Water Fasting Electrolytes: The Ultimate Guide to Maintaining Balance
1. Introduction to Water Fasting Electrolytes
Water fasting electrolytes are essential components that play a crucial role in maintaining the body’s balance during a water fast. Understanding how electrolytes function can significantly enhance the safety and effectiveness of your fasting journey.
Water fasting, a practice that involves consuming only water for a set period, has gained popularity for its potential health benefits, including weight loss, detoxification, and improved metabolic health. However, ensuring adequate intake of water fasting electrolytes is vital to prevent adverse effects and support overall well-being during the fast.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the significance of water fasting electrolytes, explore the key minerals you need to monitor, and provide actionable strategies to maintain electrolyte balance effectively.
2. The Importance of Electrolytes in Water Fasting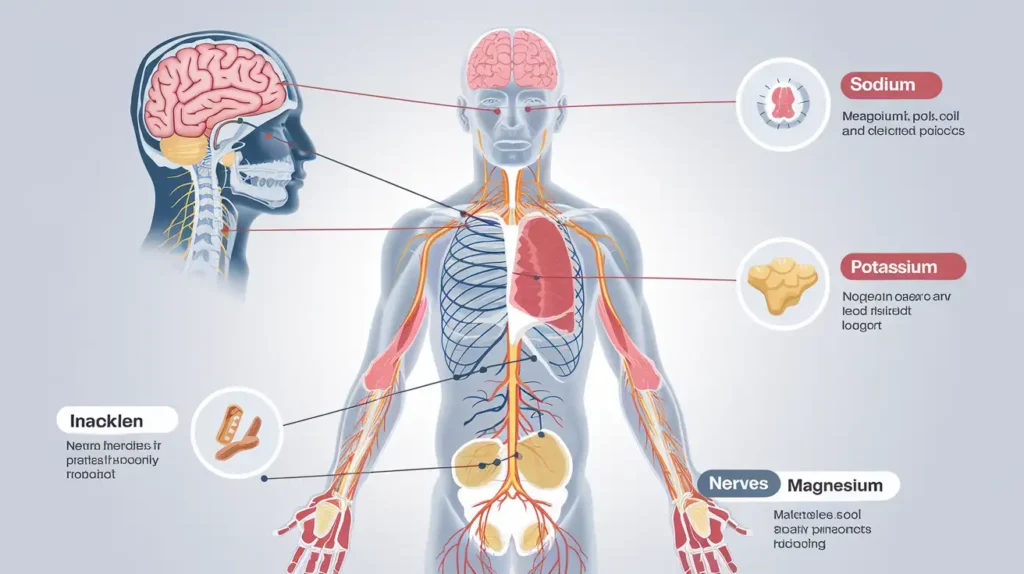
Water fasting electrolytes are vital because they help regulate nerve and muscle function, hydrate the body, balance blood acidity and pressure, and help rebuild damaged tissue. Without adequate electrolytes, prolonged fasting can lead to serious health complications.
During water fasting, your body undergoes significant physiological changes as it shifts from using glucose to burning fat for energy. This metabolic shift increases the excretion of electrolytes through urine, making it essential to replenish them to maintain bodily functions.
Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium are involved in critical processes like maintaining fluid balance, transmitting nerve impulses, and ensuring proper muscle contractions. An imbalance in these electrolytes can result in symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
Understanding the role of water fasting electrolytes helps you make informed decisions about supplementation and dietary choices, ensuring a safe and effective fasting experience.
3. Key Electrolytes to Monitor During Water Fasting
Water fasting electrolytes primarily include sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Each of these plays a unique role in bodily functions:
- Sodium: Maintains fluid balance and is essential for nerve function.
- Potassium: Crucial for heart and muscle function.
- Magnesium: Supports muscle and nerve function, as well as energy production.
- Calcium: Important for bone health and muscle function.
Let’s explore each of these electrolytes in detail to understand their significance during water fasting.
3.1 Sodium
Water fasting electrolytes include sodium, which plays a critical role in maintaining fluid balance and nerve transmission. Sodium helps regulate blood pressure and volume, ensuring that your body’s cells function optimally.
During a water fast, sodium levels can decrease due to reduced intake and increased excretion. Symptoms of sodium deficiency may include headaches, fatigue, and muscle cramps. To prevent these, it’s essential to incorporate adequate sodium sources into your fasting regimen.
3.2 Potassium
Potassium is another vital water fasting electrolyte that supports heart health and muscle function. It helps regulate heartbeat, ensures proper muscle contractions, and maintains fluid balance within cells.
