to the presence of persin, which is toxic to birds.
Carbohydrate Sources:
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and barley offer sustained energy.
- Vegetables: Sweet potatoes, carrots, and peas are excellent sources of carbohydrates.
2.4 Fiber
Fiber aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy gastrointestinal tract. A cockatiel diet rich in fiber prevents digestive issues and promotes regular bowel movements.
Fiber-Rich Foods:
- Whole Grains: Provide essential fiber for digestive health.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and romaine lettuce are excellent fiber sources.
- Vegetables: Carrots, broccoli, and bell peppers contribute to fiber intake.
Incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods ensures that your cockatiel’s digestive system functions optimally, reducing the risk of constipation and other digestive ailments.
3. Recommended Foods for a Balanced Diet

Incorporating a variety of foods ensures that your cockatiel receives a balanced diet. Here are some recommended options that cover all necessary nutritional bases:
- Seeds: A staple in many cockatiel diets, seeds like millet and canary grass are nutritious and enjoyed by birds.
- Pellets: High-quality pellets should make up a significant portion of the diet, providing essential vitamins and minerals.
- Fresh Fruits: Apples, pears, berries, and bananas offer natural sugars and vital nutrients.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, carrots, sweet potatoes, and bell peppers contribute fiber and vitamins.
- Legumes: Cooked beans and lentils are excellent protein sources.
3.1 Seeds
Seeds are not only tasty but also provide necessary fats and proteins. However, they should be offered in moderation to prevent weight gain and nutritional imbalances. Opt for a variety of seeds to ensure a broader nutrient intake.
Recommended Seeds:
- Millet: A favorite among cockatiels, rich in carbohydrates and proteins.
- Canary Grass Seed: High in fiber, aiding digestion.
- Safflower Seeds: Offer healthy fats and proteins but should be limited due to higher fat content.
3.2 Pellets
Pellets are formulated to meet the complete nutritional needs of cockatiels. They help reduce selective eating and ensure a balanced diet. Look for pellets that are free from artificial colors and preservatives.
Benefits of Pellets:
- Balanced Nutrition: Designed to provide all essential nutrients in appropriate proportions.
- Consistent Quality: Unlike seeds, pellets have a consistent nutritional profile.
- Promotes Healthy Eating Habits: Encourages birds to eat a variety of foods rather than overconsuming favorites.
3.3 Fruits and Vegetables
Offering a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables not only enhances the visual appeal of meals but also introduces different flavors and textures to the diet. This variety can prevent dietary boredom and ensure a wider range of nutrient intake.
Recommended Fruits:
- Apples: High in fiber and vitamin C.
- Pears: Offer natural sweetness and hydration.
- Berries: Rich in antioxidants and vitamins.
- Bananas: Provide potassium and energy.
Recommended Vegetables:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and romaine lettuce are nutrient-dense and fiber-rich.
- Carrots: High in beta-carotene, promoting eye health.
- Sweet Potatoes: Excellent source of vitamins A and C.
- Bell Peppers: Packed with vitamins and add vibrant color to the diet.
3.4 Legumes
Cooked beans and lentils are excellent protein sources that should be included regularly in a cockatiel diet. They provide essential amino acids necessary for muscle maintenance and overall health.
Recommended Legumes:
- Black Beans: Rich in protein and fiber.
- Lentils: Provide a complete amino acid profile.
- Chickpeas: High in protein and iron.
Always ensure that legumes are thoroughly cooked and free from any seasoning or additives that could be harmful to your cockatiel.
