Nutrition for Healthy Living: Your Comprehensive Guide
1. Introduction to Nutrition for Healthy Living
Nutrition for healthy living is the foundation of overall well-being, influencing everything from physical health to mental clarity. Understanding the principles of good nutrition empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices that support a vibrant and active lifestyle.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the key components of nutrition for healthy living, offering practical advice and evidence-based insights to help you optimize your diet and achieve your health goals.
2. Building a Balanced Diet
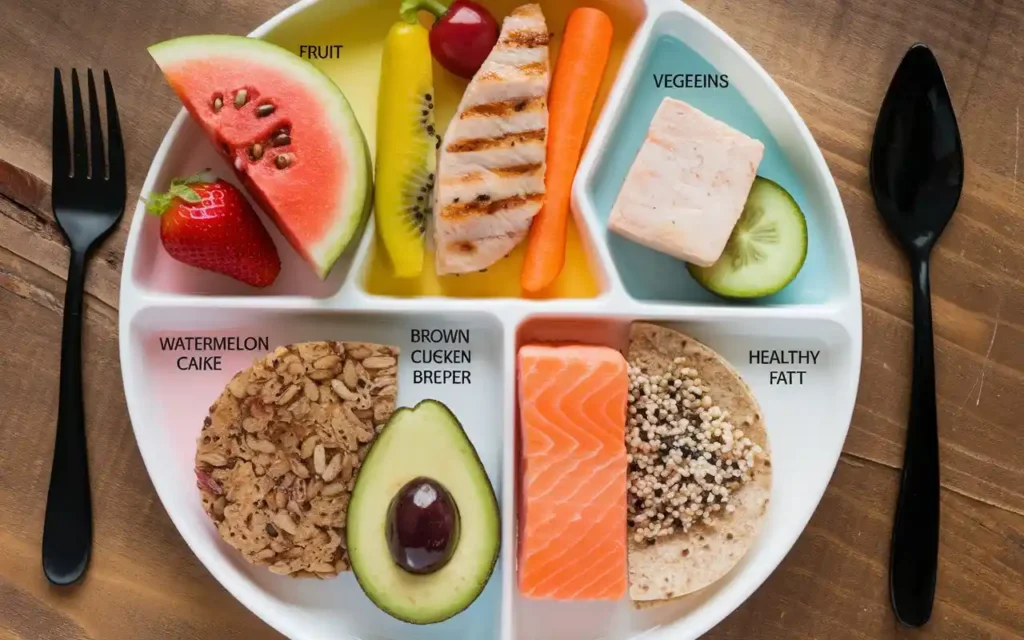

Nutrition for healthy living begins with a balanced diet that provides all the essential nutrients your body needs. A balanced diet typically includes a variety of foods from different food groups, ensuring that you receive a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and other vital nutrients.
Components of a Balanced Diet
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Whole Grains: Provide sustained energy and essential B vitamins.
- Proteins: Essential for muscle repair and immune function.
- Healthy Fats: Important for brain health and hormone production.
- Dairy or Alternatives: Source of calcium and vitamin D.
Tips for Maintaining a Balanced Diet
- Include a variety of foods in your meals to cover all nutrient bases.
- Limit processed foods and added sugars.
- Stay mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating.
- Plan your meals ahead to ensure nutritional balance.
