How to Keep Knees Healthy: Comprehensive Guide
1. Understanding Knee Anatomy
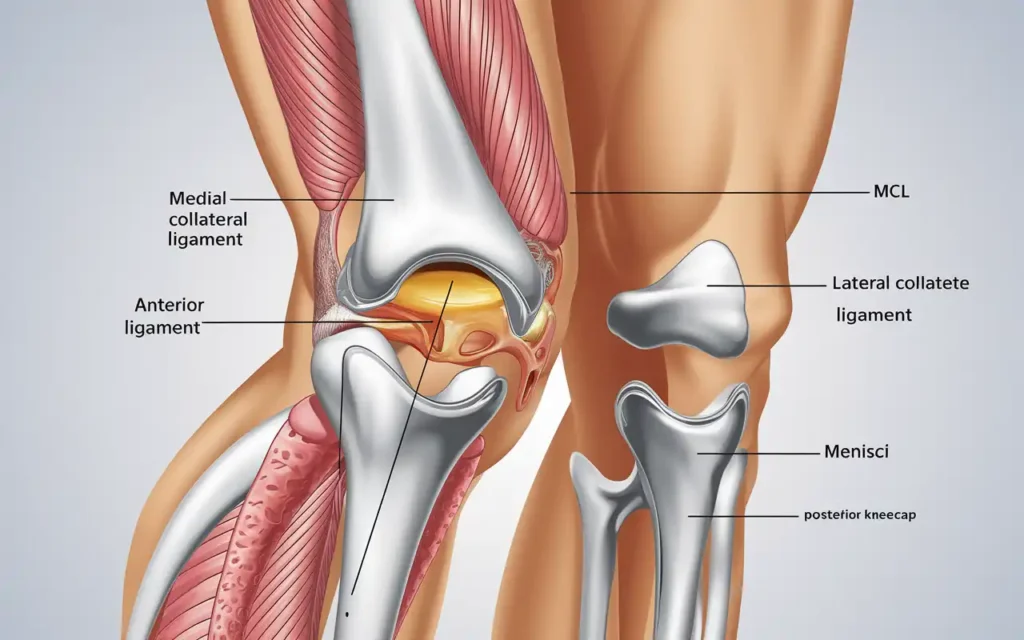
How to keep knees healthy starts with understanding their structure and function. The knee is a complex joint that connects the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone), and includes the patella (kneecap) and the fibula.
The Structure of the Knee
- Bones: Femur, tibia, fibula, and patella.
- Cartilage: Menisci and articular cartilage provide cushioning.
- Ligaments: ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL stabilize the knee.
- Tendons: Connect muscles to bones, such as the quadriceps tendon.
- Synovial Fluid: Lubricates the joint for smooth movement.
Functionality
The knee allows for various movements including bending, straightening, and slight rotation. Its design supports both stability and flexibility, making it crucial for activities like walking, running, and jumping.
2. Common Knee Problems
How to keep knees healthy involves recognizing and addressing common knee issues that can impede their function and cause pain.
Osteoarthritis
A degenerative joint disease that wears down cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
An autoimmune condition causing inflammation and damage to the knee joint.
Ligament Injuries
Includes ACL and MCL tears, often resulting from sports or accidents.
Meniscal Tears
Injuries to the cartilage that acts as a cushion between the femur and tibia.
Bursitis
Inflammation of the bursae, fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction in the knee.
3. Exercise and Physical Activity
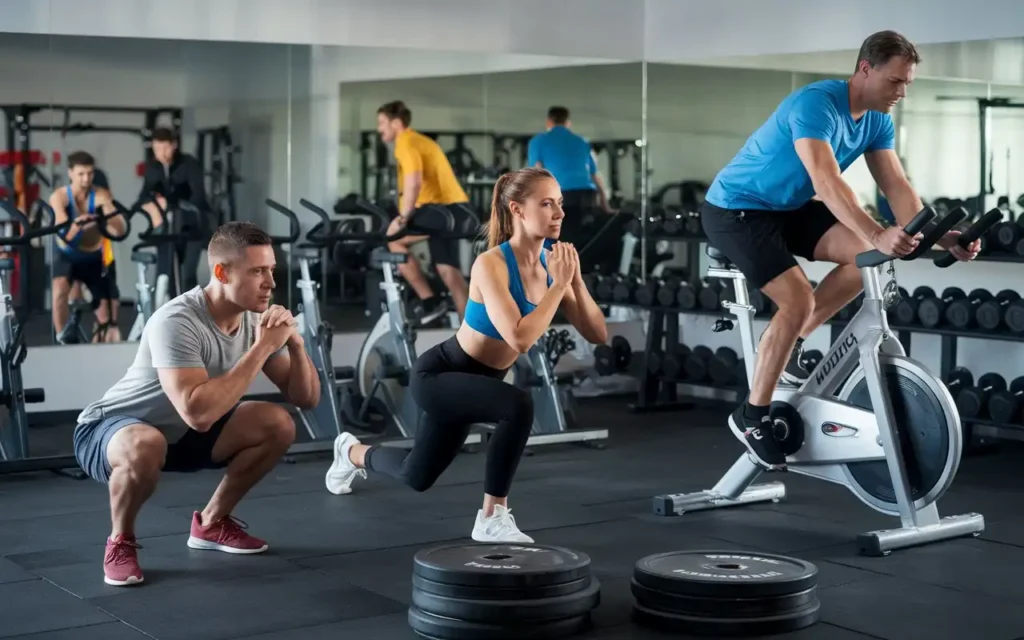

How to keep knees healthy heavily relies on regular exercise and maintaining physical activity to strengthen the muscles supporting the knee.