4. Foods to Avoid in Your Cockatiel Diet
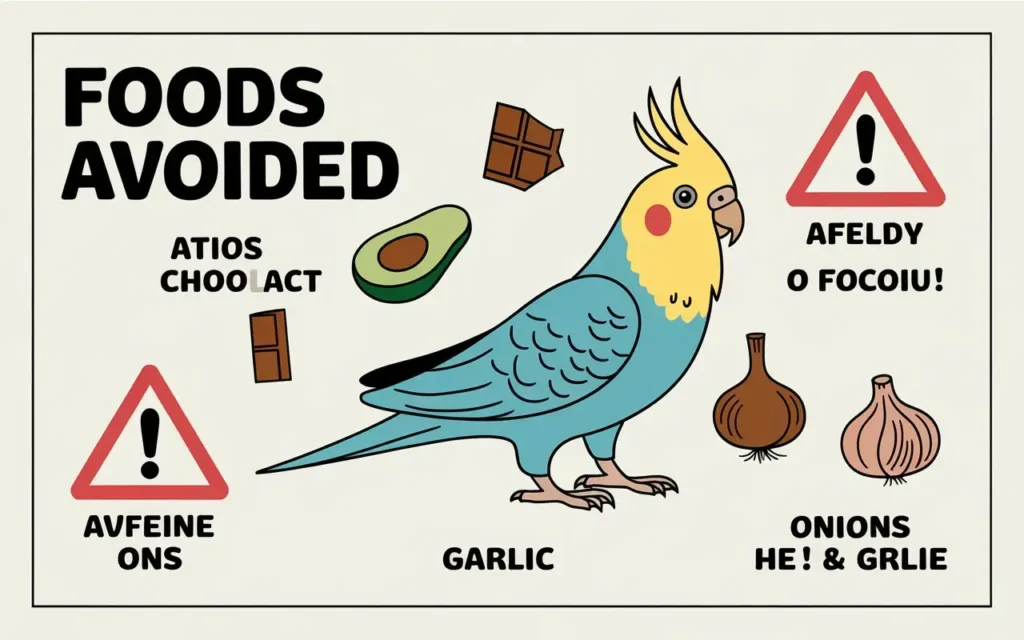
Just as important as knowing what to include is understanding what to exclude from your cockatiel diet. Certain foods can be harmful or even toxic to birds, leading to serious health issues or even death.
4.1 Avocado
Avocado contains persin, which is toxic to cockatiels and can cause respiratory distress and heart issues. Even small amounts can be dangerous, so it’s best to avoid feeding avocado to your bird entirely.
4.2 Chocolate and Caffeine
Both chocolate and caffeine are stimulants that can lead to severe health problems, including seizures and death. These substances affect the central nervous system and heart rate, making them extremely dangerous for cockatiels.
4.3 Alcohol and Nicotine
These substances are highly toxic and should never be present in the environment of your cockatiel. Even inhaling fumes from cigarettes or other tobacco products can be harmful.
4.4 High-Fat and Salty Foods
Foods high in fat and salt can lead to obesity and cardiovascular issues, disrupting the balance of a healthy cockatiel diet. These types of foods can also contribute to liver and kidney problems over time.
4.5 Onions and Garlic
These vegetables can cause digestive issues and damage red blood cells in birds. Symptoms of onion or garlic toxicity include lethargy, weakness, and difficulty breathing.
4.6 Fruit Pits and Seeds
Pits and seeds from fruits like cherries, apples, and peaches contain cyanogenic glycosides, which can release cyanide and are toxic to cockatiels. Always remove pits and seeds before offering fruits to your bird.
4.7 Rhubarb
Rhubarb leaves contain oxalic acid and anthraquinone glycosides, which are toxic to birds. Ingestion can lead to kidney failure and other severe health issues.
4.8 Processed Foods
Avoid giving your cockatiel processed foods, including chips, candies, and baked goods, as they often contain preservatives, artificial colors, and unhealthy fats that can be harmful.
4.9 Dairy Products
Cockatiels are lactose intolerant, and dairy products can cause digestive upset, including diarrhea and discomfort.
4.10 Moldy or Spoiled Foods
Always ensure that the food you provide is fresh and free from mold or spoilage. Moldy or spoiled foods can cause a range of health problems, including respiratory issues and digestive disturbances.
Key Takeaway: Maintaining a safe cockatiel diet involves careful selection and preparation of foods. Always research or consult with an avian veterinarian before introducing new foods to your bird’s diet.