3. Understanding Macronutrients
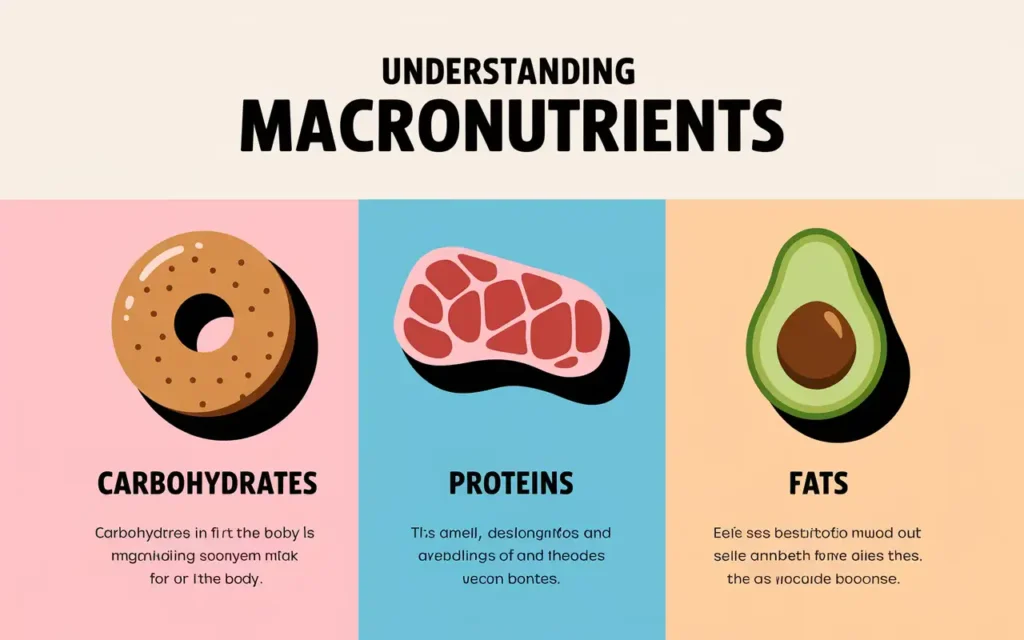
Nutrition for healthy living relies heavily on the proper intake of macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each macronutrient plays a unique role in maintaining bodily functions and supporting overall health.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source. They are found in foods like bread, rice, pasta, and fruits. Choosing complex carbohydrates over simple sugars can provide sustained energy and prevent blood sugar spikes.
Proteins
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. Sources include meat, fish, eggs, legumes, and nuts.
Fats
Healthy fats are crucial for brain health, hormone production, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Incorporate sources like avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish into your diet.
Balancing Macronutrients
Maintaining the right balance of macronutrients is key to achieving optimal health. A general guideline is to have 45-65% of your daily calories from carbohydrates, 20-35% from fats, and 10-35% from proteins.
4. The Importance of Micronutrients
Nutrition for healthy living isn’t just about macronutrients; micronutrients like vitamins and minerals are equally vital. These nutrients support a myriad of bodily functions, including immune response, bone health, and energy production.
Essential Vitamins
- Vitamin A: Supports vision and immune function.
- Vitamin C: Important for skin health and antioxidant protection.
- Vitamin D: Crucial for bone health and calcium absorption.
- Vitamin E: Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting and bone metabolism.
Essential Minerals
- Calcium: Necessary for strong bones and teeth.
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport in the blood.
- Magnesium: Supports muscle and nerve function.
- Potassium: Helps regulate fluid balance and blood pressure.
- Zinc: Important for immune function and wound healing.