Strengthening Exercises
- Quadriceps Strengthening: Exercises like squats and lunges.
- Hamstring Strengthening: Leg curls and deadlifts.
- Calf Raises: Strengthen the lower legs for better knee support.
Flexibility and Stretching
Maintaining flexibility through stretches like hamstring stretches, calf stretches, and quadriceps stretches can prevent stiffness and improve range of motion.
Low-Impact Activities
Engaging in activities such as swimming, cycling, and yoga reduces stress on the knees while promoting overall joint health.
4. Nutrition for Knee Health
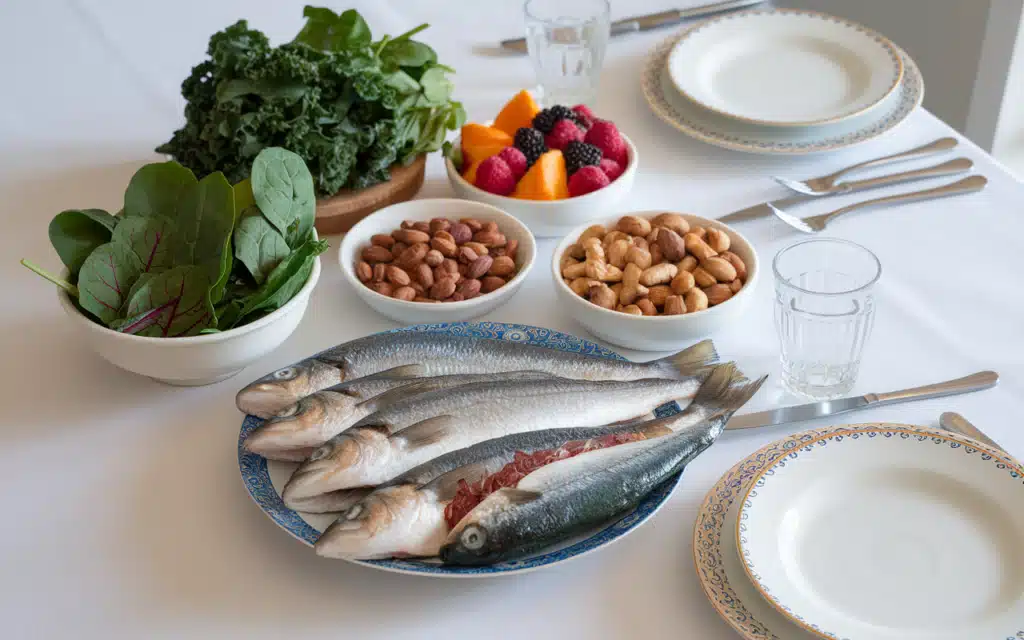

How to keep knees healthy is also supported by a balanced diet rich in nutrients that promote joint health and reduce inflammation.
Essential Nutrients
| Nutrient | Benefits | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduce inflammation | Fish, flaxseeds, walnuts |
| Vitamin D | Supports bone health | Sunlight, fortified dairy products |
| Calcium | Strengthens bones | Dairy products, leafy greens |
| Vitamin C | Promotes collagen formation | Citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers |
| Glucosamine and Chondroitin | Support cartilage health | Supplements, shellfish |
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as turmeric, ginger, and green leafy vegetables can help in maintaining knee health by reducing joint inflammation.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated ensures that the synovial fluid in the knees remains effective in lubricating the joints.
5. Maintaining a Healthy Weight

How to keep knees healthy is significantly influenced by maintaining a healthy weight, which reduces unnecessary stress on the knee joints.
Impact of Excess Weight
Extra weight increases the load on the knees, accelerating wear and tear and increasing the risk of conditions like osteoarthritis.