5. Meal Planning for Cockatiels
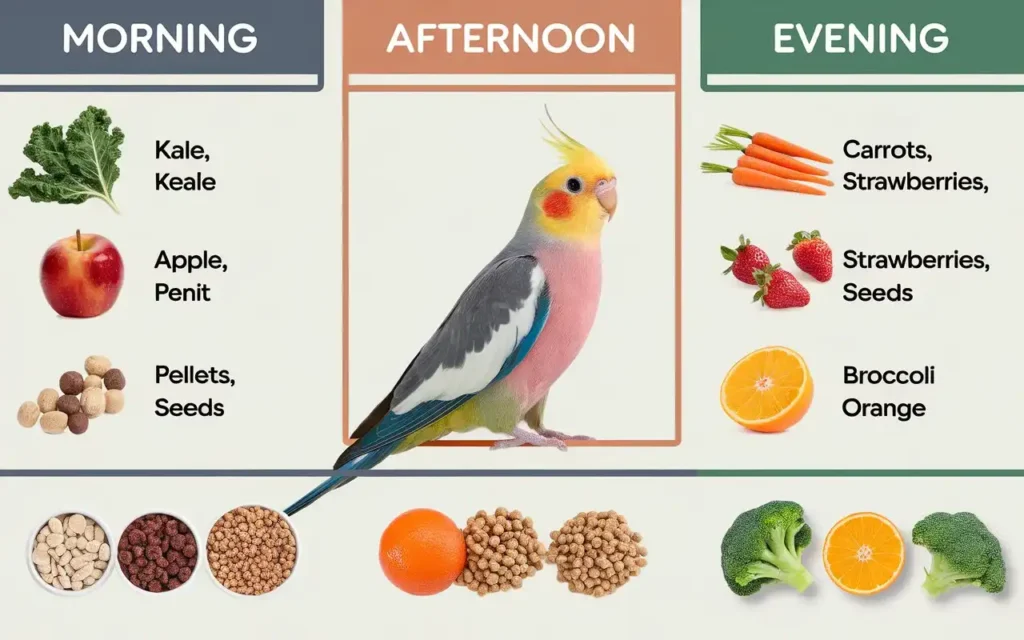
Effective meal planning ensures that your cockatiel receives a balanced diet consistently. Here’s how to structure meals to meet all nutritional needs:
5.1 Daily Feeding Schedule
Establishing a routine is crucial for maintaining a healthy cockatiel diet. Provide fresh food daily and remove uneaten portions after a few hours to prevent spoilage and overconsumption.
Sample Daily Schedule:
- Morning: Fresh vegetables and a portion of pellets.
- Afternoon: Fresh fruits and a small serving of seeds.
- Evening: Fresh vegetables and pellets to conclude the day.
This routine ensures that your cockatiel receives a steady supply of nutrients throughout the day, supporting their active lifestyle.
5.2 Portion Control
Monitoring portion sizes is vital to maintain a healthy weight. Overfeeding can lead to obesity, while underfeeding may cause nutrient deficiencies. A balanced cockatiel diet should include:
- Seeds: Limited to about 10-15% of the daily diet to prevent excess fat intake.
- Pellets: Approximately 50-60% of the diet to ensure balanced nutrition.
- Fruits and Vegetables: The remaining 30-40%, offering variety and essential nutrients.
Adjust portions based on your cockatiel’s activity level, age, and health status. Regularly weighing your bird can help monitor and adjust food intake accordingly.
5.3 Variety and Rotation
Rotating different food items prevents dietary boredom and ensures a wide range of nutrients are consumed. Introduce new foods gradually and observe your cockatiel’s acceptance and any potential allergic reactions.
Benefits of Variety:
- Prevents Picky Eating: Offering a range of foods encourages your bird to try and accept new items.
- Ensures Comprehensive Nutrition: Different foods provide different nutrient profiles, covering all dietary needs.
- Enhances Mental Stimulation: Variety in diet can provide mental enrichment, keeping your cockatiel engaged and happy.
5.4 Incorporating Treats
Offering healthy treats in moderation can reward your bird and add variety to the cockatiel diet. However, treats should not exceed 5-10% of the daily diet to maintain nutritional balance.
Healthy Treat Options:
- Small Pieces of Fruits: Such as apple slices or berries.
- Vegetable Sticks: Carrot or celery sticks offer a crunchy texture.