Ensuring Adequate Micronutrient Intake
Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and dairy products to meet your micronutrient needs. Consider consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
5. Hydration and Its Role in Nutrition
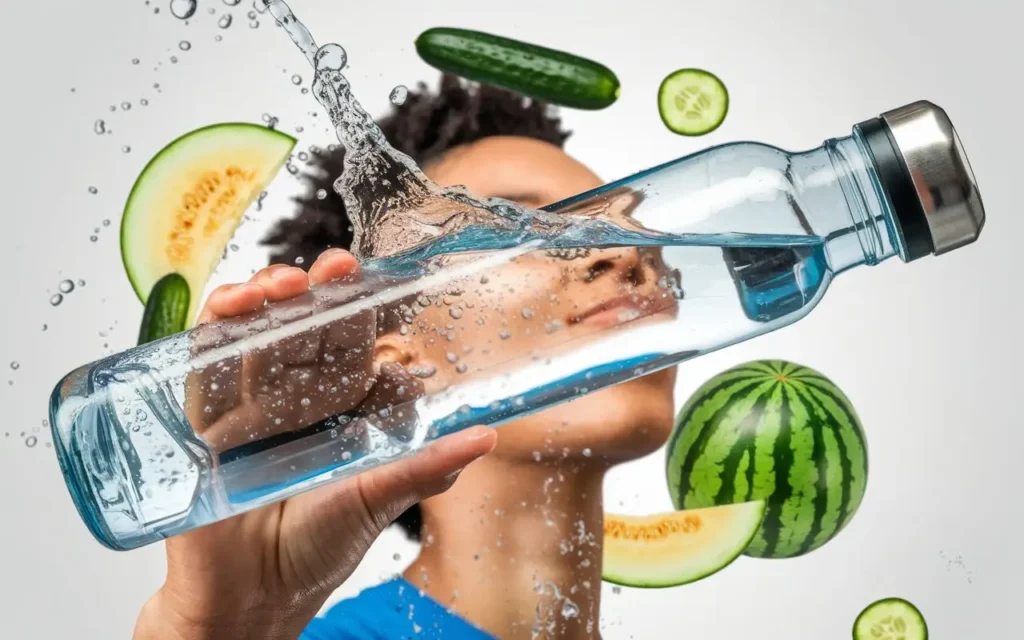

Nutrition for healthy living includes adequate hydration, which is essential for maintaining bodily functions such as digestion, circulation, and temperature regulation. Water is involved in every cellular process, making it a critical component of a healthy diet.
Benefits of Staying Hydrated
- Maintains electrolyte balance.
- Supports kidney function and detoxification.
- Aids in nutrient transportation and absorption.
- Promotes healthy skin and hair.
- Enhances cognitive performance and mood.
How Much Water Do You Need?
General guidelines suggest drinking at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water daily. However, individual needs may vary based on factors like age, sex, activity level, and climate.
Tips for Staying Hydrated
- Carry a reusable water bottle throughout the day.
- Set reminders to drink water at regular intervals.
- Include hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges in your diet.
- Limit dehydrating beverages such as excessive caffeine and alcohol.
6. Effective Meal Planning Strategies
Nutrition for healthy living is significantly enhanced by effective meal planning. Planning your meals in advance helps ensure that you maintain a balanced diet, manage portion sizes, and make healthier food choices.
Benefits of Meal Planning
- Reduces the likelihood of unhealthy snacking.
- Helps control calorie intake for weight management.
- Saves time and reduces stress during busy days.
- Facilitates the inclusion of a variety of nutrients in your diet.
Steps to Successful Meal Planning
- Assess Your Needs: Determine your nutritional requirements based on your lifestyle and health goals.
- Plan Your Meals: Outline breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks for the week.
- Create a Shopping List: List all the ingredients needed to prepare your planned meals.
- Prepare in Advance: Consider batch cooking or prepping ingredients ahead of time to streamline meal preparation.
Sample Meal Plan
| Meal | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with fresh berries | Greek yogurt with honey and nuts | Scrambled eggs and whole-grain toast | Smoothie with spinach and banana | Avocado toast with poached eggs |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad | Quinoa and vegetable bowl | Tuna sandwich on whole-grain bread | Lentil soup with side salad | Turkey and avocado wrap |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with steamed broccoli | Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables | Beef and vegetable stir-fry | Spaghetti with marinara sauce and meatballs | Chicken curry with brown rice |
| Snacks | Apple slices with almond butter | Carrot sticks with hummus | Mixed nuts | Protein bar | Fresh fruit salad |
7. Incorporating Superfoods into Your Diet

Nutrition for healthy living can be significantly boosted by incorporating superfoods—nutrient-dense foods that offer a range of health benefits. Superfoods are packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds that support overall health.
Top Superfoods to Include
- Blueberries: High in antioxidants and vitamins C and K.
