Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
- How Semaglutide Works for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
- Clinical Trials and Efficacy of Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
- Dosage and Administration of Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
- Potential Side Effects of Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
- Semaglutide vs. Traditional Weight Loss Methods
- Cost and Accessibility of Semaglutide for Weight Loss in the US
- FDA Approval and Regulatory Considerations
- Integrating Semaglutide into a Comprehensive Weight Loss Plan
- Long-Term Effects and Sustainability
- Navigating the Prescription Process for Semaglutide
- Conclusion
- References
1. Introduction to Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics has gained significant attention as a promising treatment option. Originally developed to manage type 2 diabetes, semaglutide has demonstrated substantial efficacy in promoting weight loss among individuals without diabetes. This comprehensive guide explores the various aspects of semaglutide, from its mechanism of action to its long-term effects, providing valuable insights for those considering it as part of their weight management strategy.
2. How Semaglutide Works for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics operates through several biological pathways to facilitate weight reduction. As a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, semaglutide enhances insulin secretion, suppresses appetite, and slows gastric emptying. These actions collectively contribute to reduced caloric intake and increased satiety, making it easier for individuals to adhere to a calorie-restricted diet and engage in regular physical activity.
Mechanism of Action
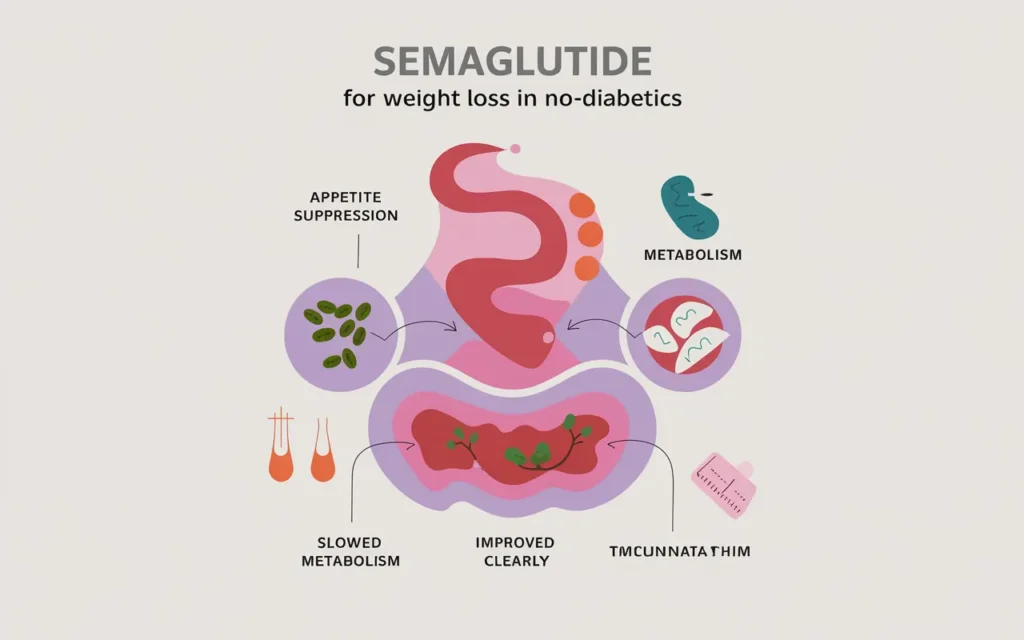
- Appetite Suppression: Semaglutide interacts with appetite centers in the brain, leading to decreased hunger and increased feelings of fullness.
- Slowed Gastric Emptying: By delaying stomach emptying, semaglutide prolongs the feeling of satiety after meals.
- Improved Metabolism: It enhances metabolic processes, aiding in more efficient calorie burning.
3. Clinical Trials and Efficacy of Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics has been extensively studied in various clinical trials, showcasing its effectiveness in promoting significant weight reduction. Notably, the STEP (Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with Obesity) trials have provided robust evidence supporting its use.
Key Findings from Clinical Trials
| Study | Participants | Weight Loss (%) | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| STEP 1 | 1,961 Adults with Obesity | 14.9% | 68 Weeks |
| STEP 2 | 1,210 Adults with Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Factors | 9.6% | 68 Weeks |
| STEP 3 | 611 Adults with Obesity | 16.0% | 68 Weeks |
These studies demonstrate that semaglutide can lead to substantial weight loss, with some participants losing up to 16% of their body weight over a period of 68 weeks. These results highlight semaglutide’s potential as a powerful tool in the fight against obesity.
4. Dosage and Administration of Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics is administered via subcutaneous injection. The dosage regimen typically starts with a lower dose to minimize gastrointestinal side effects, gradually increasing to the maintenance dose as tolerated.
Recommended Dosage
- Starting Dose: 0.25 mg once weekly for 4 weeks.