Low potassium levels can lead to irregular heartbeats, muscle weakness, and fatigue. Monitoring potassium intake through supplements or appropriate dietary sources is crucial to avoid these adverse effects during fasting.
3.3 Magnesium
Magnesium is a key water fasting electrolyte involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including energy production, protein synthesis, and muscle and nerve function.
Deficiency in magnesium can cause symptoms such as muscle cramps, mental disorders, and osteoporosis over time. Ensuring adequate magnesium intake helps mitigate these risks and supports overall health during water fasting.
3.4 Calcium
Calcium, another essential water fasting electrolyte, is primarily known for its role in bone health. However, it also contributes to muscle function, nerve signaling, and blood clotting.
Maintaining proper calcium levels during fasting is important to prevent muscle spasms and support cardiovascular health. While calcium deficiency is less common during short-term fasts, it becomes a concern in prolonged fasting scenarios.
4. Benefits of Maintaining Electrolyte Balance
Maintaining water fasting electrolytes ensures that your body functions optimally during a fast. Benefits include:
- Prevention of muscle cramps and spasms.
- Improved heart health and reduced risk of arrhythmias.
- Enhanced energy levels and reduced fatigue.
- Better hydration and overall bodily functions.
Let’s delve deeper into these benefits to understand how electrolyte balance contributes to a successful water fast.
4.1 Prevention of Muscle Cramps and Spasms
Water fasting electrolytes like potassium and magnesium play a pivotal role in muscle contraction and relaxation. Adequate levels prevent involuntary muscle cramps and spasms, which can be both painful and disruptive during fasting periods.
By maintaining electrolyte balance, you ensure that your muscles function smoothly, allowing you to engage in daily activities without discomfort.
4.2 Improved Heart Health
Electrolytes such as potassium and calcium are essential for maintaining a regular heartbeat. Imbalances can lead to arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats that can be dangerous if left unchecked.
By keeping water fasting electrolytes in check, you support your cardiovascular system, reducing the risk of heart-related complications during fasting.
4.3 Enhanced Energy Levels
Maintaining electrolyte balance helps sustain energy levels during water fasting. Electrolytes are involved in energy production at the cellular level, ensuring that your body can efficiently convert stored fat into usable energy.
Proper electrolyte intake minimizes feelings of fatigue and lethargy, making the fasting experience more manageable and effective.
4.4 Better Hydration and Bodily Functions
Electrolytes are crucial for maintaining proper hydration levels. They help balance the amount of water in and around your cells, ensuring that all bodily functions operate smoothly.
From regulating body temperature to facilitating nutrient transport, adequate electrolyte levels support a wide range of physiological processes, contributing to overall health during water fasting.
5. Symptoms of Electrolyte Deficiency
Ignoring water fasting electrolytes can lead to deficiencies, presenting various symptoms such as:
- Muscle weakness and cramps.
- Irregular heartbeat.
- Fatigue and lethargy.
- Headaches and dizziness.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial to prevent more severe health issues. Let’s explore each symptom in detail.
5.1 Muscle Weakness and Cramps
One of the most common signs of electrolyte deficiency during water fasting is muscle weakness and cramps. This occurs because electrolytes like potassium and magnesium are essential for muscle contraction and relaxation.
When electrolyte levels drop, muscles may not function properly, leading to involuntary contractions and discomfort.
5.2 Irregular Heartbeat
Electrolyte imbalances, particularly in potassium and calcium, can disrupt the electrical signals that regulate heartbeats. This can result in arrhythmias, which are irregular or abnormal heart rhythms.
An irregular heartbeat can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly, highlighting the importance of maintaining electrolyte balance during fasting.
5.3 Fatigue and Lethargy
Electrolytes play a key role in energy production and cellular function. Deficiencies can lead to a significant drop in energy levels, causing persistent fatigue and lethargy.
These symptoms can make fasting more challenging and may indicate that your body is struggling to maintain essential functions.
5.4 Headaches and Dizziness
Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances can lead to headaches and dizziness. Electrolytes help regulate fluid balance and blood pressure, and their deficiency can disrupt these processes.
Experiencing these symptoms during a fast is a clear sign that you need to adjust your electrolyte intake to restore balance.
6. Electrolyte Supplementation Strategies
Implementing effective water fasting electrolytes supplementation can help maintain balance. Strategies include:
- Using electrolyte powders or tablets specifically designed for fasting.
- Incorporating bone broth, which is rich in essential minerals.
- Monitoring electrolyte levels through blood tests when possible.