- Homemade Treats: Baked millet cakes or seed-free biscuits can be a healthy alternative.
Avoid high-fat, sugary, or processed treats that can disrupt the balance of a healthy cockatiel diet.
5.5 Monitoring and Adjusting
Regularly monitor your cockatiel’s weight, feather condition, and overall behavior to ensure the meal plan is effective. Adjust portions and food types as needed based on these observations and in consultation with an avian veterinarian.
Signs of an Imbalanced Diet:
- Weight Fluctuations: Sudden weight gain or loss may indicate dietary issues.
- Feather Condition: Dull or sparse feathers can signal nutritional deficiencies.
- Energy Levels: Excessive lethargy or hyperactivity might reflect imbalanced nutrient intake.
By staying attentive and proactive, you can ensure that your cockatiel maintains optimal health through a well-planned cockatiel diet.
6. Supplements in Cockatiel Diet
While a balanced cockatiel diet should cover most nutritional needs, supplements can be beneficial in certain cases. They can help address specific deficiencies or support particular health conditions.
6.1 Calcium Supplements
Calcium is essential for bone health and egg production in female cockatiels. A deficiency can lead to weak bones and reproductive issues.
Sources of Calcium:
- Broccoli: High in calcium and fiber.
- Kale: Another excellent vegetable source of calcium.
- Calcium Supplements: Available in powder or block form; should be used sparingly to avoid excess intake.
Usage Tips:
- Provide calcium supplements only when necessary, such as during breeding season.
- Consult with a veterinarian before introducing supplements to determine the appropriate dosage.
6.2 Vitamin Supplements
Occasionally, additional vitamins may be necessary, particularly in the absence of fresh produce or if your cockatiel has specific health needs.
Common Vitamin Supplements:
- Vitamin A: Supports eye health and immune function.
- Vitamin D3: Essential for calcium absorption, especially if UVB lighting is inadequate.
- Vitamin E: Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
Usage Tips:
- Use supplements as directed by a veterinarian to prevent overdosing.
- Ensure supplements are specifically formulated for birds to meet their unique nutritional requirements.
6.3 Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are beneficial for feather quality, skin health, and overall immune function. They also help reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular health.
Sources of Omega-3:
- Flaxseeds: Can be ground and added to meals.
- Fish Oil Supplements: Available in liquid or capsule form; ensure they are free from contaminants.
- Chia Seeds: Another plant-based source of Omega-3 fatty acids.
Usage Tips:
- Introduce Omega-3 supplements gradually to monitor for any adverse reactions.
- Consult with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate dosage based on your cockatiel’s needs.
6.4 Multivitamins
Comprehensive multivitamins can help cover any gaps in the diet, ensuring that your cockatiel receives all necessary nutrients. However, they should be used under veterinary guidance to avoid excessive intake of certain vitamins or minerals.
Benefits of Multivitamins:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Address multiple nutrient deficiencies simultaneously.
- Convenience: Easy to administer, especially for birds with selective eating habits.
Usage Tips:
- Choose multivitamins specifically formulated for birds.
- Follow dosage instructions carefully to prevent toxicity.
- Regularly consult with an avian veterinarian to assess the need for multivitamin supplementation.
6.5 Probiotics
Probiotics support digestive health and enhance nutrient absorption. They help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which is crucial for efficient digestion and overall health.
Sources of Probiotics:
- Probiotic Supplements: Available in powder or liquid forms, specifically designed for birds.
- Yogurt: Plain, unsweetened yogurt can be offered in small amounts, but many cockatiels are lactose intolerant.
Usage Tips:
- Introduce probiotics gradually to monitor for any adverse reactions.
- Consult with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate type and dosage of probiotics for your cockatiel.
Key Takeaway: Supplements can play a crucial role in a cockatiel diet, especially when addressing specific health needs. Always seek professional guidance to ensure safe and effective supplementation.
7. Seasonal Diet Adjustments
Adjusting your cockatiel’s diet according to the seasons can help accommodate changes in activity levels, environmental factors, and natural dietary variations. Seasonal adjustments ensure that your bird remains healthy and comfortable throughout the year.