- Intermediate Dose: 0.5 mg once weekly for 4 weeks.
- Maintenance Dose: 1 mg once weekly thereafter.
Administration Guidelines
- Choose an injection site (abdomen, thigh, or upper arm) and rotate sites with each dose.
- Inject semaglutide subcutaneously, preferably at the same time each week.
- Do not exceed the recommended dose to avoid potential side effects.
5. Potential Side Effects of Semaglutide for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics
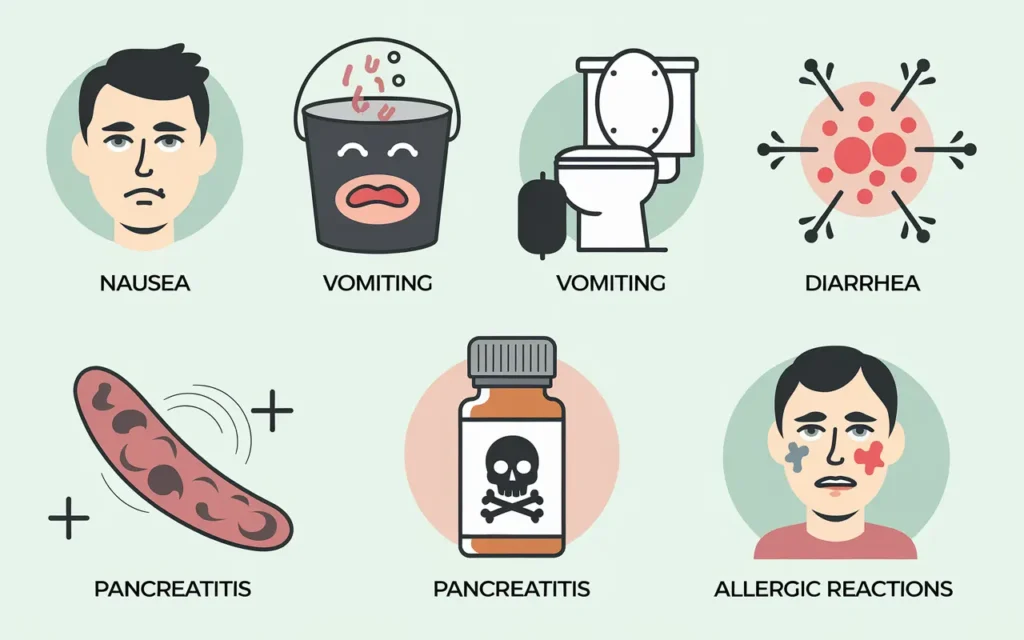
While semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics is generally well-tolerated, it may cause certain side effects. Understanding these potential adverse effects is crucial for making an informed decision about its use.
Common Side Effects
- Nausea: Often occurs when starting treatment but usually diminishes over time.
- Vomiting: May accompany nausea in some individuals.
- Diarrhea: Can lead to dehydration if not managed properly.
- Constipation: Affects some users, necessitating dietary adjustments.
Serious Side Effects
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Kidney Problems: Severe dehydration from gastrointestinal side effects can impact kidney function.
- Allergic Reactions: Signs include rash, itching, or swelling.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting semaglutide to discuss potential risks and ensure it’s appropriate for your health profile.
6. Semaglutide vs. Traditional Weight Loss Methods

Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics offers an alternative to traditional weight loss methods such as diet and exercise. Comparing its efficacy and sustainability with these conventional approaches provides a clearer picture of its role in weight management.
Effectiveness
While diet and exercise are foundational for weight loss, semaglutide has been shown to produce more significant and consistent weight loss results. Clinical trials indicate that participants on semaglutide lose more weight compared to those relying solely on lifestyle changes.
Sustainability
One of the challenges with traditional methods is maintaining weight loss over the long term. Semaglutide, when combined with lifestyle modifications, can help sustain weight loss by addressing the physiological aspects of hunger and metabolism.
Combination Therapy
Integrating semaglutide with diet and exercise can enhance overall weight loss outcomes, making it a complementary tool rather than a replacement for traditional methods.
7. Cost and Accessibility of Semaglutide for Weight Loss in the US
Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics is becoming more accessible, but cost remains a significant factor for many individuals. Understanding the financial aspects can help in planning and decision-making.
Pricing
The cost of semaglutide can vary based on dosage and insurance coverage. On average, the price ranges from $700 to $1,200 per month without insurance. However, prices may fluctuate depending on the pharmacy and location.
Insurance Coverage
Insurance coverage for semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics is limited, as it is often approved primarily for diabetes management. Some insurance plans may offer partial coverage, so it’s advisable to check with your provider.
Assistance Programs
- Manufacturer Discounts: Novo Nordisk, the manufacturer of semaglutide, may offer savings programs or coupons.