Let’s examine each supplementation strategy to determine the best approach for maintaining water fasting electrolytes.
6.1 Electrolyte Powders and Tablets
One of the most convenient ways to supplement water fasting electrolytes is through specially formulated powders or tablets. These products are designed to provide a balanced mix of essential electrolytes without added sugars or calories.
When selecting an electrolyte supplement, look for options that include sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium in appropriate ratios. Always follow the recommended dosage instructions to avoid overconsumption, which can lead to imbalances.
6.2 Bone Broth
Bone broth is a natural source of water fasting electrolytes, particularly rich in sodium and potassium. It also contains collagen, which supports joint and skin health.
Incorporating bone broth into your fasting regimen can provide a nourishing way to replenish electrolytes while still adhering to the principles of water fasting. Ensure that the bone broth is low in carbohydrates and free from additives to maintain the integrity of your fast.
6.3 Monitoring Electrolyte Levels
For those undertaking extended water fasts, monitoring electrolyte levels through blood tests can be beneficial. Regular testing helps identify any deficiencies early, allowing for timely adjustments to supplementation strategies.
Consult with a healthcare professional before and during your fast to determine the appropriate frequency of testing and to interpret the results accurately.
6.4 Balanced Supplementation Approach
Maintaining water fasting electrolytes requires a balanced approach to supplementation. Avoid over-supplementing any single electrolyte, as this can lead to imbalances and adverse effects.
Instead, aim for a holistic supplementation plan that addresses all essential electrolytes in proportionate amounts. This ensures comprehensive support for your body’s needs during the fast.
7. Dietary Sources of Essential Electrolytes
While water fasting primarily involves consuming water, incorporating certain dietary sources can aid in maintaining electrolyte levels:
- Sodium: Sea salt or Himalayan salt can be added to water.
- Potassium: Potassium chloride supplements are an option.
- Magnesium: Magnesium citrate or glycinate supplements.
- Calcium: Calcium supplements can be considered if necessary.
Let’s explore each of these sources to understand how they contribute to water fasting electrolytes balance.
7.1 Sodium Sources
Sodium is readily available through various salt types. Adding a small amount of sea salt or Himalayan salt to your water can help maintain sodium levels during fasting.
It’s important to use these salts in moderation, as excessive sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure and other health issues.
7.2 Potassium Sources
Potassium chloride supplements are a convenient way to increase potassium intake during water fasting. These supplements provide potassium without adding calories or carbohydrates.
Ensure you follow the recommended dosage to prevent hyperkalemia, a condition characterized by excessively high potassium levels that can affect heart function.
7.3 Magnesium Sources
Magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate are popular supplements for maintaining magnesium levels during fasting. These forms are highly bioavailable, meaning they are easily absorbed by the body.
Magnesium supplements can help prevent muscle cramps, support nerve function, and contribute to overall relaxation and well-being.
7.4 Calcium Sources
Calcium supplements can be considered if necessary, especially during prolonged fasting periods. Calcium carbonate and calcium citrate are common forms used in supplements.
While calcium deficiency is less common during short-term fasts, ensuring adequate intake supports bone health and muscle function.
7.5 Combining Dietary Sources with Supplementation
Combining dietary sources with supplementation can provide a comprehensive approach to maintaining water fasting electrolytes. For example, adding a pinch of sea salt to your water while taking a balanced electrolyte supplement ensures a steady intake of essential minerals.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen to tailor it to your specific needs and health conditions.
8. Hydration Tips for Effective Water Fasting
Proper hydration is intertwined with water fasting electrolytes. Tips include:
- Drink plenty of filtered water throughout the day.
- Monitor urine color to ensure adequate hydration.
- Avoid excessive caffeine or alcohol, which can dehydrate.
Maintaining optimal hydration levels is crucial for supporting water fasting electrolytes. Let’s explore each tip in detail.
8.1 Drink Plenty of Filtered Water
Consistently drinking filtered water throughout the day helps maintain hydration levels and supports the balance of water fasting electrolytes. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, adjusting based on individual needs and activity levels.
Filtered water is preferred as it removes impurities and contaminants, ensuring that the water you consume is clean and safe.
8.2 Monitor Urine Color
Monitoring the color of your urine is an effective way to gauge your hydration status. Light yellow or clear urine typically indicates adequate hydration, while dark yellow or amber-colored urine suggests dehydration.
During water fasting, keeping an eye on urine color can help you adjust your water and electrolyte intake accordingly to maintain optimal hydration.