7.1 Spring and Summer
Increased activity levels during warmer months may require more calories to sustain energy. Incorporate fresh fruits and vegetables that are in season to provide hydration and essential nutrients.
Spring and Summer Diet Tips:
- Increase Fresh Produce: Offer more hydrating vegetables like cucumbers and leafy greens.
- Provide Fresh Herbs: Basil, cilantro, and parsley can add variety and additional nutrients.
- Monitor Weight: Ensure that the increased activity is matched with appropriate caloric intake to prevent weight loss.
7.2 Autumn and Winter
Cooler temperatures might reduce activity, necessitating a slightly reduced calorie intake. Focus on foods that provide sustained energy to support metabolism.
Autumn and Winter Diet Tips:
- Introduce More Whole Grains: Provide brown rice, quinoa, and barley for sustained energy release.
- Offer Root Vegetables: Sweet potatoes and carrots are excellent sources of vitamins and minerals.
- Maintain Hydration: Ensure that water sources remain clean and free from freezing, as hydration needs remain constant despite temperature changes.
7.3 Holiday Seasons
Holiday seasons often introduce a variety of new foods and treats. Be cautious with holiday treats and avoid high-fat and sugary foods to prevent dietary imbalances.
Holiday Diet Tips:
- Avoid High-Fat Foods: Steer clear of nuts and seeds high in fat content unless offered sparingly.
- Limit Sugary Treats: Offer natural sweeteners like fresh fruits instead of processed sugary snacks.
- Ensure Safe Environment: Keep harmful holiday foods, such as chocolate and certain baked goods, out of reach.
7.4 Environmental Changes
Changes in daylight and temperature can affect metabolism and energy needs. Monitor your cockatiel’s weight and adjust the diet accordingly to maintain optimal health.
Environmental Adjustment Tips:
- Light Exposure: Ensure adequate exposure to natural sunlight or UVB lighting to support vitamin D synthesis.
- Temperature Control: Maintain a comfortable cage environment to prevent stress, which can impact appetite and digestion.
- Monitor Behavior: Changes in activity levels can indicate a need to adjust food intake.
Key Takeaway: Seasonal adjustments to the cockatiel diet help accommodate natural changes in the environment, ensuring that your bird remains healthy and active year-round.
8. Hydration and Its Role in Diet
Proper hydration is a critical component of a balanced cockatiel diet. Water aids in digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall cellular function. Ensuring your cockatiel stays well-hydrated is essential for their health and well-being.
8.1 Fresh Water Availability
Ensure that clean, fresh water is available at all times. Change water daily to prevent bacterial growth and contamination. Provide multiple water sources if your cockatiel is particularly thirsty or if the cage is large.
Tips for Maintaining Fresh Water:
- Use Clean Containers: Regularly wash water bottles and bowls to prevent algae and bacterial buildup.
- Check Water Levels: Ensure that water containers are always filled, especially during warmer months.
- Provide Multiple Sources: Place water containers at different locations within the cage to encourage regular drinking.
8.2 Hydration Through Food
Fruits and vegetables with high water content contribute significantly to your cockatiel’s hydration. Including these foods in their diet can help supplement their water intake.
Hydrating Foods:
- Cucumbers: High in water content and low in calories.
- Melons: Such as cantaloupe and watermelon provide hydration and natural sweetness.
- Leafy Greens: Lettuce and spinach offer moisture along with essential nutrients.
8.3 Signs of Dehydration
Recognizing the signs of dehydration early can prevent serious health issues. Look for the following symptoms in your cockatiel:
- Drooping Feathers: Feathers may appear dull and less vibrant.
- Lethargy: Reduced activity levels and increased sleepiness.
- Dry Droppings: Lack of moisture in feces can indicate dehydration.
- Sunken Eyes: Eyes may appear sunken or dull.
Immediate Action: If you suspect dehydration, provide immediate access to fresh water and consult with an avian veterinarian if symptoms persist.
8.4 Encouraging Water Intake
Some cockatiels may be reluctant to drink enough water. Implementing strategies to encourage water intake can help maintain proper hydration.