- Patient Assistance Programs: These programs can provide financial support for eligible individuals.
Regional Availability
Semaglutide is widely available across the US, but access may vary in rural versus urban areas. Telemedicine services can bridge the gap, providing consultations and prescriptions remotely.
8. FDA Approval and Regulatory Considerations
Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics has undergone rigorous evaluation by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Understanding its approval status and regulatory framework is essential for informed use.
Approval Status
In June 2021, the FDA approved a higher dose of semaglutide specifically for chronic weight management in adults with obesity or overweight with at least one weight-related condition. This approval marked a significant milestone in obesity treatment.
Regulatory Guidelines
The FDA’s approval includes guidelines on dosage, administration, and patient eligibility. It emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive weight management program that includes diet, exercise, and behavioral therapy alongside semaglutide treatment.
Implications for Consumers
FDA approval ensures that semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics meets safety and efficacy standards. It also facilitates insurance coverage and wider acceptance among healthcare providers.
9. Integrating Semaglutide into a Comprehensive Weight Loss Plan
Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics is most effective when integrated into a holistic weight management strategy. Combining medication with lifestyle changes can enhance results and promote long-term success.
Dietary Modifications
- Balanced Nutrition: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Calorie Control: Monitor caloric intake to create a sustainable calorie deficit.
- Meal Planning: Plan meals to avoid impulsive eating and ensure nutritional adequacy.
Exercise Regimen
- Cardiovascular Activities: Engage in activities like walking, running, or cycling to burn calories.
- Strength Training: Build muscle mass to boost metabolism.
- Consistency: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Behavioral Therapy
- Goal Setting: Establish realistic and achievable weight loss goals.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Address emotional eating and develop coping strategies.
- Support Groups: Participate in groups for motivation and accountability.
Monitoring Progress
- Regular Check-Ins: Schedule appointments with healthcare providers to assess progress.
- Tracking Tools: Use apps or journals to monitor food intake and physical activity.
- Adjustments: Modify the weight loss plan as needed based on progress and feedback.
10. Long-Term Effects and Sustainability
Understanding the long-term effects and sustainability of semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics is crucial for making informed decisions about its use.
Benefits
- Sustained Weight Loss: Clinical trials indicate that semaglutide can help maintain weight loss over extended periods.
- Improved Metabolic Health: Reduced weight can lead to lower blood pressure, improved cholesterol levels, and decreased risk of chronic diseases.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Weight loss can improve mobility, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Potential Risks
- Dependency: Long-term use may lead to dependency on the medication for weight maintenance.
- Side Effects: Chronic use may exacerbate gastrointestinal issues or other side effects.
- Cost Implications: Ongoing treatment can be financially burdensome without adequate insurance coverage.
Ongoing Research
Researchers continue to study the long-term impacts of semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics, focusing on its safety profile, effectiveness in diverse populations, and potential benefits beyond weight reduction.
11. Navigating the Prescription Process for Semaglutide

Obtaining semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics involves a specific prescription process. Understanding the steps can facilitate a smoother experience for those seeking this treatment.
Eligibility Criteria
- BMI Requirements: Typically, a BMI of 30 or higher, or 27 with at least one weight-related condition such as hypertension.
- Previous Weight Loss Attempts: Evidence of prior unsuccessful weight loss efforts through diet and exercise.
- Health Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation to ensure suitability and rule out contraindications.
Consultation with Healthcare Provider
The first step is to consult with a healthcare provider who can assess your eligibility and discuss the potential benefits and risks of semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics. This consultation may involve:
- Reviewing medical history and current medications.
- Conducting a physical examination.
- Discussing lifestyle habits and weight loss goals.
Obtaining a Prescription
If deemed appropriate, the healthcare provider will prescribe semaglutide, providing instructions on dosage and administration. Some providers may offer telemedicine services, making the prescription process more accessible.
Pharmacy and Delivery Options
- Local Pharmacies: Fill the prescription at a nearby pharmacy.
- Mail-Order Pharmacies: Convenient delivery options available for ongoing treatment.
- Insurance Processing: Submit the prescription to insurance for potential coverage.
12. Conclusion
Semaglutide for weight loss in non-diabetics represents a significant advancement in the field of obesity treatment. Its ability to facilitate substantial and sustained weight loss, when combined with lifestyle modifications, makes it a valuable tool for individuals struggling with obesity. However, it is essential to approach its use with a thorough understanding of its benefits, potential side effects, and financial implications. Consulting with healthcare professionals and integrating semaglutide into a comprehensive weight management plan can optimize outcomes and enhance overall health and well-being.
References
- FDA Approval of Semaglutide for Weight Management
- STEP 1 Clinical Trial Results
- Medical News Today: Semaglutide for Weight Loss
- WebMD: Semaglutide Subcutaneous