- Kale: Rich in fiber, vitamins A, C, and K, and calcium.
- Salmon: Excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids and protein.
- Quinoa: Complete protein containing all nine essential amino acids.
- Chia Seeds: Packed with fiber, omega-3s, and protein.
Benefits of Superfoods
Incorporating superfoods into your diet can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve immune function, enhance brain health, and promote healthy skin. Their high nutrient density ensures that you receive maximum benefits with relatively small portions.
How to Add Superfoods to Your Meals
- Add berries to your morning oatmeal or yogurt.
- Incorporate leafy greens like kale into smoothies or salads.
- Use quinoa as a base for salads or as a side dish.
- Include fatty fish like salmon in your weekly meal plan.
- Sprinkle chia seeds on cereals, smoothies, or baked goods.
8. Embracing a Plant-Based Lifestyle
Nutrition for healthy living is often associated with plant-based diets, which emphasize the consumption of vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Adopting a plant-based lifestyle can lead to numerous health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
- High in essential nutrients and fiber.
- Low in saturated fats and cholesterol.
- Supports weight management and healthy body composition.
- Promotes sustainable and environmentally friendly eating habits.
- Enhances digestive health and regularity.
Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
Making the switch to a plant-based diet doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Start by gradually increasing your intake of plant-based foods while reducing animal products. Here are some tips to ease the transition:
- Start with Meatless Meals: Incorporate a few vegetarian meals into your weekly schedule.
- Explore Plant-Based Proteins: Try lentils, chickpeas, tofu, and tempeh as protein sources.
- Experiment with New Recipes: Discover delicious plant-based dishes to keep your meals exciting.
- Ensure Nutrient Adequacy: Pay attention to nutrients like B12, iron, and omega-3s, and consider supplements if necessary.
Common Plant-Based Foods
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Vegetables | Broccoli, spinach, kale, carrots, bell peppers |
| Fruits | Apples, bananas, berries, oranges, mangoes |
| Legumes | Beans, lentils, chickpeas, peas |
| Whole Grains | Quinoa, brown rice, oats, barley, whole wheat |
| Nuts and Seeds | Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds |
9. Nutrition and Mental Health
Nutrition for healthy living extends beyond physical health to significantly impact mental well-being. A balanced diet can influence mood, cognitive function, and overall mental health.
How Nutrition Affects Mental Health
- Brain Function: Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins B6 and B12, and antioxidants support brain health and cognitive function.
- Mood Regulation: Balanced blood sugar levels and adequate nutrient intake can help stabilize mood and reduce the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Stress Management: Certain nutrients, such as magnesium and vitamin C, play a role in managing stress and reducing cortisol levels.
Foods That Boost Mental Health
- Fatty Fish: Rich in omega-3s, which are linked to lower rates of depression.
- Dark Leafy Greens: High in folate, which helps regulate mood.
- Whole Grains: Provide a steady supply of glucose to the brain.
- Fermented Foods: Support gut health, which is connected to mental health.
- Dark Chocolate: Contains antioxidants and can improve mood.
Tips for Supporting Mental Health Through Nutrition
- Incorporate a variety of nutrient-dense foods into your diet.
- Maintain regular meal times to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Stay hydrated to support cognitive function.
- Limit intake of processed foods and sugars that can negatively impact mood.
- Consider consulting a mental health professional or nutritionist for personalized advice.
10. Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Nutrition for healthy living is a multifaceted concept that encompasses balanced eating, understanding macronutrients and micronutrients, staying hydrated, effective meal planning, incorporating superfoods, embracing plant-based options, and recognizing the connection between diet and mental health.
By prioritizing good nutrition, you can enhance your physical health, boost your energy levels, support your mental well-being, and cultivate a sustainable and enjoyable relationship with food.
Remember, making gradual changes and seeking professional guidance when necessary can lead to lasting improvements in your health and quality of life.
References and Further Reading