Strategies to Encourage Drinking:
- Water Fountains: Birds often enjoy drinking from moving water sources.
- Multiple Water Containers: Placing water at different locations within the cage can encourage more frequent drinking.
- Flavoring Water: Adding a small amount of fresh fruit juice can entice your cockatiel to drink, but ensure it’s free from added sugars and artificial ingredients.
- Misting: Lightly misting your cockatiel or the cage can aid hydration, especially during hot weather.
8.5 Impact of Diet on Hydration
A balanced diet rich in moisture-containing foods supports adequate hydration, reducing the reliance solely on water intake. Proper hydration impacts all aspects of health, from digestion to feather quality.
Diet and Hydration Connection:
- High-Water Foods: Incorporating foods like cucumbers and melons adds moisture to the diet.
- Balanced Nutrients: Proper nutrient intake supports efficient hydration and cellular function.
- Reduced Risk of Health Issues: Adequate hydration helps prevent digestive problems and supports overall health.
Key Takeaway: Ensuring proper hydration through both water intake and moisture-rich foods is essential for maintaining a healthy cockatiel diet and overall well-being.
9. Common Dietary Deficiencies
Recognizing and preventing dietary deficiencies is crucial for maintaining your cockatiel’s health. Common deficiencies include vitamin A, calcium, protein, iron, and vitamin D. Understanding the symptoms and prevention strategies can help ensure your bird maintains optimal health through proper nutrition.
9.1 Vitamin A Deficiency
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy vision, immune function, and skin health. A deficiency can lead to poor feather quality and respiratory issues.
Symptoms of Vitamin A Deficiency:
- Respiratory Problems: Increased susceptibility to infections and respiratory distress.
- Poor Feather Quality: Dull, brittle feathers and reduced growth.
- Vision Issues: Difficulty seeing in low light conditions.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Dietary Sources: Include carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens like spinach and kale.
- Supplementation: Vitamin A supplements can be administered under veterinary guidance.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular health check-ups to detect early signs of deficiency.
9.2 Calcium Deficiency
Calcium is crucial for bone health and egg-laying in female cockatiels. A deficiency can result in weak bones and reproductive issues.
Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency:
- Weak Bones: Increased risk of fractures and skeletal deformities.
- Egg-Laying Problems: Females may experience difficulties in laying eggs or produce eggs with soft shells.
- Muscle Weakness: Reduced muscle tone and strength.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Dietary Sources: Provide calcium-rich foods like broccoli, kale, and fortified pellets.
- Calcium Supplements: Use sparingly and under veterinary supervision to avoid excessive intake.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure a balanced intake of calcium and phosphorus to promote optimal absorption.
9.3 Protein Deficiency
Protein is essential for muscle maintenance, feather growth, and overall cellular repair. A deficiency can cause muscle wasting and poor feather growth.
Symptoms of Protein Deficiency:
- Muscle Wasting: Noticeable reduction in muscle mass and strength.
- Poor Feather Growth: Incomplete or brittle feathers.
- Delayed Healing: Slower recovery from injuries or illnesses.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Dietary Sources: Incorporate legumes, seeds, and high-quality pellets.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure adequate protein intake without over-relying on seeds to prevent fat imbalance.
- Regular Monitoring: Observe feather quality and muscle tone to detect early signs of deficiency.
9.4 Iron Deficiency
Iron is important for blood health, particularly in preventing anemia. A deficiency can lead to lethargy and weakness.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency:
- Anemia: Pale mucous membranes and lethargy.
- Lethargy: Reduced activity levels and energy.
- Weakness: Difficulty in flying or climbing.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Dietary Sources: Include iron-rich foods like spinach, beans, and fortified pellets.
- Iron Supplements: Can be administered under veterinary supervision if necessary.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure a balanced intake of iron and other essential nutrients to support overall health.
9.5 Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and bone health. A deficiency can lead to weakened bones and metabolic bone disease.
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency:
- Weak Bones: Increased susceptibility to fractures and skeletal deformities.
- Egg-Laying Problems: Females may produce eggs with soft shells.