8.3 Avoid Excessive Caffeine and Alcohol
Caffeine and alcohol are diuretics, meaning they increase urine production and can lead to dehydration. During water fasting, it’s best to limit or avoid these substances to prevent unnecessary loss of water fasting electrolytes.
If you choose to consume caffeine, do so in moderation and ensure you compensate with additional water intake.
8.4 Incorporate Herbal Teas
Herbal teas can be a beneficial addition to your hydration strategy during water fasting. They provide variety in your fluid intake without adding calories or disrupting the fast.
Choose caffeine-free herbal teas like chamomile, peppermint, or ginger to support hydration and provide soothing effects.
8.5 Establish a Hydration Schedule
Creating a hydration schedule can help ensure you consistently consume enough water throughout the day. Set reminders or establish specific times to drink water, making it a regular part of your routine.
Regular hydration supports the maintenance of water fasting electrolytes and overall health during the fast.
9. Common Mistakes to Avoid During Water Fasting
Avoiding pitfalls related to water fasting electrolytes can enhance your fasting experience:
- Neglecting electrolyte supplementation.
- Overconsumption of water without electrolyte balance.
- Ignoring signs of electrolyte deficiency.
Let’s discuss these common mistakes and how to prevent them to ensure a successful and safe water fast.
9.1 Neglecting Electrolyte Supplementation
One of the most significant mistakes during water fasting is neglecting electrolyte supplementation. Fasting increases the excretion of electrolytes, and without proper supplementation, deficiencies can occur.
Ensure you incorporate electrolyte supplements or dietary sources to maintain balance and support your body’s essential functions during the fast.
9.2 Overconsumption of Water Without Electrolyte Balance
While staying hydrated is crucial, overconsuming water without balancing electrolytes can lead to a condition known as hyponatremia, where sodium levels become dangerously low.
To prevent this, balance your water intake with appropriate electrolyte supplementation, ensuring that you hydrate without disrupting electrolyte levels.
9.3 Ignoring Signs of Electrolyte Deficiency
Ignoring the symptoms of electrolyte deficiency can lead to severe health issues. Symptoms like muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, fatigue, and dizziness should not be overlooked.
Pay attention to your body’s signals and take immediate action by adjusting your electrolyte intake or consulting a healthcare professional if necessary.
9.4 Inadequate Planning and Preparation
Embarking on a water fast without proper planning can result in inadequate electrolyte management. Failing to research and prepare a supplementation plan can jeopardize your health during the fast.
Take the time to understand your electrolyte needs and develop a structured plan that includes supplementation and hydration strategies.
9.5 Not Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Water fasting can have significant effects on your body, especially concerning electrolyte balance. Not consulting a healthcare professional before and during the fast can increase the risk of complications.
Seek medical advice to tailor your fasting and supplementation plan to your individual health needs and conditions.
10. Expert Advice and Best Practices
Experts emphasize the importance of consulting healthcare professionals before starting a fast, especially regarding water fasting electrolytes. Best practices include:
- Getting a health check-up prior to fasting.
- Following a structured fasting plan.
- Listening to your body’s signals and adjusting accordingly.
Let’s explore expert advice and best practices to ensure a safe and effective water fasting experience.
10.1 Consult with Healthcare Professionals
Before embarking on a water fast, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Healthcare providers can offer personalized advice, help you create a safe fasting plan, and monitor your health throughout the fasting period.
10.2 Follow a Structured Fasting Plan
Adhering to a structured fasting plan helps manage water fasting electrolytes effectively. A well-designed plan outlines the duration of the fast, supplementation schedules, and hydration strategies.
Structured plans reduce the risk of electrolyte imbalances and ensure that you maintain optimal health during the fast.
10.3 Listen to Your Body
Paying attention to your body’s signals is essential during water fasting. If you experience symptoms of electrolyte deficiency or other adverse effects, take immediate action by adjusting your electrolyte intake or seeking medical assistance.
Listening to your body helps prevent complications and promotes a more comfortable and successful fasting experience.
10.4 Educate Yourself
Understanding the science behind water fasting electrolytes empowers you to make informed decisions. Educate yourself about the roles of different electrolytes, their sources, and the signs of imbalance.
Reliable sources include scientific journals, reputable health websites, and guidance from healthcare professionals.
10.5 Gradual Transition In and Out of Fasting
Transitioning into and out of a water fast should be done gradually to allow your body to adjust. Start with shorter fasting periods and slowly increase the duration as your body adapts.
Similarly, when ending a fast, reintroduce foods and electrolytes gradually to prevent digestive issues and electrolyte imbalances.