Weight Management Strategies
- Balanced Diet: Focus on nutrient-dense foods to manage weight effectively.
- Regular Exercise: Combines cardiovascular and strength training for optimal weight control.
- Behavioral Changes: Adopt healthy habits such as mindful eating and regular physical activity.
6. Proper Footwear and Ergonomics
How to keep knees healthy includes wearing appropriate footwear and maintaining good ergonomics to support proper knee alignment and reduce strain.
Choosing the Right Footwear
- Supportive Shoes: Provide proper arch support and cushioning.
- Avoid High Heels: Prevent excessive pressure on the knees.
- Sport-Specific Shoes: Enhance performance and reduce injury risk.
Ergonomic Practices
Adopting ergonomic practices such as proper sitting posture, using supportive chairs, and adjusting workstations can help maintain knee health.
7. Preventive Measures and Injury Avoidance
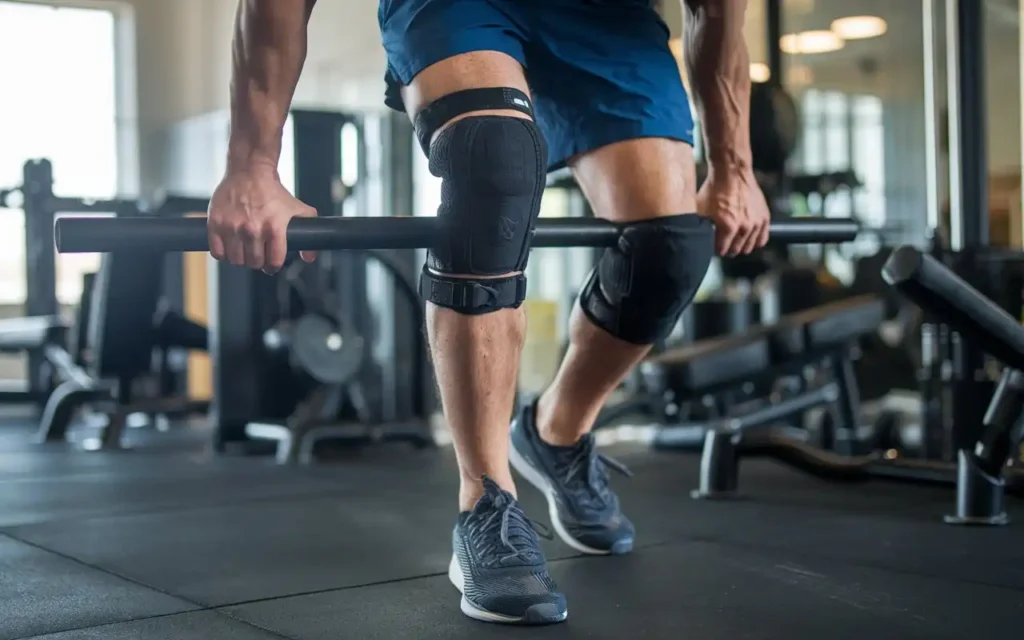

How to keep knees healthy involves taking preventive measures to avoid injuries that can lead to long-term knee problems.
Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Incorporate proper warm-up and cool-down routines before and after physical activities to prepare the knees for movement and aid recovery.
Proper Technique
Using correct techniques during sports and exercises minimizes the risk of knee injuries.
Protective Gear
Wearing knee braces or supports during high-risk activities provides additional protection to the knees.
8. Rehabilitation and Recovery
How to keep knees healthy also includes proper rehabilitation and recovery practices following any knee injury or surgery.
Physical Therapy
Engaging in physical therapy helps restore strength, flexibility, and function to the knee.
Rest and Recovery
Allowing adequate time for rest and recovery prevents further injury and promotes healing.
Gradual Return to Activity
Gradually resuming activities ensures that the knee adapts safely to increased demands.
9. Alternative Therapies
How to keep knees healthy can be complemented with alternative therapies that support joint health and reduce pain.
Acupuncture
May help alleviate knee pain and improve mobility through targeted stimulation of pressure points.
Massage Therapy
Relieves muscle tension around the knee and enhances blood flow to promote healing.
Supplements
Natural supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin, and turmeric can support joint health.
10. When to Seek Medical Advice
How to keep knees healthy sometimes requires professional medical intervention, especially when experiencing persistent pain or mobility issues.
Recognizing Serious Symptoms
- Severe or worsening pain
- Swelling and inflammation
- Inability to bear weight
- Locking or instability of the knee
Consulting Specialists
Seeing an orthopedic specialist or a physiotherapist can provide targeted treatments and rehabilitation plans.
Diagnostic Procedures
Imaging tests like X-rays, MRI, or CT scans help in diagnosing underlying knee issues accurately.