- Lethargy: Reduced activity levels and energy.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Sunlight Exposure: Provide adequate access to natural sunlight or UVB lighting to facilitate vitamin D synthesis.
- Dietary Sources: Include foods fortified with vitamin D, such as certain pellets.
- Supplementation: Use vitamin D supplements under veterinary guidance if necessary.
9.6 Addressing Deficiencies
Regular veterinary check-ups and a varied diet help identify and address deficiencies promptly, ensuring a healthy cockatiel diet. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing long-term health issues associated with nutrient deficiencies.
Proactive Measures:
- Regular Health Check-Ups: Schedule routine visits with an avian veterinarian to monitor your bird’s health.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure a diverse and balanced cockatiel diet to cover all nutritional bases.
- Observation: Keep a close eye on your cockatiel’s behavior, feather condition, and physical appearance for any signs of nutritional issues.
Key Takeaway: Understanding common dietary deficiencies and their symptoms allows for timely intervention and ensures that your cockatiel remains healthy and vibrant through a well-maintained cockatiel diet.
10. Conclusion and Best Practices
Maintaining a balanced cockatiel diet is fundamental to your bird’s health and happiness. By understanding the essential nutrients, recommended foods, and foods to avoid, you can create a diet that supports all aspects of your cockatiel’s well-being.
10.1 Regular Monitoring
Keep an eye on your cockatiel’s weight, feather condition, and overall behavior to ensure the diet is meeting their needs. Regular monitoring allows for early detection of any nutritional imbalances or health issues, enabling timely adjustments to the diet.
Monitoring Tips:
- Weighing: Regularly weigh your bird to track any significant changes in weight.
- Feather Inspection: Check for dullness, brittleness, or abnormal growth patterns.
- Behavior Observation: Notice any changes in activity levels, appetite, or social interactions.
10.2 Consult Professionals
Seek advice from avian veterinarians or certified avian nutritionists to tailor the diet to your cockatiel’s specific requirements. Professionals can provide personalized recommendations based on your bird’s health status, age, and lifestyle.
When to Consult a Professional:
- Health Concerns: If you notice any signs of illness or nutritional deficiencies.
- Dietary Changes: When introducing new foods or supplements to your cockatiel’s diet.
- Breeding: To ensure adequate nutrition for breeding and egg production.
10.3 Continuous Learning
Stay informed about the latest research and recommendations in avian nutrition to provide the best care for your pet. Avian nutrition is an evolving field, and new insights can help enhance your cockatiel’s diet and overall health.
Learning Resources:
- Books and Publications: Read reputable books on avian care and nutrition.
- Online Resources: Utilize trusted websites and forums dedicated to bird care.
- Workshops and Seminars: Attend events focused on avian health and nutrition.
10.4 Balanced Approach
Strive for a balanced approach that combines seeds, pellets, fresh produce, and occasional treats, ensuring variety and comprehensive nutrition. This balance helps prevent overconsumption of any single food type and promotes overall health.
Balanced Diet Components:
- Seeds: Limited portion to provide fats and proteins without excess calories.
- Pellets: A significant portion to cover essential vitamins and minerals.
- Fresh Produce: A variety of fruits and vegetables for vitamins, minerals, and hydration.
- Treats: Healthy treats in moderation to add variety and enrichment.
10.5 Creating a Safe Feeding Environment
Ensure that all food is fresh, clean, and free from contaminants. Maintain a clean feeding area to promote your cockatiel’s health and prevent the spread of diseases.
Safe Feeding Practices:
- Clean Containers: Regularly wash feeding dishes and water containers to prevent mold and bacteria.
- Proper Storage: Store seeds and pellets in airtight containers to maintain freshness and prevent pest infestations.
- Sanitization: Disinfect the cage and feeding areas regularly to ensure a hygienic environment.
Key Takeaway: A balanced and well-planned cockatiel diet is integral to your bird’s health and happiness. By following best practices in meal planning, supplementation, and environmental management, you can ensure your cockatiel thrives.
References
- Avian Web – Avian Nutrition
- VetInfo – Cockatiel Diet Guide
- PetMD – Cockatiel Nutrition
- BirdChannel – Bird Nutrition




